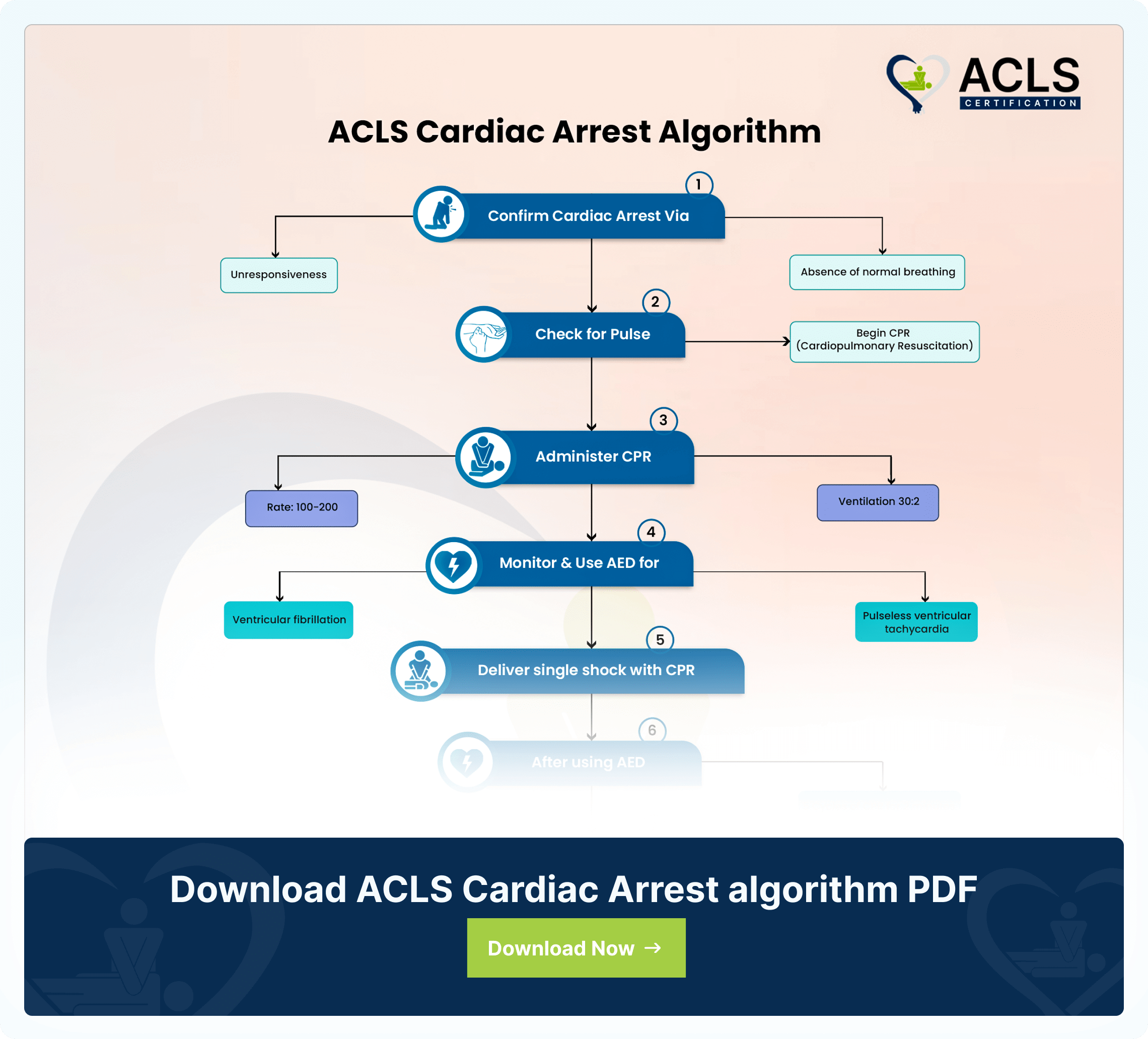
The ACLS (Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support) cardiac arrest algorithm is a structural, step by step guideline designed for medical professionals. This enables seamless intervention to effectively manage cardiac or respiratory arrest. Outlining the series of critical steps chronologically, this algorithm maximizes the chances of positive patient outcomes. Presenting to you an overview of the key components of this algorithm. Along with the importance of timely intervention, this flowchart completely abides by evidence based guidelines.
Step by step analysis of flowchart
- Confirm Cardiac Arrest Via
- Unresponsiveness
- Absence of normal breathing
- Check for Pulse
- Begin CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation)
- Administer CPR
- Rate: 100-200
- Ventilation 30:2
- Monitor & Use AED for
- Ventricular fibrillation
- Pulseless ventricular tachycardia
- Deliver single shock with CPR
- After using AED
- 5 Cycles of CPR for 2 minutes
- Assess shockable rhythm
- If Yes: Deliver another shock and resume CPR immediately.
- If No: Continue CPR
- Administer Epinephrine
- Dosage: 1 mg IV/IO
- Time: 3-5 minutes
- Continue
- CPR
- Rhythm assessment
- Defibrillation (if needed)
- Using Amiodarone or Lidocaine
- Optimize Oxygenation and Ventilation by
- Endotracheal Intubation
- Supraglottic airway
- Treat reversible causes H’s
- Hypoxia
- Hypovolemia
- Hydrogen ion [acidosis]
- Hypo-/Hyperkalemia
- Hypothermia
- Treat reversible causes T’s:
- Tension pneumothorax
- Tamponade
- Toxins
- Thrombosis
- Post-resuscitation care with
- Targeted temperature management
- Optimize hemodynamics
- Supportive care post-return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC)
Highlights of ACLS Cardiac Arrest Algorithm
- Recognition of Cardiac Arrest:
Identify cardiac arrest through assessing unresponsiveness, absence of normal breathing, and lack of pulse. - Activation of Emergency Response:
Initiate emergency response system and assign roles to team members for efficient coordination. - High-Quality CPR:
Initiate high-quality chest compressions at a rate of 100 to 120 compressions per minute. Ensure adequate depth and allow for full chest recoil between compressions. - Defibrillation:
Deliver a shock if indicated for shockable rhythms such as ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia. - Medication Administration:
Administer medicines like epinephrine to support blood circulation and optimize outcomes. Amiodarone or lidocaine may be administered per ACLS guidelines based on the patient’s rhythm and condition. - Systematic Rhythm Assessment:
Patient’s cardiac rhythm should be assessed to determine the need for defibrillation and to guide further interventions. - Management of Reversible Causes:
Manage underlying reversible causes of cardiac arrest, such as hypoxia, hypovolemia, electrolyte imbalances, toxins, tension pneumothorax, tamponade, and thrombosis. - Advanced Airway Management:
Consider and implement advanced airway management techniques. This can include endotracheal intubation or supraglottic airway placement. - Post-Resuscitation Care:
Initiate targeted temperature management (if indicated). - Transport:
Arrange for immediate transfer to an appropriate care facility for further evaluation and management post-ROSC.
Download ACLS Cardiac Arrest algorithm PDF
Resources:
- Algorithms https://cpr.heart.org/en/resuscitation-science/cpr-and-ecc-guidelines/algorithms
- Emergency Medical Services Response to Cardiac Arrest https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK321505/
- Immediate Post-Cardiac Arrest Care Algorithm https://acls.com/articles/post-cardiac-arrest/
- BLS, ACLS, & PALS Algorithms https://www.aclsmedicaltraining.com/acls-algorithms/
- Management of Cardiac Arrest https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.166557
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1344081-overview?form=fpf
- Resuscitation https://academic.oup.com/book/31761/chapter-abstract/265757398?redirectedFrom=fulltext
- Advanced Life Support Algorithm https://lms.resus.org.uk/modules/m25-v2-als-algorithm/11118/resources/chapter_6.pdf
- Shockable vs. Non Shockable Heart Rhythms https://avive.life/blog/shockable-vs-non-shockable-heart-rhythms/
All ACLS Algorithms
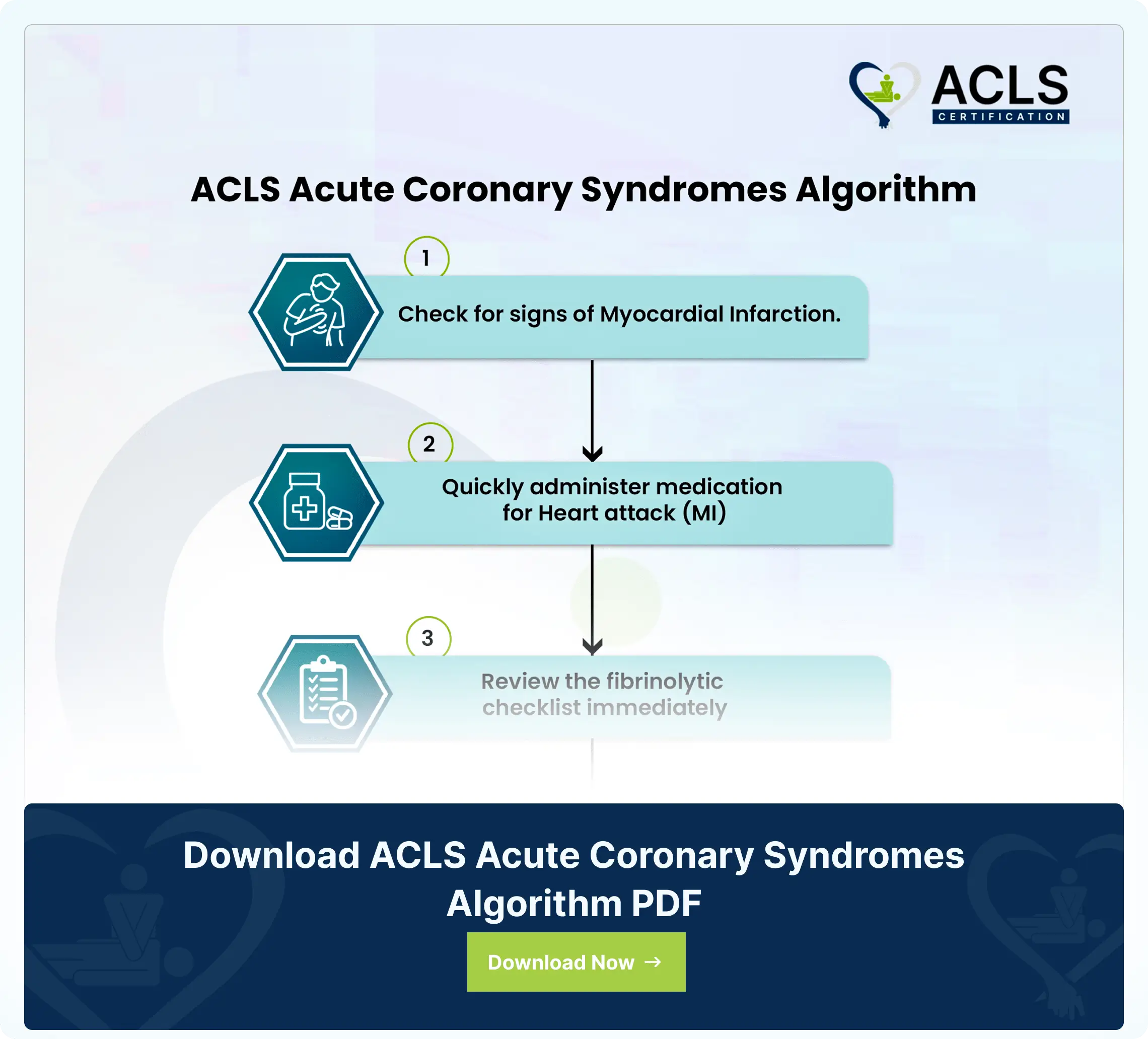
ACLS Acute Coronary Syndromes Algorithm
The ACLS Acute Coronary Syndromes Algorithm guides healthcare providers in the assessment, diagnosis, and treatment of patients with suspected or confirmed acute coronary syndromes
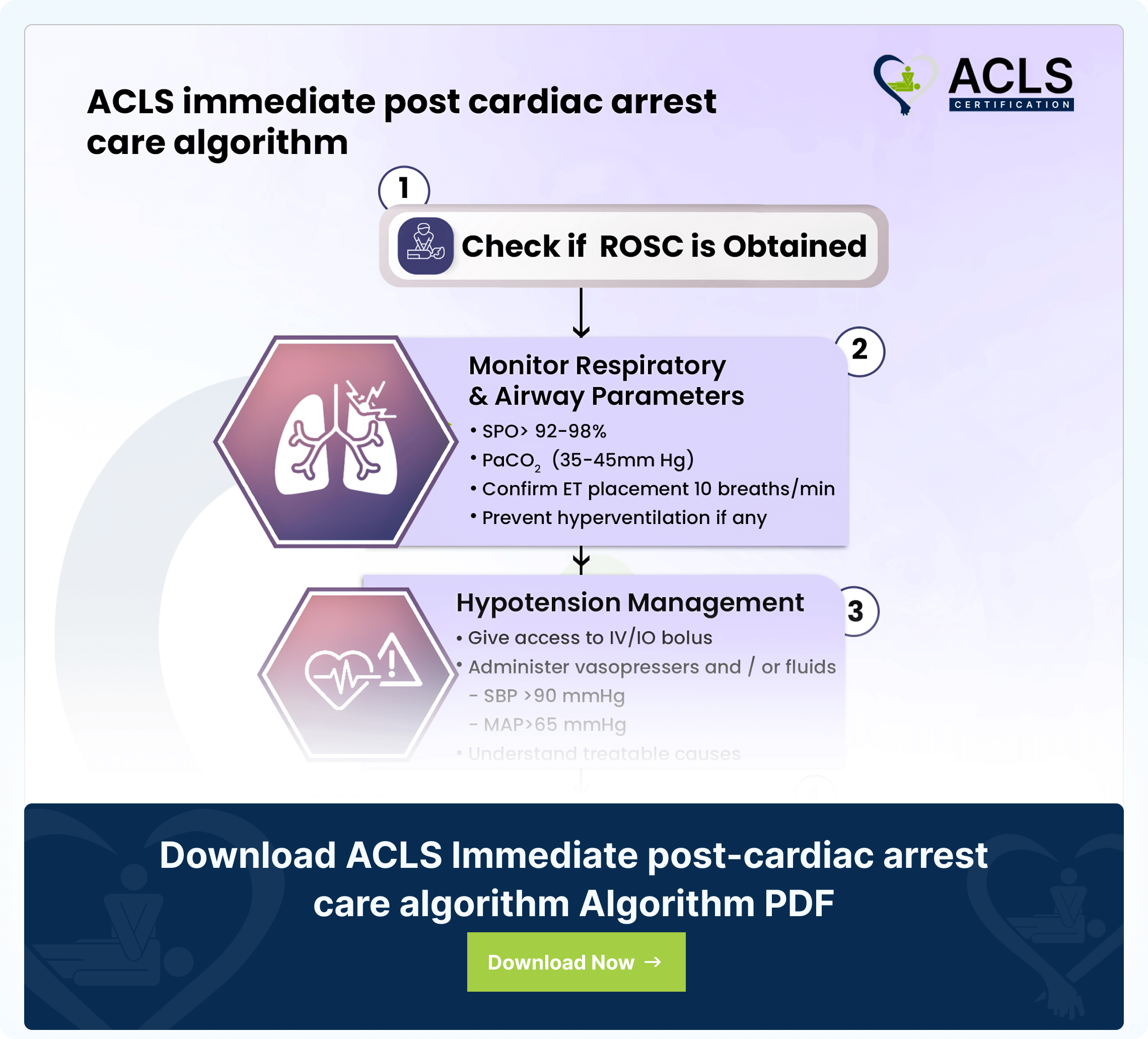
ACLS Immediate post-cardiac arrest care algorithm
The ACLS immediate post-cardiac arrest care algorithm guides critical interventions for patients post-resuscitation
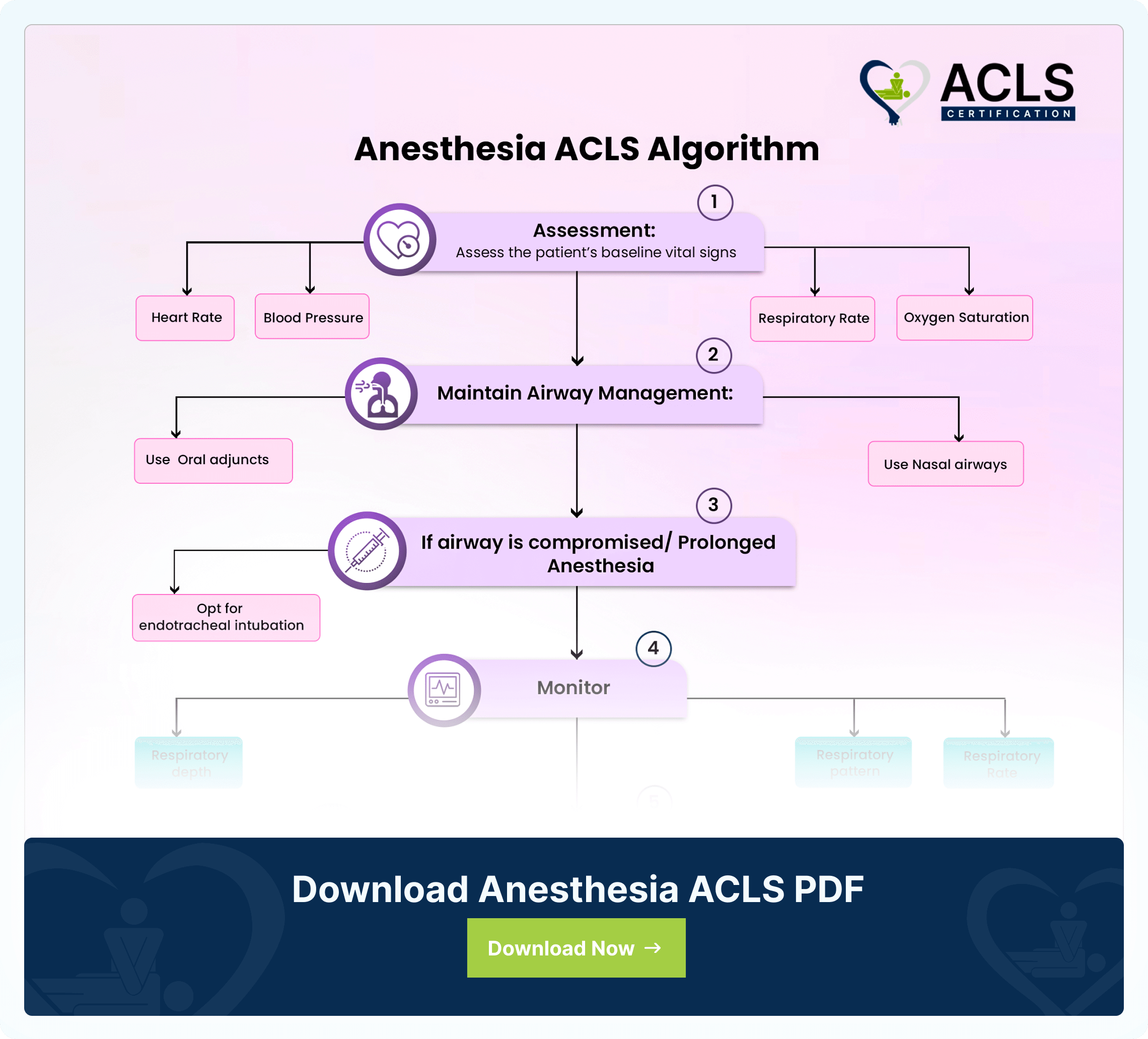
Anesthesia ACLS Algorithm
The ACLS Anesthesia Algorithm manages patients undergoing anesthesia, focusing on the importance of monitoring vital signs to avoid complications.