Table of content(s)
- Introduction
- Will an AED detect a pulse?
- How does an AED work?
- Can an AED detect a pulse?
- What happens if AED is used on someone with a pulse?
- How to use an AED safely and effectively?
- Conclusion
When someone collapses and stops breathing, every second counts. An Automated External Defibrillator (AED) is a life-saving device designed to quickly assess a person’s heart rhythm and, if necessary, deliver a shock to help restore a normal heartbeat. But what happens if the person still has a pulse? Are you confused about whether AED can detect a pulse or not? It is crucial to find the answer, especially in emergencies where each second counts. The blog explores more about an AED shockable rhythms, how they work, and whether they will detect a pulse or not.
Master ACLS Now
Get ACLS certified with confidence
How does an AED work?
An automated external defibrillator helps save lives during cardiac emergencies. It is a user-friendly tool and enables you to take quick action. It checks the heart’s rhythm and delivers electric shock if there is an irregular heartbeat. This helps restore the heart rhythm. Here are ways how an AED works:
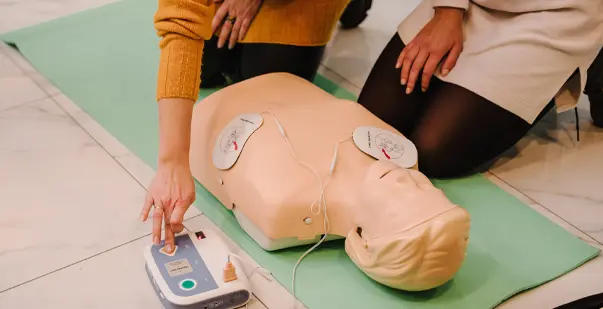
- Power On the AED: Turn on the device by pressing the power button. Most AEDs will immediately start giving voice prompts to guide you through the process.
- Apply the Pads: Place the adhesive pads on the patient’s bare chest as shown on the pads or AED instructions. One pad goes on the upper right side of the chest, the other on the lower left.
- Analyze the Heart Rhythm: The AED will automatically analyze the heart’s rhythm once the pads are in place. Make sure no one is touching the patient during this analysis.
- Deliver the Shock (if advised): If the AED determines a shock is needed, it will instruct you to press the shock button. Ensure everyone is clear of the patient before delivering the shock.
- Follow Further Instructions: After the shock is delivered, the AED will provide further instructions, such as starting CPR if needed. Continue to follow the device’s prompts until emergency medical help arrives.
Can an AED detect a pulse?
An AED (Automated External Defibrillator) is a remarkable device designed to save lives during sudden cardiac arrest. However, one common question is whether an AED can detect a pulse. The answer is no—AEDs are not designed to detect a pulse. Instead, they are built to recognize certain life-threatening heart rhythms, like ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia, where the heart is beating irregularly or not at all.
When you apply the AED pads to a person’s chest, the device analyzes the heart’s electrical activity to determine if a shock is necessary. If the AED detects a shockable rhythm, it will advise delivering a shock. If the rhythm is not shockable or if the heart is beating normally, the AED will not deliver a shock, but it doesn’t directly assess whether there is a pulse.
By simplifying the process for respondents, it ensures that they can act quickly in an emergency without having to find a pulse. This can be difficult, especially during emergencies. Hence, you must follow the AED’s prompts and continue monitoring the person. If necessary, provide CPR until professional medical help arrives.
Read more: CPR vs. BLS Training: What’s the Difference?
What happens if AED is used on someone with a pulse?
Using an AED on someone with a pulse may seem concerning, but AEDs are designed to be safe and prevent unnecessary shocks. If you apply the AED pads to a person with a pulse, the device will analyze the heart’s rhythm. AEDs only deliver a shock if they detect a life-threatening rhythm like ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia.
If the heart is beating normally, the AED will not advise or deliver a shock. Instead, it will guide you on what to do next. This safety feature ensures that you can’t accidentally harm someone by using the AED incorrectly. Always follow the AED’s prompts and continue to provide care until professional medical help arrives.
How to use an AED safely and effectively?
It can be difficult to use an AED, especially in an emergency. But you must stay calm and follow the instructions. Start preparing well and follow these tips:
Tips for using an AED safely and effectively:
- Stay calm and follow the prompts: The AED will guide you step-by-step, so listen carefully to its instructions and act quickly.
- Ensure the Area is Safe: Before using the AED, make sure the area around the patient is clear of water, metal, or anything that could interfere with the device.
- Remove clothing and apply pads: Quickly remove any clothing from the chest area and place the pads as indicated on the AED. Proper placement is crucial for the device to work effectively.
- Stand Clear During Analysis and Shocking: When the AED is analyzing or delivering a shock, make sure no one is touching the patient to avoid interference or injury.
- Continue Care Until Help Arrives: After using the AED, continue following the prompts, whether it’s performing CPR or monitoring the patient, until emergency medical professionals take over.
Read more: How To Get BLS Certification?
When to use an AED?
An AED should be used when someone is unresponsive and not breathing or not breathing normally. In these critical moments, every second counts, and using an AED can make a life-saving difference. Knowing when to use an AED is key to acting quickly and effectively.
When to Use an AED:
- Sudden Cardiac Arrest: If a person collapses suddenly, is unresponsive, and has no signs of normal breathing, use an AED immediately.
- No Pulse Detected: If you cannot detect a pulse and the person is unconscious, apply the AED as soon as possible.
- During CPR: If you’re performing CPR on someone who has no signs of life, use the AED alongside chest compressions for the best chance of reviving them.
Conclusion
It is useful for anyone who might need to use an AED at any given time to know if the device can detect the pulse. An AED does not have the ability to check whether a pulse is present or not. But it is very important equipment that helps in checking the heart’s rhythm to decide if a shock is required or not. This helps the respondents, as they do not have time to check once manually; this feature makes work easier and more straightforward. So, with the aid of AED, care should be provided, remembering that AED is going to shock only in case it is necessary.