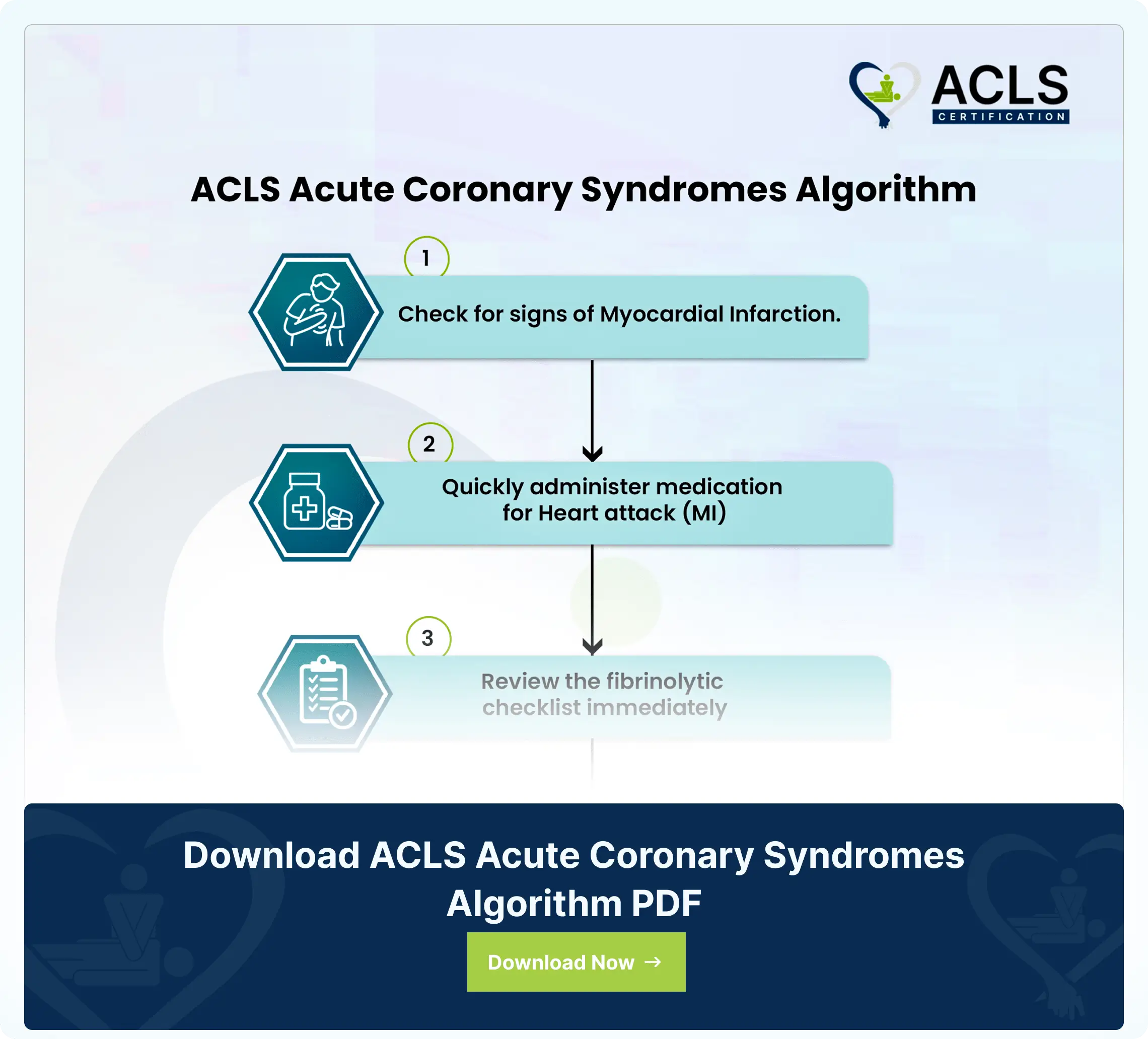
The ACLS (Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support) Acute Coronary Syndromes Algorithm provides a systematic approach to managing patients with acute coronary syndromes (ACS). These could include unstable angina and myocardial infarction. This algorithm guides healthcare providers in the assessment, diagnosis, and treatment of ACS, with a focus on timely intervention to minimize myocardial damage and improve patient outcomes. The ACLS Acute Coronary Syndromes Algorithm emphasizes the importance of a coordinated and multidisciplinary approach to caring for patients with ACS. By following this algorithm, healthcare providers can optimize outcomes for patients with MI and provide timely and effective interventions to reduce the chances of death associated with these conditions.
Details of the Flowchart
- Sign Identification:
Myocardial infarction or heart attack shows typical signs like nausea, heartburn, and pain in the left arm. As the lay responder or healthcare provider, you must identify these signs to follow the steps below. - Give Medication:
Once MI is confirmed, you must administer the proper medication, usually via injection. - Fibrinolytic Checklist:
Quickly review the checklist to take down the patient’s medical history, trauma, accidents, or past injuries. - Time:
You must note the time of onset of symptoms and ensure you take the following steps accordingly. - <12 Hours:
If the symptoms started less than 12 hours, you must begin the reperfusion protocol and deliver adjunctive therapy. - >12 Hours:
This time is critical, and the patient will need immediate hospital administration and care. - Adjunctive Therapy:
In either situation, the final step is delivering inhibitors or beta blockers to save the patient’s life.
Highlights of the Graph
- Signs of MI:
The common signs include crushing chest pain that travels to the jaw, arm, and back. The patient would experience nausea/vomiting and excessive sweating. Some people also experience shortness of breath. - Medication for MI:
Aspirin is the most common medication for MI. You may need to administer morphine if required . - Reperfusion Protocol:
It includes steps to open the blocked artery. The medical team may perform an angioplasty or an intravenous thrombolysis. - Adjunctive Therapy:
This therapy is for people suffering from MI and includes beta-adrenergic blocking agents, enzyme inhibitors, and other chemicals.
Download ACLS Acute Coronary Syndromes Algorithm pdf
Resources
- Acute Coronary Syndromes: Diagnosis and Management, Part I https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2755812/
- Myocardial Infarction: Symptoms and Treatments https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25638347/#:~:text=The%20symptoms%20of%20MI%20include,%2C%20depression%2C%20and%20other%20factors
- Conventional drug therapy of patients with acute myocardial infarction https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2653636/
- 68 Adjunctive Therapy in Acute Myocardial Infarction https://academic.oup.com/book/25195/chapter-abstract/189658882?redirectedFrom=fulltext
- ACUTE MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION: REPERFUSION TREATMENT https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1767333/
- The Underutilization of Adjunctive Pharmacotherapy in Treating Acute Coronary Syndrome Patients Admitted to a Tertiary Care Hospital in Southwest Region, Saudi Arabia https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3089826/#:~:text=Adjunctive%20therapy%20for%20ACS%20includes,%2Dlowering%20agents%20(statin).&text=Several%20guidelines%20were%20established%20to%20improve%20care%20for%20ACS%20patients
All ACLS Algorithms
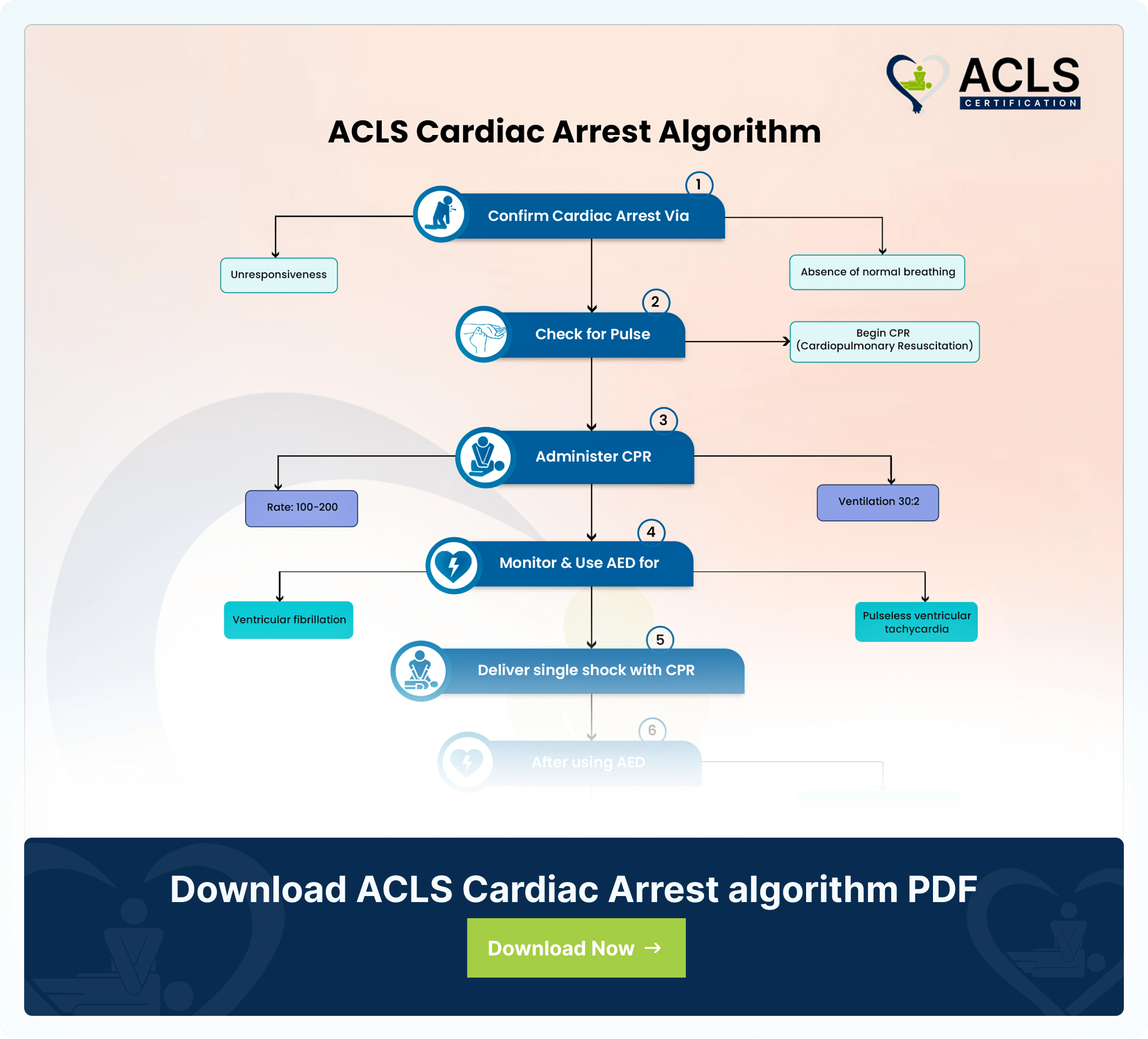
ACLS Cardiac Arrest Algorithm
The ACLS Cardiac Arrest Algorithm emphasizes CPR, defibrillation, drug therapy, and post-resuscitation care. It also highlights the importance of teamwork in optimizing outcomes during cardiac emergencies
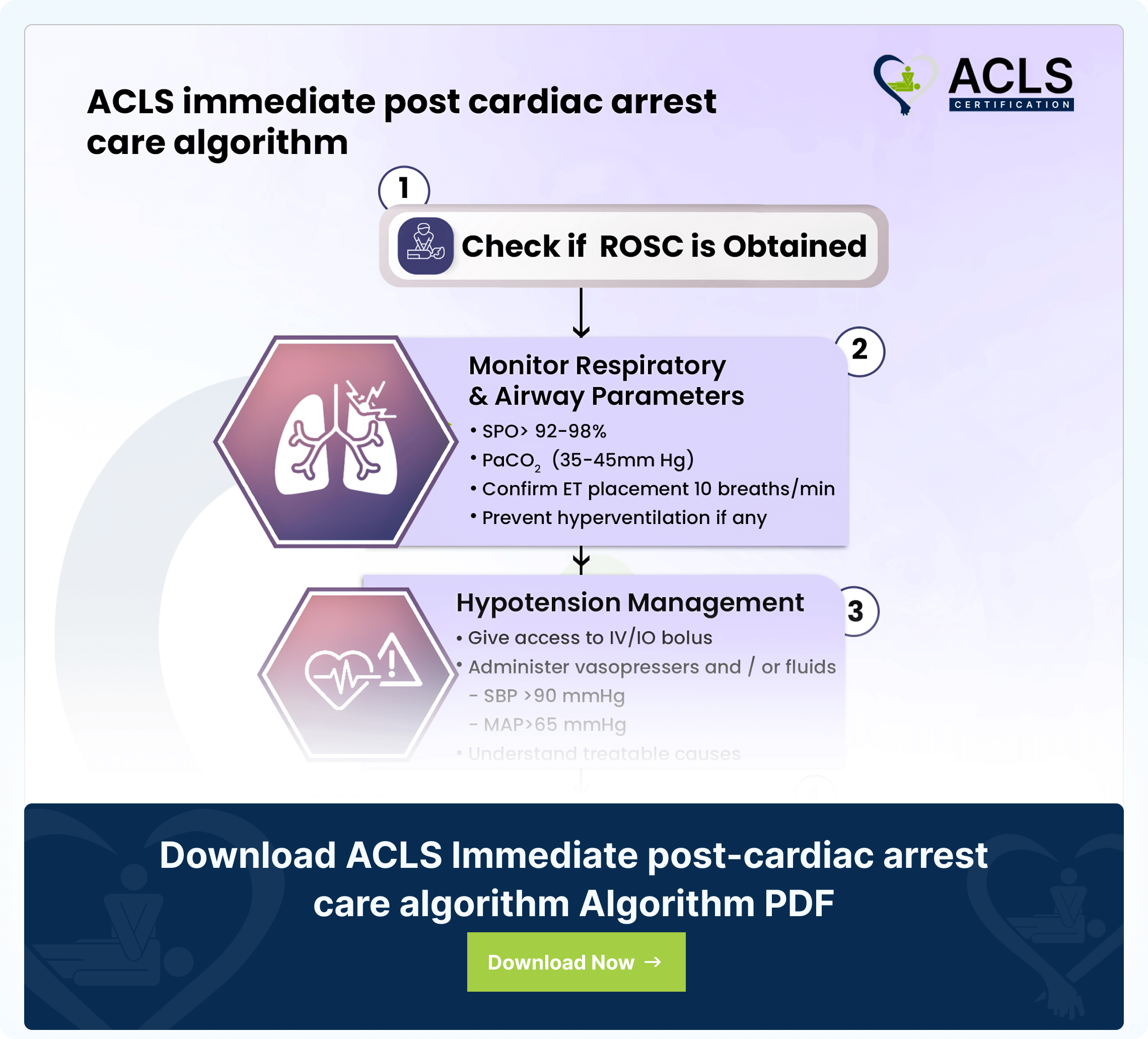
ACLS Immediate post-cardiac arrest care algorithm
The ACLS immediate post-cardiac arrest care algorithm guides critical interventions for patients post-resuscitation
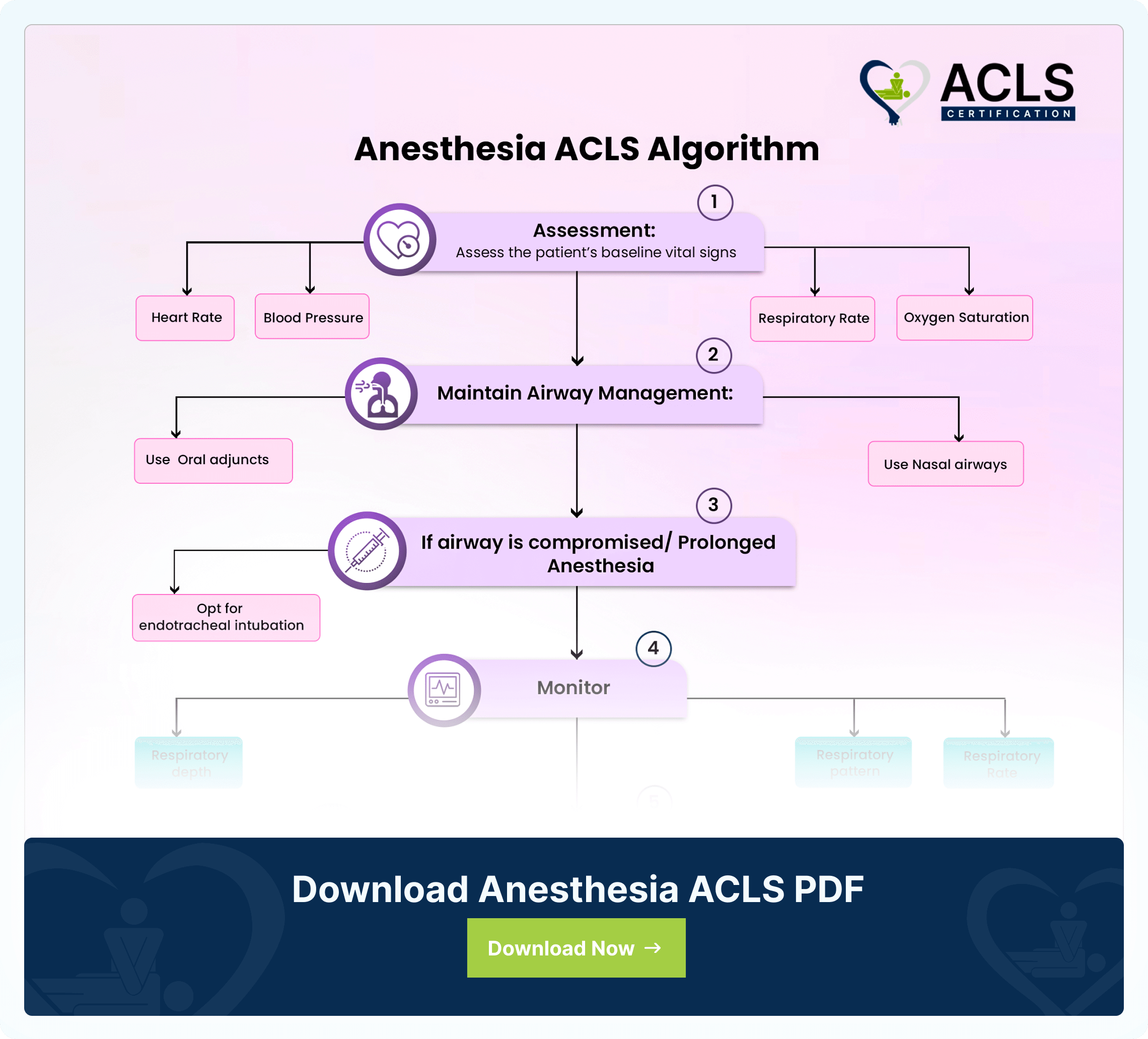
Anesthesia ACLS Algorithm
The ACLS Anesthesia Algorithm manages patients undergoing anesthesia, focusing on the importance of monitoring vital signs to avoid complications.