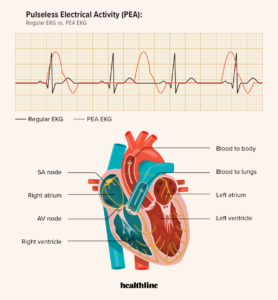
Pulseless electrical activity (PEA) is one of the most misunderstood cardiac arrest rhythms, mainly because the cardiac monitor shows an organized rhythm, yet there’s no palpable pulse. It’s easy to assume the heart is working just fine, but in reality, it’s not pumping at all.
According to an article published in the StatsPearls, PEA is the first documented rhythm in 30–38% of adults with cardiac arrest, and it accounts for 68% of recorded in-hospital deaths related to cardiac events in the US. Misreading a pulseless electrical activity ECG or delaying action because the rhythm “looks normal” can cost valuable time. Women and adults over 70 are especially at higher risk, often with overlooked causes like pulmonary embolism (blood clot in the lungs) or drug-induced contractility issues.
So, how do you spot PEA quickly and accurately? And what should you look for on the ECG? Read on to learn what PEA really looks like and how to catch it before it’s too late.
Master ACLS Now
Get ACLS certified with confidence
What is Pulseless Electrical Activity?
Pulseless electrical activity (PEA) is a life-threatening condition in which the heart’s electrical system continues to function, but it fails to produce an effective heartbeat. This means that, despite a visible rhythm on the Electrocardiogram (ECG), there is no detectable pulse or blood circulation.
PEA is classified as a non-shockable rhythm, which means defibrillation is not effective as an immediate treatment. Instead, it requires quick identification of the underlying cause and immediate cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). If left untreated, PEA can lead to sudden cardiac death or heart blockage within minutes. Although conditions like pulseless ventricular tachycardia (VT) and ventricular fibrillation (VF) also present without a pulse, they are different from PEA. VT and VF are considered shockable rhythms and can be treated with defibrillation.
Read More: How to Become a Cardiologist?
Common Organized Rhythms Seen in PEA
PEA can manifest as different forms of electrical activity on an ECG. Healthcare providers consider the echocardiogram one of the best techniques for analyzing and measuring a PEA rhythm strip. The condition can usually take two different forms:
Pseudo-PEA
This happens when the electrical activity in your heart causes the muscles to contract very weakly. This contraction may move some blood, but it does not count as a proper heartbeat. This also means the heart isn’t strong enough to pump blood effectively because you still don’t have a pulse.
True PEA
In true PEA, there is electrical activity but no muscle movement at all. The heart doesn’t contract, so no blood is pumped, and there’s no pulse.
Common Rhythms Seen in PEA
Pulseless Electrical Activity can present with various ECG rhythms that may appear deceptively normal or organized. Despite this electrical activity, there’s no effective heartbeat. Below are some common rhythms where PEA may be observed, each with its clinical relevance:
Sinus Rhythm
A sinus rhythm refers to the pattern of electrical activity that is usually seen on an ECG when the heart beats normally. Normal sinus rhythm includes certain waves in the cycle that correspond to events in the cardiac cycle. These waves are named P, QRS, and T.
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)
AFib is an irregular and often rapid heartbeat that disrupts normal blood flow and increases the risk of stroke or heart failure. In cases of PEA, AFib may be present without a palpable pulse, indicating poor or absent cardiac output.
Atrial Flutter
Atrial flutter is a type of heart rhythm disorder, also known as an arrhythmia. In this condition, the heart rhythm is more organized and less chaotic than what is usually recorded in AFib. An individual can have both atrial flutter and AFib.
Idioventricular Rhythm
Idioventricular rhythm is a condition in which the specific chambers of the lower heart beat slower than usual. If your heart’s natural pacemaker in the upper chambers stops working, the lower chambers or ventricles may take over and start the heartbeat.
Read More: Normal vs Dangerous Heart Rate: An Overview
How to Identify PEA on ECG?
Recent data from a study published in the Resuscitation Journal indicate that approximately 19.1% of patients with an initial PEA rhythm during in-hospital cardiac arrest survived to hospital discharge. Therefore, analyzing what an echocardiogram shows is a key skill for emergency healthcare providers. The following features can help in identifying the condition with ECG PEA:
Organized Rhythm
Unlike other cardiac arrest rhythms, like asystole, PEA shows organized electrical activity on the ECG. This means that the ECG may resemble sinus rhythm, atrial fibrillation, or other regular rhythms. However, these rhythms do not result in a pulse.
Absence of a Pulse
The most important diagnostic clue is that despite the presence of organized electrical activity, there is no palpable pulse. To confirm PEA, healthcare providers often assess for a pulse manually or through a monitor, and its absence helps differentiate PEA from other rhythms, such as pulseless ventricular tachycardia or asystole.
Patient’s Condition
In cases of Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA), the patient is usually unconscious and doesn’t respond to any stimuli. Their blood pressure is very low, and the oxygen levels in their blood are also low. Even though the heart’s electrical activity may still be present, it’s not strong enough to pump blood effectively. This lack of blood flow and oxygen to the body indicates the presence of PEA, requiring urgent medical help to restore normal circulation.
What Does PEA Look Like on ECG?
A PEA usually appears as a normal heartbeat on an ECG. The lines on the monitor may show a regular rhythm during the diagnosis. But even though the heart appears to be working, there is no pulse. That means the heart isn’t pumping blood the way it should in this condition.
Pulseless Electrical Activity Vs Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia
Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA) and Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia (pVT) are both life-threatening cardiac arrest rhythms. Though both present without a pulse, they differ in cause, ECG appearance, and treatment. Knowing how to identify and treat them quickly is a key requirement in emergency care.
The table below showcases the primary differences between PEA and pVT in detail:
| Feature | Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA) | Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia (pVT) |
| Definition | ECG shows a rhythm, but the heart isn’t pumping | Very fast rhythm from the ventricles with no pulse |
| ECG Appearance | Normal sinus rhythm, bradycardia, or other organized rhythm | Wide QRS complexes; regular, rapid ventricular rhythm |
| Pulse | Absent | Absent |
| Cause | Usually from reversible causes (e.g., H’s & T’s: hypoxia, tamponade, toxins) | Often due to heart disease, low potassium, or electrical instability |
| Shockable Rhythm | No (Do not defibrillate) | Yes (Immediate defibrillation required) |
| Treatment Approach | High-quality CPR + identify and reverse the underlying cause | Immediate CPR + defibrillation + ACLS medications |
| Prognosis | Poor unless a cause is found and fixed quickly | Better than PEA if defibrillated early |
| Common Causes | Hypoxia, hypovolemia, acidosis, cardiac tamponade, tension pneumothorax | Myocardial infarction, drug toxicity, and electrolyte imbalance |
| Seen In | Many in-hospital cardiac arrests | Cardiac patients, sudden cardiac death |
Recognize PEA on ECG Correctly to Save a Life!
Pulseless electrical activity on an ECG appears as organized rhythms such as sinus rhythm, atrial fibrillation, or bradycardia, but the key issue is the absence of a pulse. Despite the heart showing electrical activity, it is not pumping blood effectively. In these critical moments, immediate actions such as CPR, epinephrine administration at the correct dose, and timely defibrillation (if necessary) can make all the difference.
Want to learn more about the PEA rhythm? Enroll in an online advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) certification and learn more about cardiac emergencies, other medical conditions, and their treatment options in detail.