List of ACLS Acronyms and Abbreviations You Need to Know
Are you on your path to advancing your career? If you have begun the journey of pursuing your advanced cardiovascular life support certification, you are already aware of the list of abbreviations you will need to know to pass your exam.
There are several ACLS medical abbreviations, and luckily, most of them are general. However, there are some that might be new to you. That’s why you need a list handy to pass the exam successfully. If you are taking your ACLS exam online, having this list open can be a major time saver. This will help you get certified quickly and reduce the time flipping the course material back and forth. Here are the key ACLS acronyms that you need to know.
Master ACLS Now
Get ACLS certified with confidence
What does ACLS mean in medical terms?
So what does ACLS stand for? ACLS medical acronym is advanced cardiovascular life support. It refers to a set of clinical guidelines used by healthcare professionals to treat and manage patients experiencing severe cardiovascular emergencies, such as stroke. ACLS includes advanced interventions such as drug administration and defibrillation that help improve patient outcomes during emergencies.
What are the abbreviations and acronyms for ACLS?
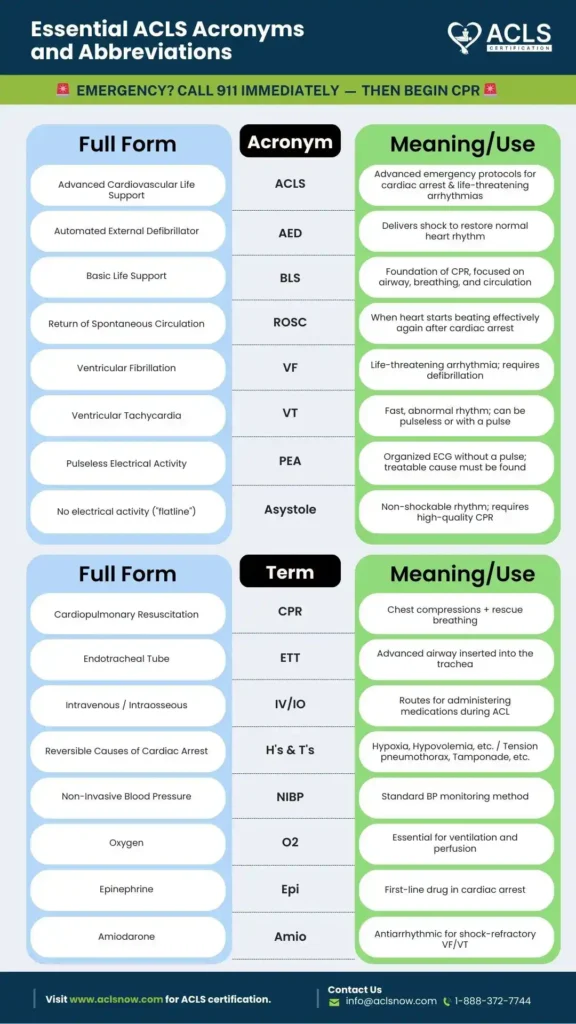
Below are the ACLS acronyms that you might come across during your ACLS course:
| Abbreviation | Full Form |
|---|---|
| ABCD | Airway, breathing, circulation, differential diagnosis |
| ACE | Angiotensin-converting enzyme |
| ACLS | Advanced cardiovascular life support |
| ACS | Acute coronary syndrome |
| AED | Automated External Defibrillator |
| AHA | American Heart Association |
| AHF | Acute heart failure |
| AICD | Automated Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator |
| AMI | Acute myocardial infarction |
| AV | Atrioventricular |
| BLS | Basic Life Support |
| BP | Blood pressure |
| CAB | Circulation, airway, breathing |
| CHF | Congestive heart failure |
| CPR | Cardiopulmonary resuscitation |
| CPSS | Cincinnati Prehospital Stroke Scale |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| DNAR | Do not attempt resuscitation |
| ECG | Electrocardiogram |
| ECPR | Extracorporeal CPR |
| ED | Emergency Department |
| EMS | Emergency Medical Services |
| ET | Endotracheal |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| FAST | Facial droop, arm drift, speech, time |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| ICU | Intensive Care Unit |
| IHCA | In-hospital cardiac arrest |
| IN | Intranasal |
| IM | Intramuscular |
| IO | Intraosseous |
| IV | Intravenous |
| LMA | Laryngeal Mask Airway |
| LV | Left ventricle |
| mA | Milliamperes |
| MACE | Major adverse cardiac events |
| MAP | Mean arterial pressure |
| MI | Myocardial infarction |
| mmHG | Millimeters of mercury |
| NIH | National Institutes of Health |
| NIHSS | National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale |
| NINDS | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke |
| NPA | Nasopharyngeal airway |
| NSTEMI | Non-ST segment myocardial infarction |
| OHCA | Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest |
| OPA | Oropharyngeal Airway |
| PAD | Public Access Defibrillation |
| PCI | Percutaneous coronary intervention |
| PE | Pulmonary embolism |
| PEA | Pulseless electrical activity |
| PETCO2 | Partial pressure of end-tidal carbon dioxide |
| PPCI | Primary percutaneous coronary intervention |
| PSVT | Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia |
| PT | Prothrombin time |
| PVCs | Premature ventricular contractions |
| PVT | Pulseless ventricular tachycardia |
| ROSC | Return of spontaneous circulation |
| RRT | Rapid Response Team |
| RV | Right Ventricle |
| SBP | Systolic blood pressure |
| STEMI | ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction |
| SVO2 | Central venous oxygen saturation |
| SVT | Supraventricular tachycardia |
| TCP | Transcutaneous pacing |
| TIMI | Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction |
| TTM | Targeted temperature management |
| UA | Unstable angina |
| VF/V-Fib | Ventricular fibrillation |
| VT | Ventricular tachycardia |
Read More: ACLS Certification in Arizona
Understanding the Core ACLS Terms and Acronyms
Advanced cardiovascular life support is a set of clinical interventions crucial for treating cardiac arrest, stroke, and other medical emergencies. Here are the core ACLS acronym medical terms.
- ACLS: ACLS abbreviation is advanced care life support and refers to a set of clinical guidelines and protocols to manage severe cardiovascular emergencies.
- BLS: Basic life support is the foundation of lifesaving care. It focuses on CPR, AED usage, and airway management.
- CPR: Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is a lifesaving technique beneficial in situations when the heart stops beating. This involves rescue breaths and chest compressions.
- AED: An automated external defibrillator is a portable device that diagnoses cardiac arrhythmias and delivers electric shock whenever needed.
- VF: Ventricular fibrillation is a dangerous heart rhythm that causes unorganized electrical activity in the ventricles. This condition needs immediate attention.
- VT: This is a rapid heart rhythm that starts in the lower chambers of the heart. This may cause a cardiac arrest when not treated well.
- ROSC: The return of spontaneous circulation is a condition in which electrical activity is present but fails to generate a pulse. This needs advanced resuscitative measures.
- Pulseless electrical activity is a condition in which the electrical activity of the heart is present but fails to generate a pulse. This needs advanced resuscitative measures.
- STEMI: ST-Elevation A myocardial infarction is a severe heart attack causing a blockage of a coronary artery.
- IO and IV access: Intraosseous and intravenous access are methods of administering drugs and fluids during ACLS interventions. While IO access is done through bones, IV access is through veins.
ACLS vs. BLS: Key Differences
Advanced cardiovascular life support and basic life support are crucial components of emergency care. BLS focuses on life-saving measures such as CPR and AED usage for immediate care. Understand the differences between these two protocols to apply the appropriate level of care.
| Aspect | ACLS | BLS |
| Focus | Advanced emergency cardiovascular care | Basic life saving techniques |
| Provider level | For healthcare professionals needing advanced training | For laypersons, healthcare providers and first responders. |
| Interventions | Includes drug administration, ECG interpretation and advanced airway management | Emphasizes CPR, airway management and AED use. |
| Equipments used | Needs advanced tools such as medication, defibrillators | Uses an AED and basic airway adjuncts |
| Duration | Longer as it involves comprehensive training | Short duration. Focuses core life-saving skills |
| Patient care scenarios | Used in complex scenarios such as arrhythmias, cardiac arrest and post-resuscitation care. | Applied in situations such as choking, and sudden cardiac arrest |
Read more: BLS Certification for Physical Therapy
Conclusion
Knowing ACLS acronyms is crucial for everyone working in the healthcare field. These are used to communicate quickly and effectively during cardiac arrest. If you are familiar with these terms, it will help you make quick decisions. Furthermore, it will also help during ACLS examinations. You can easily boost your confidence and increase your ability to provide high-level care.