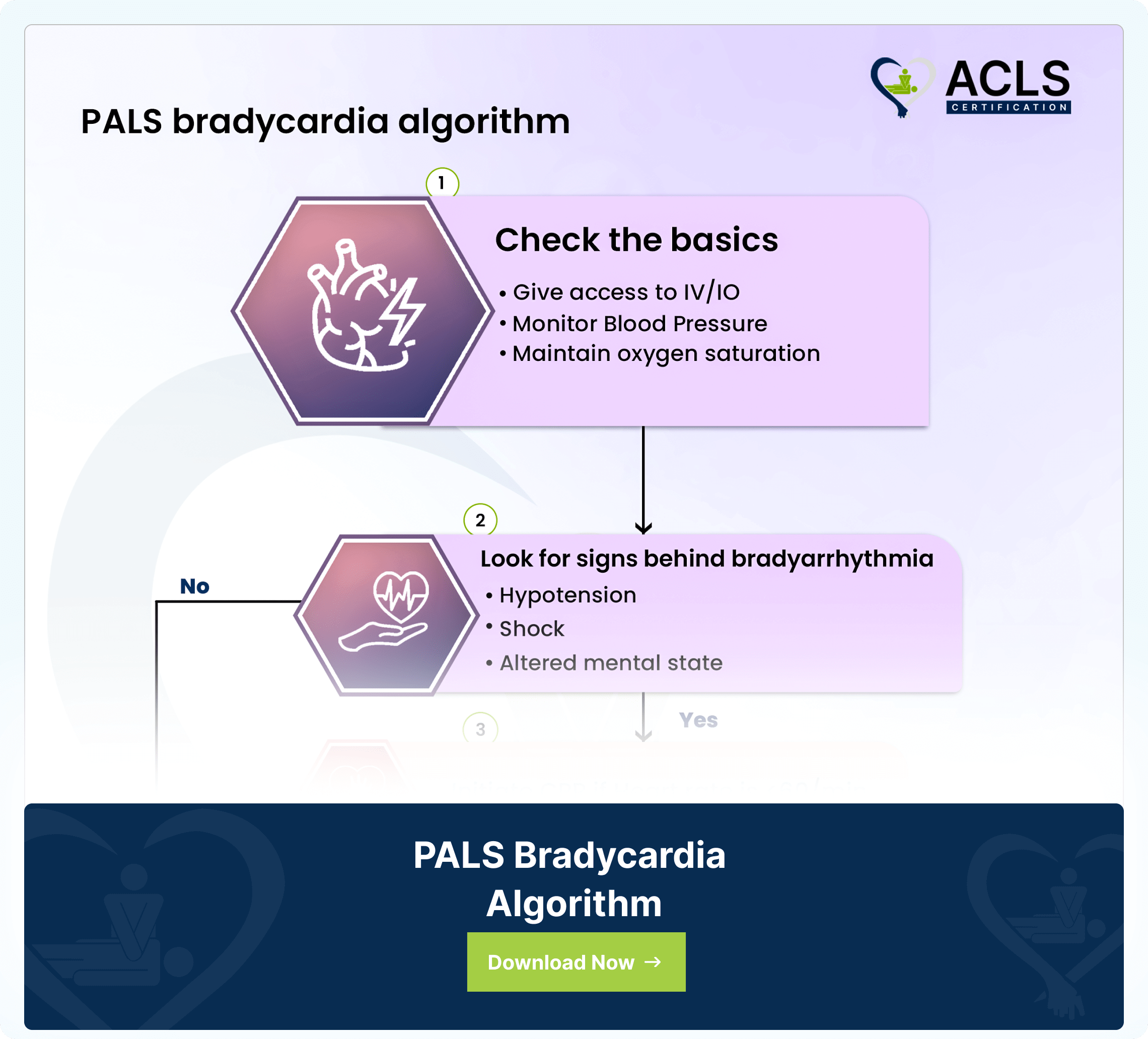
The PALS Bradycardia Algorithm outlines a methodical approach to managing slow heart rates in pediatric patients. It encompasses evaluating the need for intervention, administering suitable treatments like oxygen, establishing IV access, and considering transcutaneous pacing if required. Moreover, this algorithm systematically addresses the assessment and management of bradycardia, which includes recognizing signs and symptoms and implementing appropriate interventions. The accompanying flowchart illustrates the steps involved in determining the necessity for intervention, applying appropriate treatments such as oxygen, establishing IV access, and contemplating the utilization of medications like atropine and epinephrine to manage bradycardia.
Understanding the flowchart
- Begin by identifying the root cause of the condition while ensuring the patient’s basic functions are supported.
- Assist with breathing, administer oxygen
- Establish IV/IO access
- Monitor vital signs like BP and oxygen saturation.
- Investigate potential underlying factors contributing to bradyarrhythmia. Thoroughly examine for shock, hypotension, or alterations in mental status.
- If signs of inadequate tissue perfusion persist or the heart rate remains below 60 BPM despite oxygenation, initiate CPR and monitor closely.
- If bradycardia persists, continue essential support, monitor, and consider expert consultation.
- Administer medications judiciously. Consider epinephrine and atropine cautiously as indicated.
- In pulseless arrest, implement the Cardiac Arrest Algorithm promptly.
Note: Epinephrine and atropine dosages provided are for reference.
Essential elements of the PALS Bradycardia algorithm
- Assessment and Initial Interventions
The algorithm begins with the patient’s condition and the implementation of initial interventions. This includes identifying and treating the underlying cause along with maintaining airway patency, assisting breathing, providing oxygen, and establishing IV/IO access. - Evaluation of Cardiopulmonary Compromise
This includes evaluating the patient for signs of cardiopulmonary compromises, which are hypotension, changes in the level of the patient’s consciousness, or other signs of shock. - Doing a CPR and Perfusion Assessment
In cases of inadequate perfusion or a heart rate less than 60/min, CPR should be initiated. Furthermore, healthcare providers should continuously monitor for signs of inadequate perfusion while giving CPR. - Continuous Bradycardia Management
If bradycardia persists despite initial interventions, the algorithm recommends supporting the patient and seeking expert consultation. - Medication and Advanced Interventions
Medications should be given. These include epinephrine IV/IO or atropine if the issue is related to increasing vagal tone or primary AV block. Advanced interventions like transcutaneous pacing (TCP) or transvenous pacing (TVP) should also be considered while continuing to identify and treat the underlying cause. - Transition to Cardiac Arrest Algorithm
In the case the patient develops pulseless arrest, healthcare providers should quickly transition to the Cardiac Arrest Algorithm to initiate appropriate interventions for managing cardiac arrest.
Download PALS Bradycardia Algorithm PDF
Resources
- Importance of airway assessment for patients requiring advanced airway management. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470477/
- Understanding cardiopulmonary compromise in critically ill children https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK436018/#:~:text=Unlike%20in%20adults%2C%20cardiopulmonary%20arrest,quality%20CPR%20can%20improve%20survival
- Bradycardia With Poor Perfusion and CPR https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/circulationaha.110.971085
- Management of Symptomatic Bradycardia and Tachycardia https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.166558
- Trends over time in drug administration during pediatric in-hospital cardiac arrest in the United States: Atropine https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S030095722030530X
- What is pulseless cardiac arrest in children? https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2938492/
All PALS Algorithms
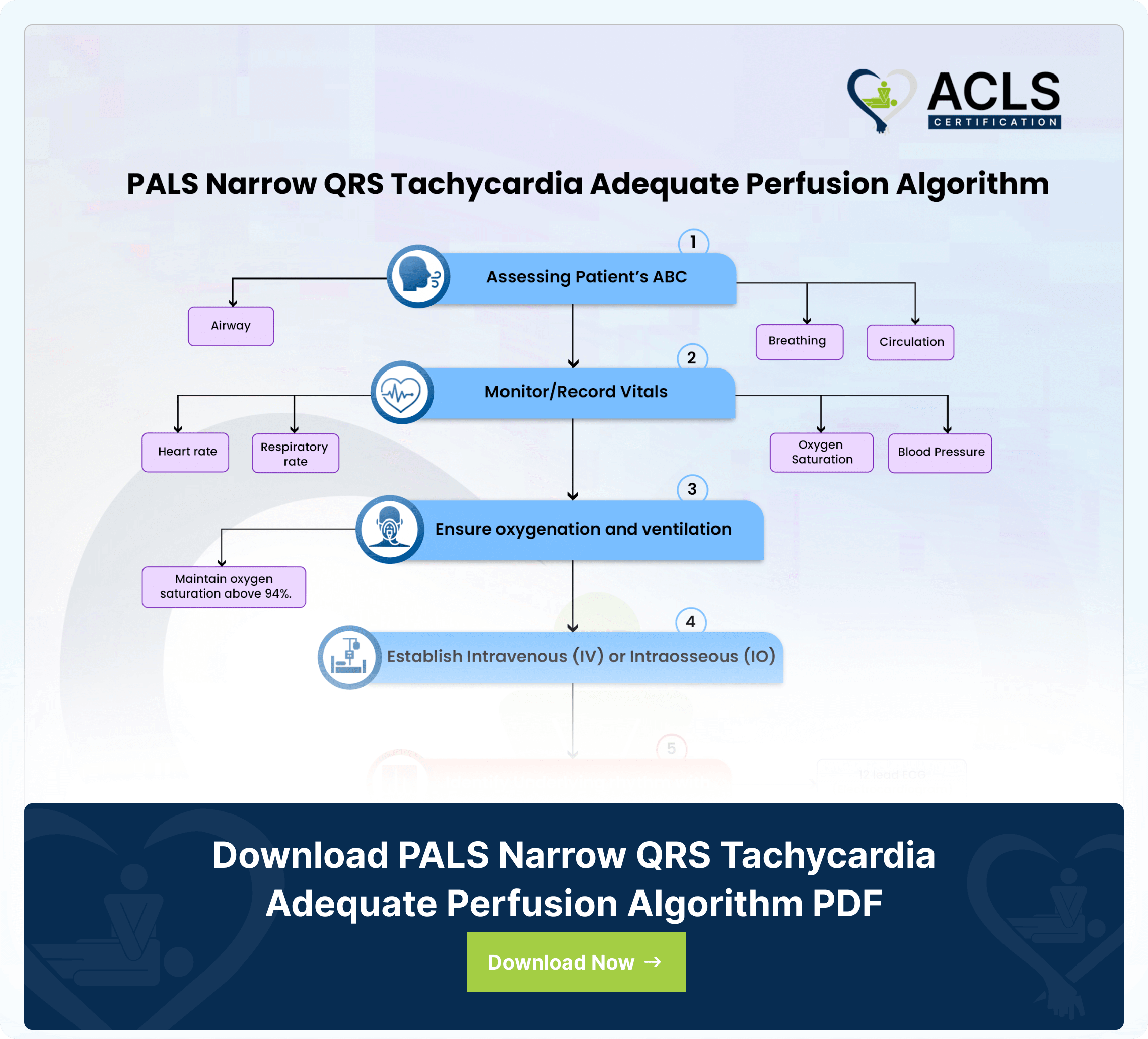
PALS Narrow QRS Tachycardia Adequate Perfusion Algorithm
The PALS Narrow QRS Tachycardia Adequate Perfusion Algorithm gives a structural approach for managing pediatric cardiac emergencies. The algorithm ensures effective treatment to maintain adequate perfusion in pediatric patients.
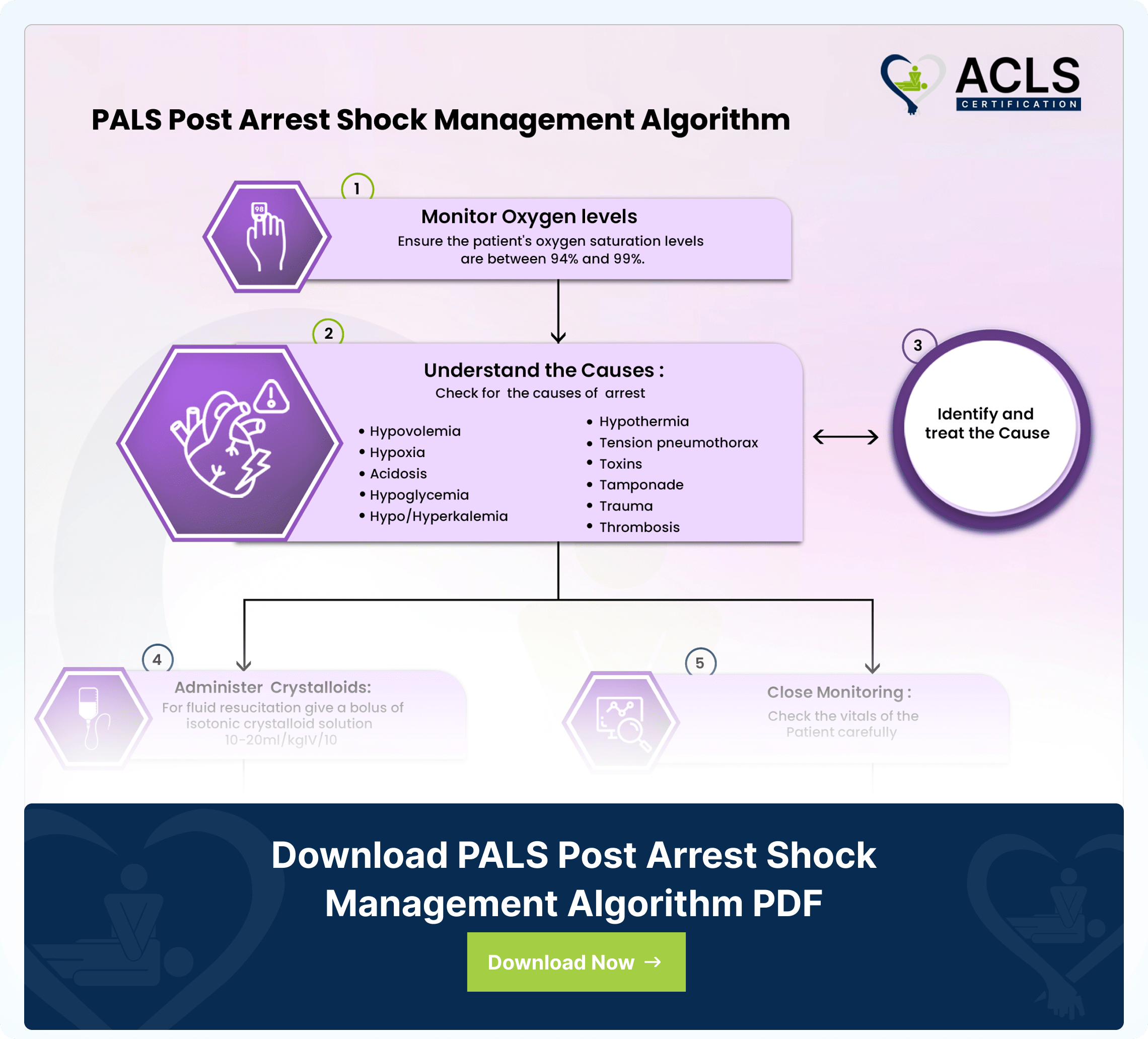
PALS Post Arrest Shock Management Algorithm
The PALS Algorithm Stabilizes pediatric patients’ post-cardiac arrest optimizing recovery through targeted interventions
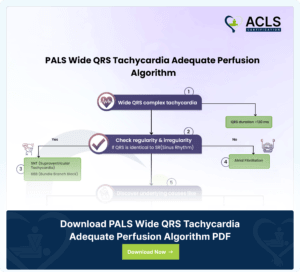
PALS Wide QRS Tachycardia Adequate Perfusion Algorithm
PALS Wide QRS Tachycardia Algorithm addresses critical pediatric cardiac conditions in an extremely systematic way. The flowchart helps medical professionals manage emergencies to ensure adequate perfusion in patients.