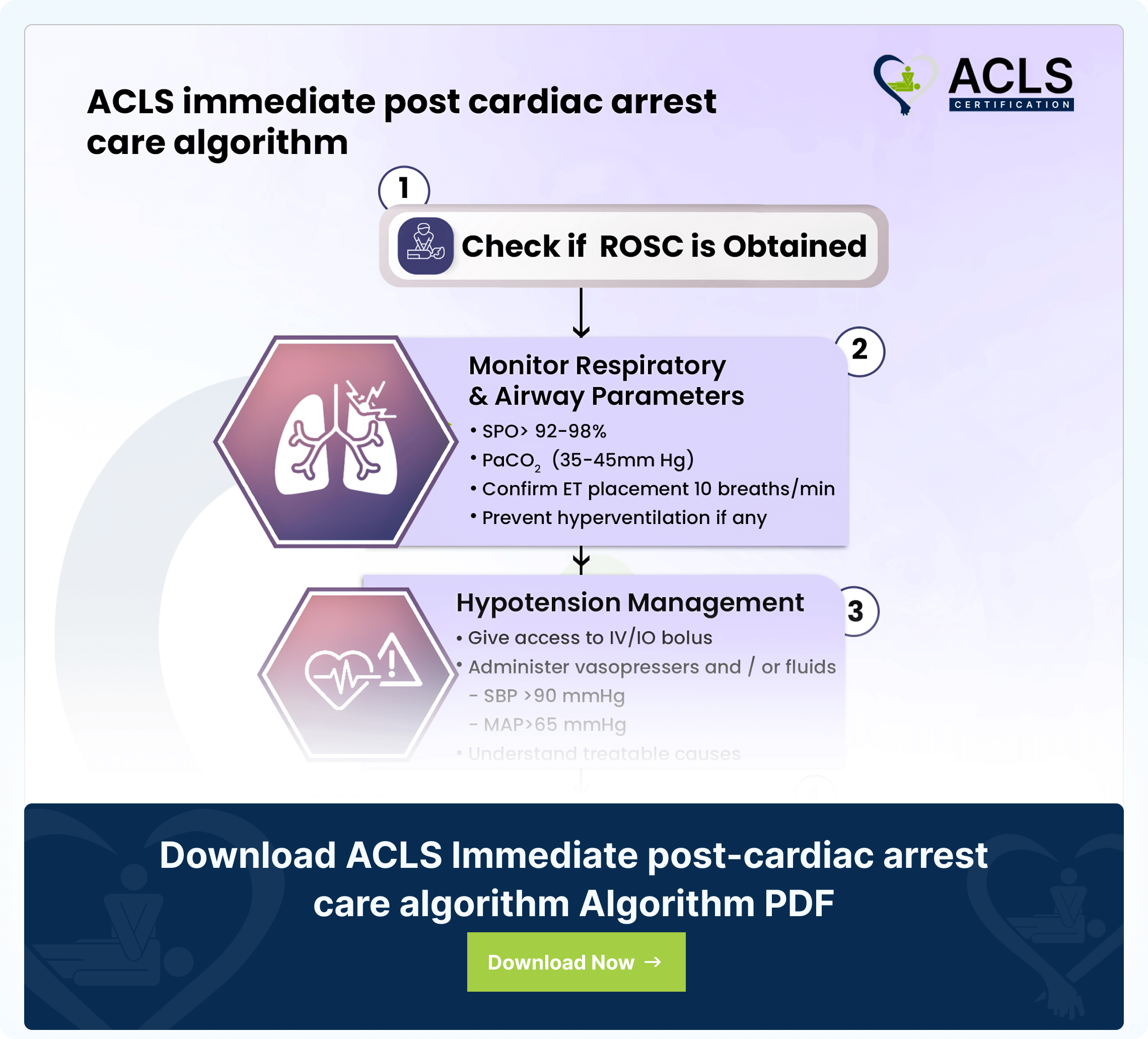
The ACLS immediate cardiac arrest care algorithm offers a systematic method for addressing cardiac arrest. It includes effective CPR, defibrillation, and medication delivery, with an emphasis on swift evaluation and intervention to enhance the likelihood of reviving spontaneous circulation and improving patient results. The flowchart given below entails the ACLS Immediate Post Cardiac Arrest Care Algorithm; the chart will guide you on the steps taken after achieving a Return of Spontaneous Circulation (ROSC). It emphasizes optimizing ventilation and oxygenation, maintaining oxygen saturation at 94%, avoiding hyperventilation, treating hypotension, and considering vasopressor infusion. Additionally, it recommends targeted temperature management and advanced critical care.
Understanding the flowchart
- ROSC Achieved: Once Return of Spontaneous Circulation is successfully obtained.</span >
- Return of Spontaneous Circulation achieved.
- Focus on Airway and Respiratory Parameters Management</span >
- While avoiding hyperventilation, maintain SPO2 levels between 92-98%.
- Confirm and monitor advanced airway placement 10 breaths/min
- Provide ventilatory rate of 10 breaths/min
- Ensure PaCO2 remains within the range of 35-45mm Hg.
- Aim to sustain oxygen saturation levels above 94% while avoiding hyperventilation.
- Follow the Hypotension Management Protocol:</span >
- Administer vasopressors and fluid resuscitation as necessary.
- Systolic Blood Pressure >90 mmHg and Mean Arterial Pressure >65 mmHg
- Identify and address any treatable factors contributing to hypotension.
- Obtaining 12-lead ECG: is STEMI present? Unstable cardiac arrhythmia? Cardiogenic shock.</span >
- If yes: Proceed with Coronary Reperfusion intervention.
- If no: Proceed to Step 5.
- Coronary Reperfusion: Initiate if indicated.</span >
- Following Commands?</span >
- If no: Initiate targeted temperature management as appropriate.</span >
- TTM if the patient not following commands is 32-26 degrees Celsius
- Consider CT head and EEG if the patient not following commands
- Address reversible etiological factors and consider implementing Critical Care Management measures.</span >
Essential elements of ACLS Immediate post-cardiac arrest care algorithm
- ROSC Obtained:
This step marks the achievement of Return of Spontaneous Circulation, indicating the restoration of a sustained pulse and blood pressure. - Manage Airway & Respiratory Parameters:
This involves maintaining the patient’s oxygen saturation (SPO2) within the range of 92-98%, ensuring the partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2) falls between 35-45mm Hg, and aiming to keep the saturation above 94% without hyperventilating the patient. - Manage Hypotension:
This involves ensuring the patient has intravenous access, administering vasopressors to support blood pressure, and identifying and addressing any reversible factors contributing to the hypotension. - Obtain 12-lead ECG:
This involves performing a 12-lead electrocardiogram to assess for signs of ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) or other cardiac abnormalities, guiding the need for immediate coronary reperfusion. - Coronary Reperfusion:
If the 12-lead ECG indicates a STEMI or suspicion of acute myocardial infarction, prompt initiation of coronary reperfusion therapy is crucial. - Following Commands:
After achieving ROSC, it is important to start targeted temperature management to optimize the patient’s neurological outcomes and reduce the risk of brain injury. - Begin targeted temperature management:
This step involves initiating measures to regulate the patient’s body temperature within a specific therapeutic range to help minimize neurological damage and improve outcomes following cardiac arrest.
Download ACLS Immediate post-cardiac arrest care algorithm Algorithm PDF
Resources
- Relating oxygen partial pressure, saturation and content: the hemoglobin–oxygen dissociation curve https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4666443/
- Understanding hypotension https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499961/
- Assessment of the 12-Lead ECG as a Screening Test for Detection of Cardiovascular Disease in Healthy General Populations of Young People (12–25 Years of Age) https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000025
- Reperfusion Strategies in Acute Coronary Syndromes https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.302744
- Therapeutic temperature management (TTM): post-resuscitation care for adult cardiac arrest https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5523092/
- Target temperature management in traumatic brain injury with a focus on adverse events, recognition, and prevention https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9732187/#:~:text=Because%20mild%2Dto%2Dmoderate%20hypothermia,treatment%20plan%20for%20TBI%20patients
- Post-cardiac arrest care and targeted temperature management https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092966462030348X
All ACLS Algorithms
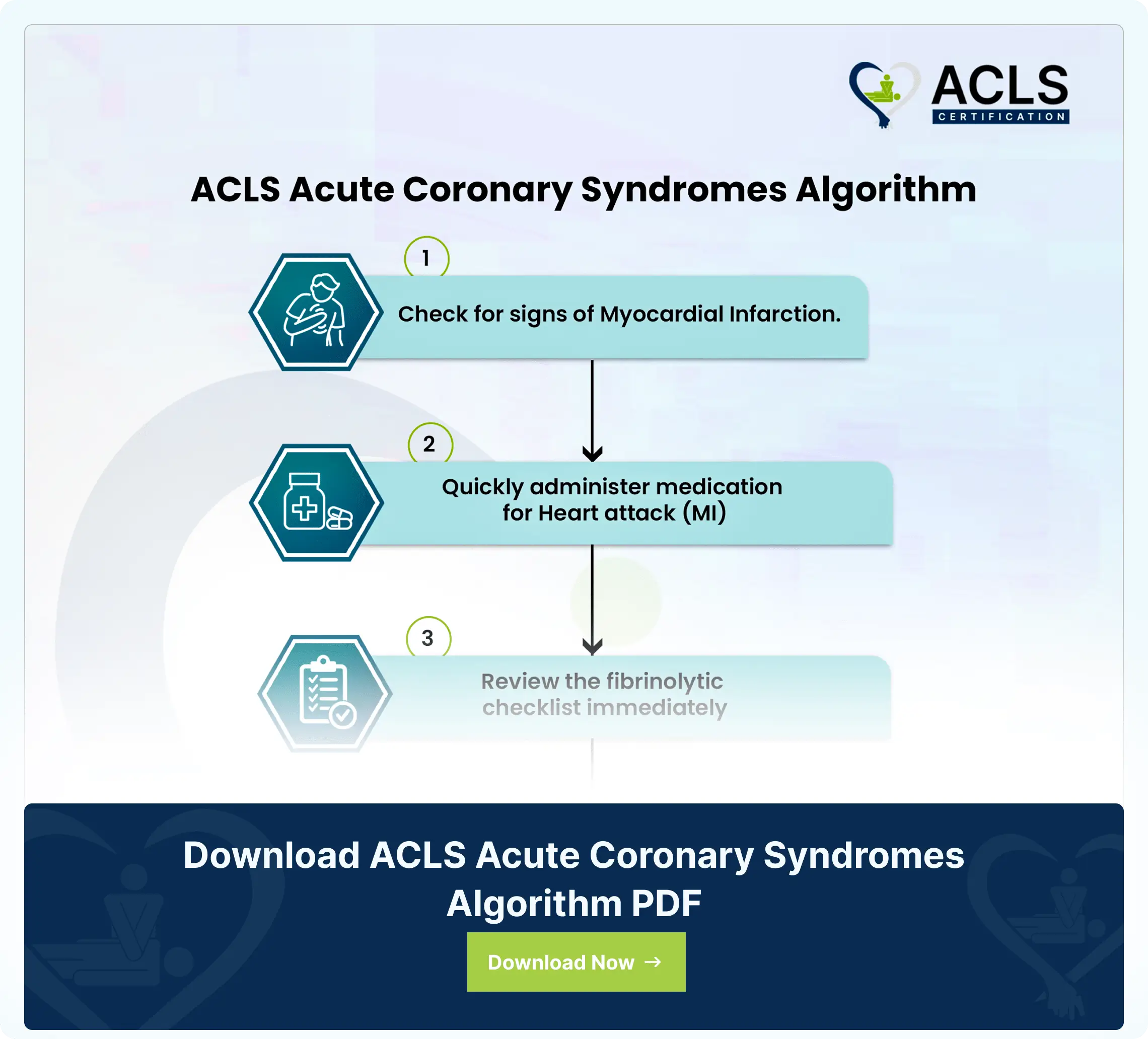
ACLS Acute Coronary Syndromes Algorithm
The ACLS Acute Coronary Syndromes Algorithm guides healthcare providers in the assessment, diagnosis, and treatment of patients with suspected or confirmed acute coronary syndromes
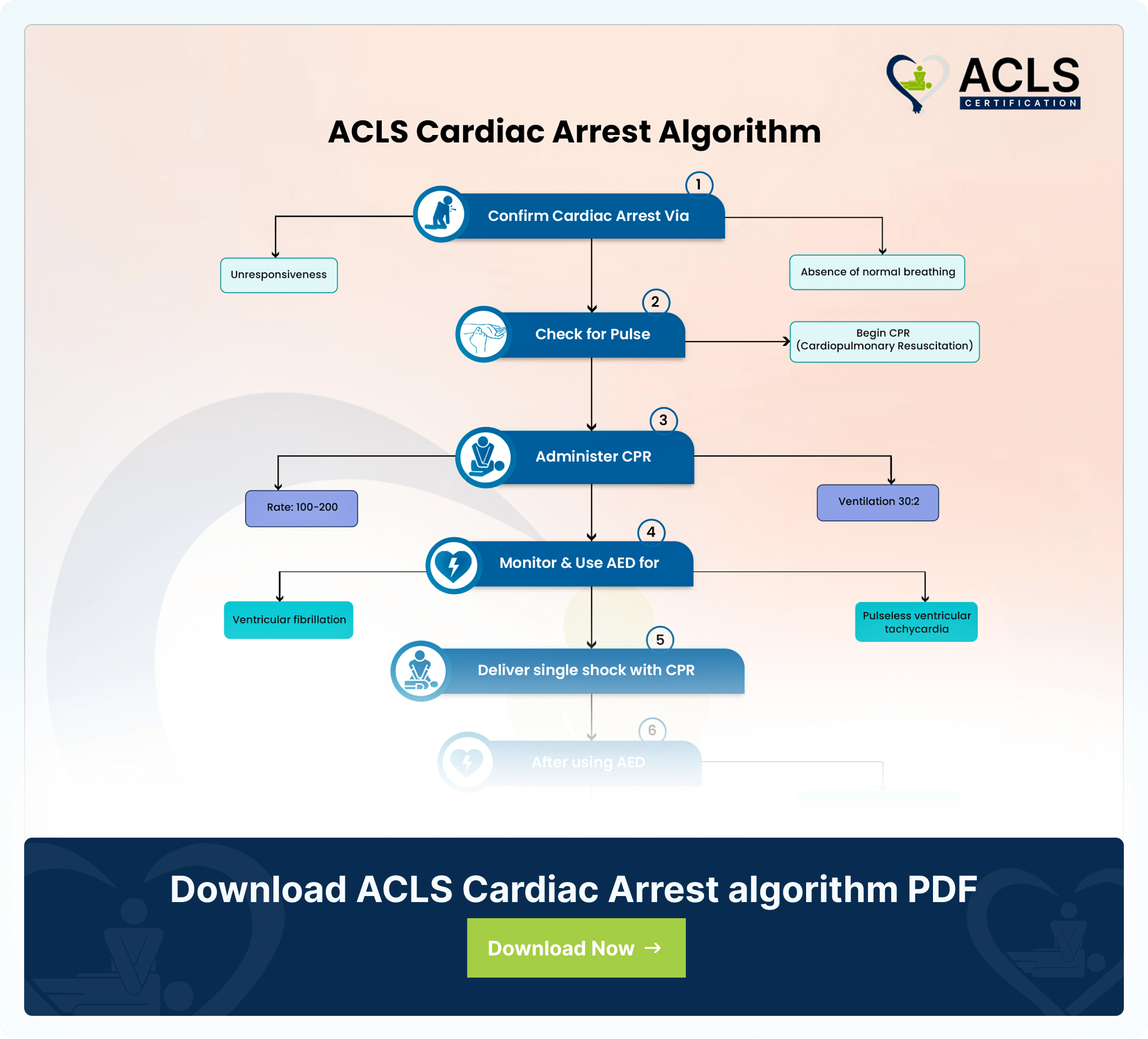
ACLS Cardiac Arrest Algorithm
The ACLS Cardiac Arrest Algorithm emphasizes CPR, defibrillation, drug therapy, and post-resuscitation care. It also highlights the importance of teamwork in optimizing outcomes during cardiac emergencies
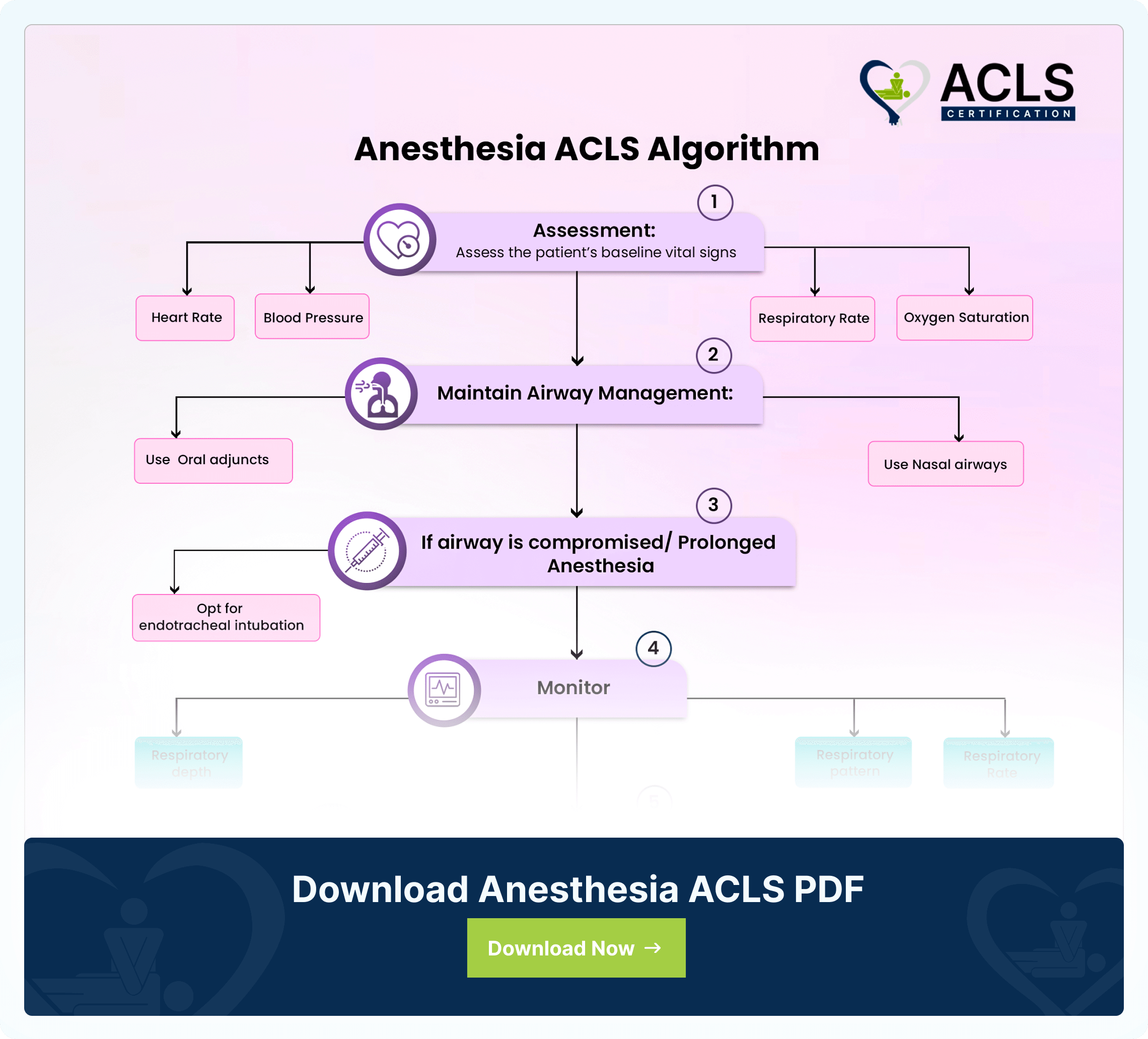
Anesthesia ACLS Algorithm
The ACLS Anesthesia Algorithm manages patients undergoing anesthesia, focusing on the importance of monitoring vital signs to avoid complications.