PALS wide QRS tachycardia perfusion algorithm is the ultimate guideline for effective intervention in pediatric resuscitation situations. When a child suffers from rapid heart rate with a widened QRS complex, it can usually be detected in electrocardiograms. This condition is often presented with adequate perfusion. This flowchart will help you find the right approach to treat wide QRS tachycardia with adequate perfusion.
Understanding the flowchart
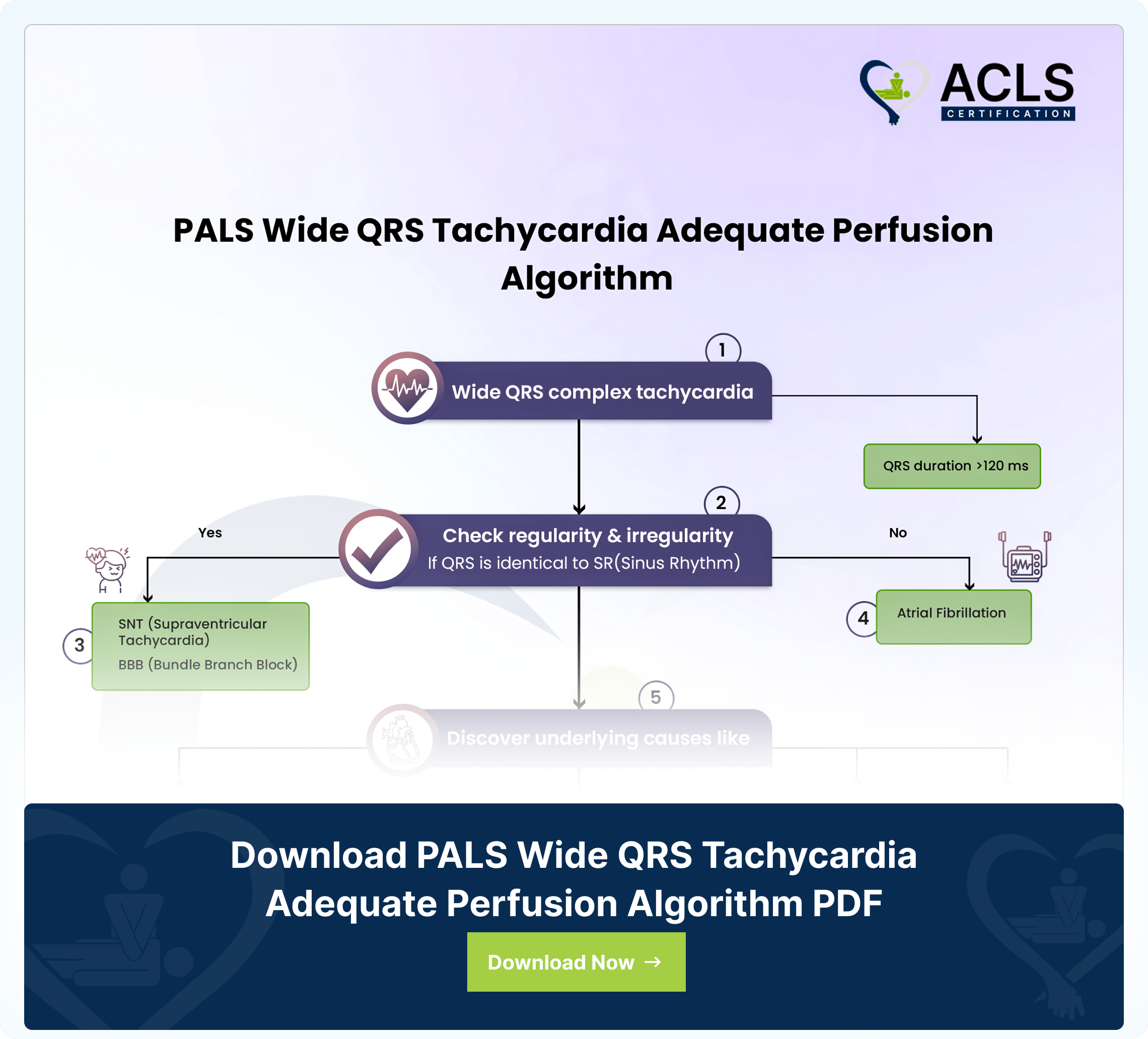
- Wide QRS complex tachycardia
- QRS duration >120 ms
- Check regularity & irregularity
- If QRS is identical to SR(Sinus Rhythm)
- If Yes consider
- SNT (Supraventricular Tachycardia)
- BBB (Bundle Branch Block)
- If No consider
- Atrial Fibrillation
- Discover underlying causes like
- Electrolyte imbalance
- Structural heart disease
- Medication toxicity
- Attempt Vagal Maneuver
- Apply firm pressure on child’s eye
- Massage the carotid sinus
- Put patient on Adenosine
- 0.1mg/kg rapid IV-6mg (1st Dose)
- 0.2mg/kg -12mg (2nd Dose)
- AED/Cardioversion
- 0.5-1 joule/kg
- 2 joules/kg (2nd Dose)
What are the key components of PALS Wide QRS Tachycardia Adequate Perfusion Algorithm?
- Assessment of Clinical Condition: Check for a palpable pulse and signs of adequate perfusion.
- Identify Underlying Cause: Understand potential causes like electrolyte imbalances or structural heart disease.
- Attempt Vagal Maneuvers: Perform maneuvers such as carotid sinus massage or Valsalva maneuver.
- Consider Adenosine: Prescribe adenosine if wide QRS tachycardia is regular and vagal maneuvers fail.
- Monitor for Stability: Consult cardiologist if the child remains stable with adequate perfusion.
- Continuous Monitoring: Continuously monitor vital signs and clinical status.
Download PALS Wide QRS Tachycardia Adequate Perfusion Algorithm PDF
Resources
- Interpreting ECG in Pediatric Patients https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7808076/
- Wide Complex Tachycardias: Understanding this Complex Condition: Part 1 – Epidemiology and Electrophysiology https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2672229/
- Sinus Rhythm https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/nursing-and-health-professions/sinus-rhythm
- Differential Diagnosis of Tachycardia https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3110901/
- Peripheral Pulse https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542175/
- Comparison of treatment of supraventricular tachycardia by Valsalva maneuver and carotid sinus massage https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9437338/
- ACLS and Adenosine https://acls-algorithms.com/acls-drugs/acls-and-adenosine/
All PALS Algorithms
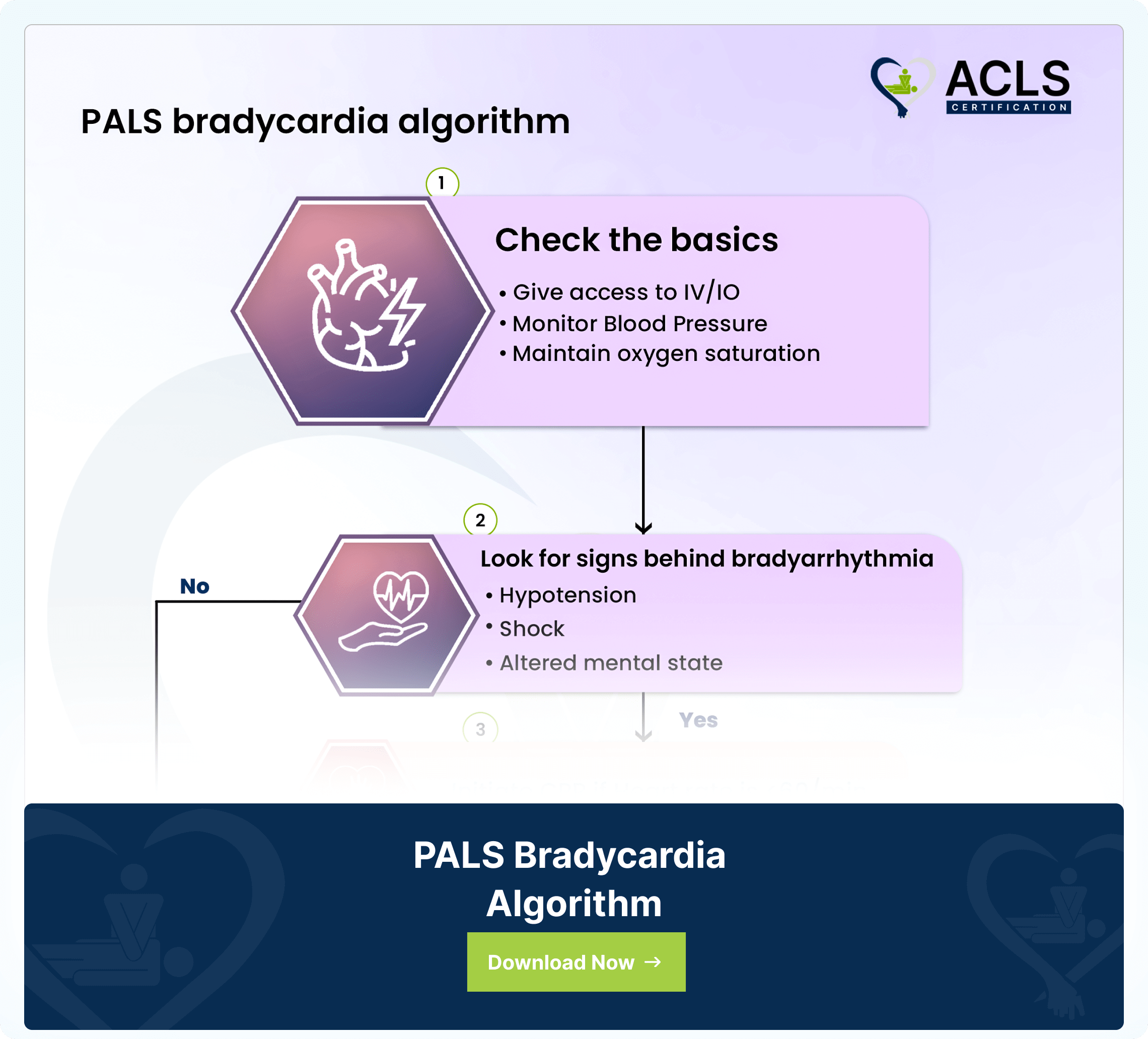
PALS Bradycardia Algorithm
The Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) Bradycardia Algorithm gives a systematic approach to managing slow heart rates
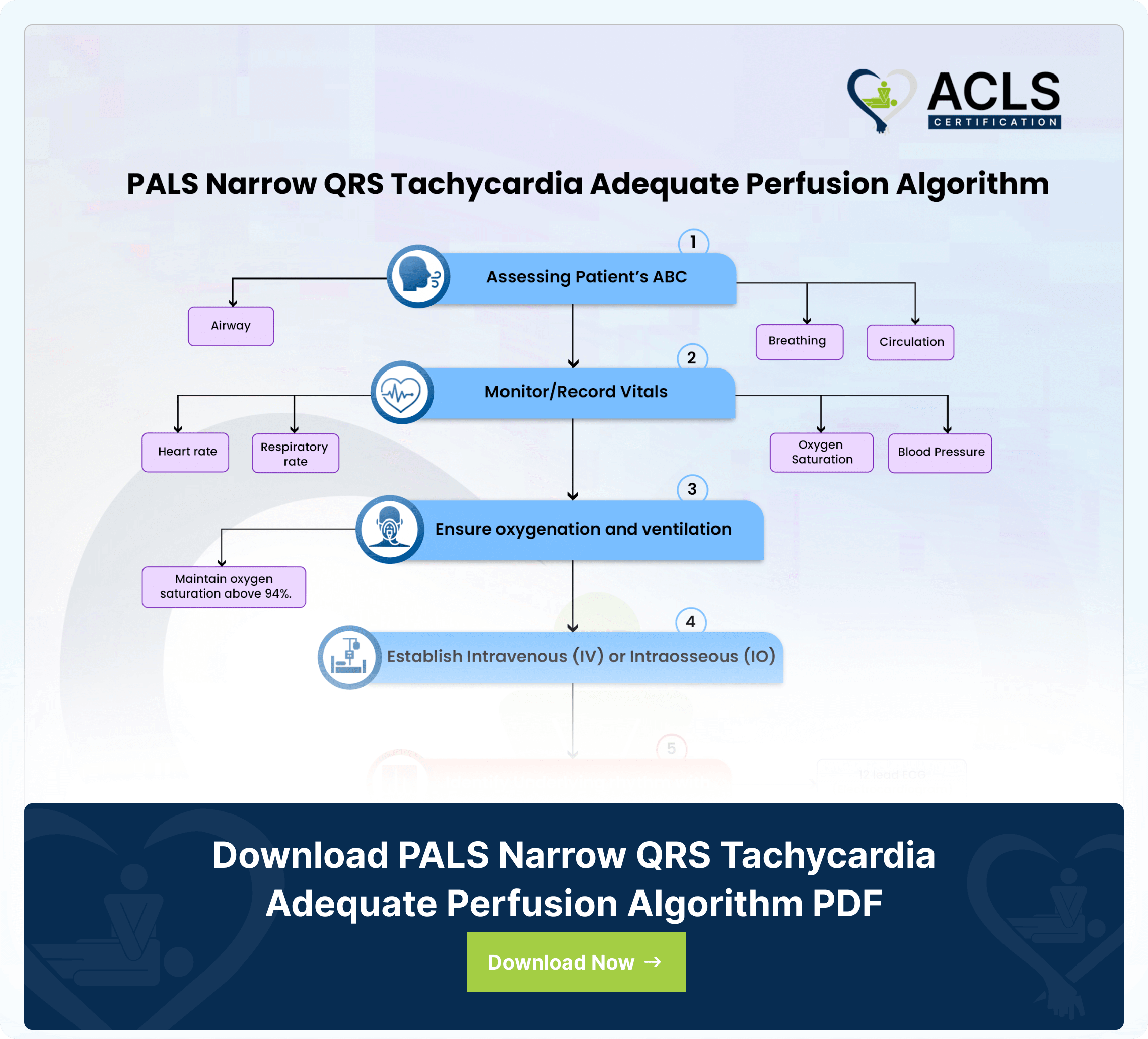
PALS Narrow QRS Tachycardia Adequate Perfusion Algorithm
The PALS Narrow QRS Tachycardia Adequate Perfusion Algorithm gives a structural approach for managing pediatric cardiac emergencies. The algorithm ensures effective treatment to maintain adequate perfusion in pediatric patients.
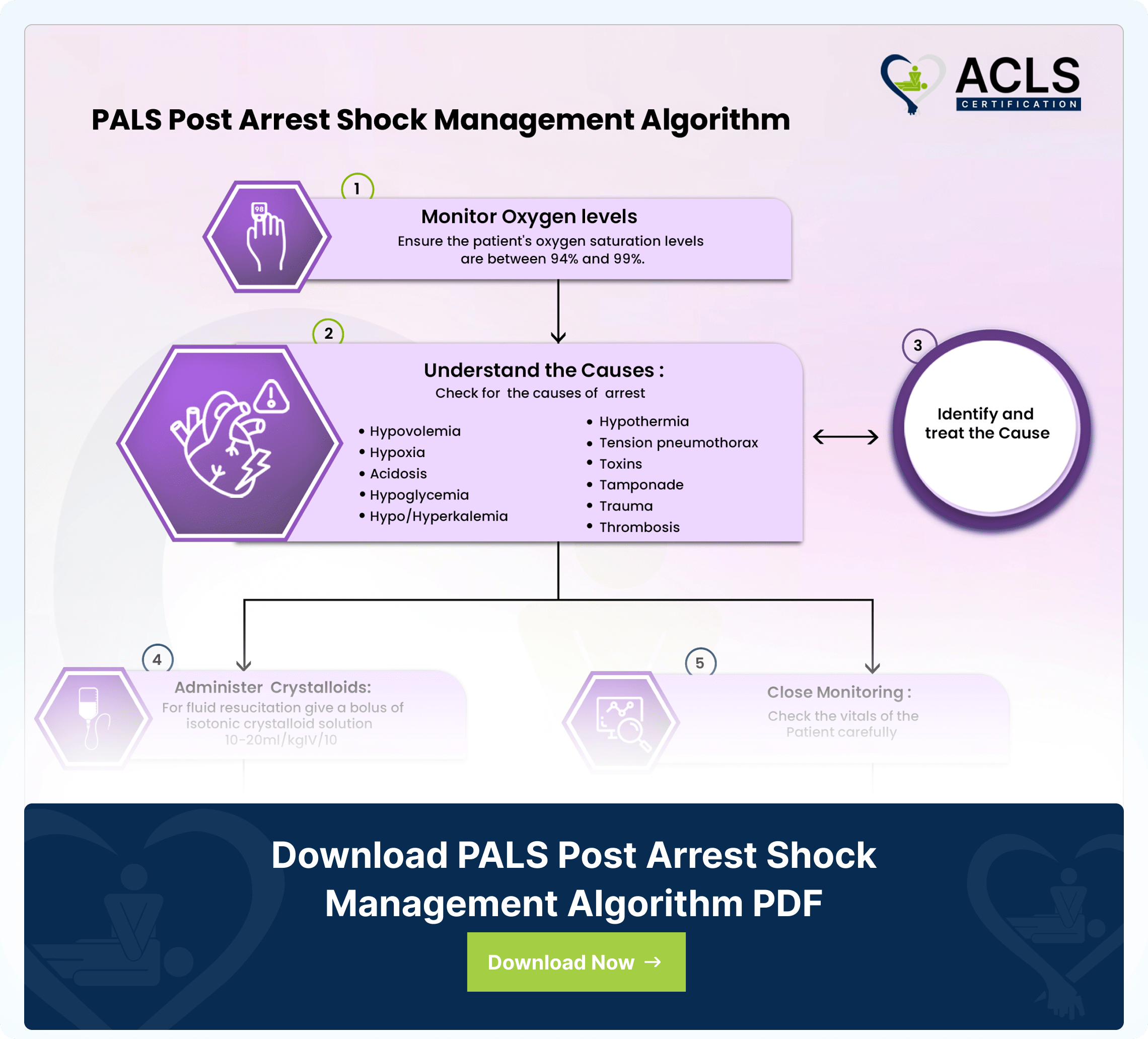
PALS Post Arrest Shock Management Algorithm
The PALS Algorithm Stabilizes pediatric patients’ post-cardiac arrest optimizing recovery through targeted interventions