The PALS Tachycardia Poor Perfusion Algorithm is a guide used in pediatric emergency medicine to assist with the management of fast heartbeats in children and infants that cause poor circulation; signs and symptoms of poor perfusion include changes in mental alertness, cold and clammy skin, and others that will be discussed in this guide. It gives clear instructions on how to assess and manage unstable fast heartbeats in children and infants to improve circulation and stabilize their condition. This algorithm is used in hospital emergency rooms, pediatric intensive care units, and other healthcare places where children and infants with heart emergencies are treated.
Details of Flowchart
- Potential Underlying Factors: Upon detecting inadequate perfusion, examine for potential underlying issues such as sepsis or lack of patent airway.
- ABC: If the child’s condition does not improve, attempt to clear the airway, administer rescue breaths, and perform chest compressions. Refer to BLS pathway immediately in this event.
- QRS Evaluation: Assess whether the QRS complex is narrow (≤0.09 sec) or wide (>0.09 sec).
- Wide QRS Assessment: If the QRS complex is wide, evaluate the child’s vital signs for stability or instability.
- Compromised Child: In the event of a compromised child, prompt cardiologist intervention is essential for synchronized cardioversion. This treatment should only be performed by experts. Begin with 0.5-1 J/kg. If the initial dose is not effective, increase dose to 2 J/kg. Synchronized cardioversion is painful to the patient; please consider sedation if able but never delay treatment.
- Uncompromised Child: If the child is not compromised, commence cardioversion. Administer adenosine via IV/IO. Adenosine first dose is 0.1 mg/kg rapid bolus. The first dose should not exceed 6mg. The second dose is 0.2 mg/kg rapid bolus and should not exceed 12mg. Adenosine should be rapidly administered; steps should be taken to immediately flush with NS after administration due to the short half life of the medication.
- Narrow QRS: In cases of narrow QRS tachycardia, assess if the patient is stable or unstable.
- If stable: Vagal Maneuvers should be considered and Adenosine should be administered if the maneuvers are ineffective. Vagal Maneuvers include the following: bag of ice to top half of infant’s face ensuring you are not occluding the airway, asking older children to bear down or blow through an impeded straw. Adenosine dosages are the same as mentioned above.
- If unstable: Sychronized Cardioversion and Adenosine administration. The same dosages apply.
Key Highlights
- Heart Range
| Age Group | Normal Heart Rate (bpm) |
| Newborns (0 to 1 month) | 70 to 190 beats per minute (bpm) |
| Infants (1 to 12 months) | 80 to 160 bpm |
| Toddlers (1 to 3 years) | 80 to 130 bpm |
| Preschoolers (3 to 5 years) | 80 to 120 bpm |
| School-age children (6 to 12 years) | 70 to 110 bpm |
| Adolescents (13 to 18 years) | 60 to 100 bpm |
*The above are general guidelines, and individual variations may occur. You must consult a healthcare provider for specific concerns about your child’s heart rate.
Download PALS Tachycardia Initial Management Algorithm PDF
Sources
- Supraventricular Tachycardia https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441972/
- Emergency diagnosis and management of pediatric arrhythmias https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2938490/
- Normal ranges of heart rate and respiratory rate in children from birth to 18 years: a systematic review of observational studies https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3789232/
- Synchronized Electrical Cardioversion https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482173/
All PALS Algorithms
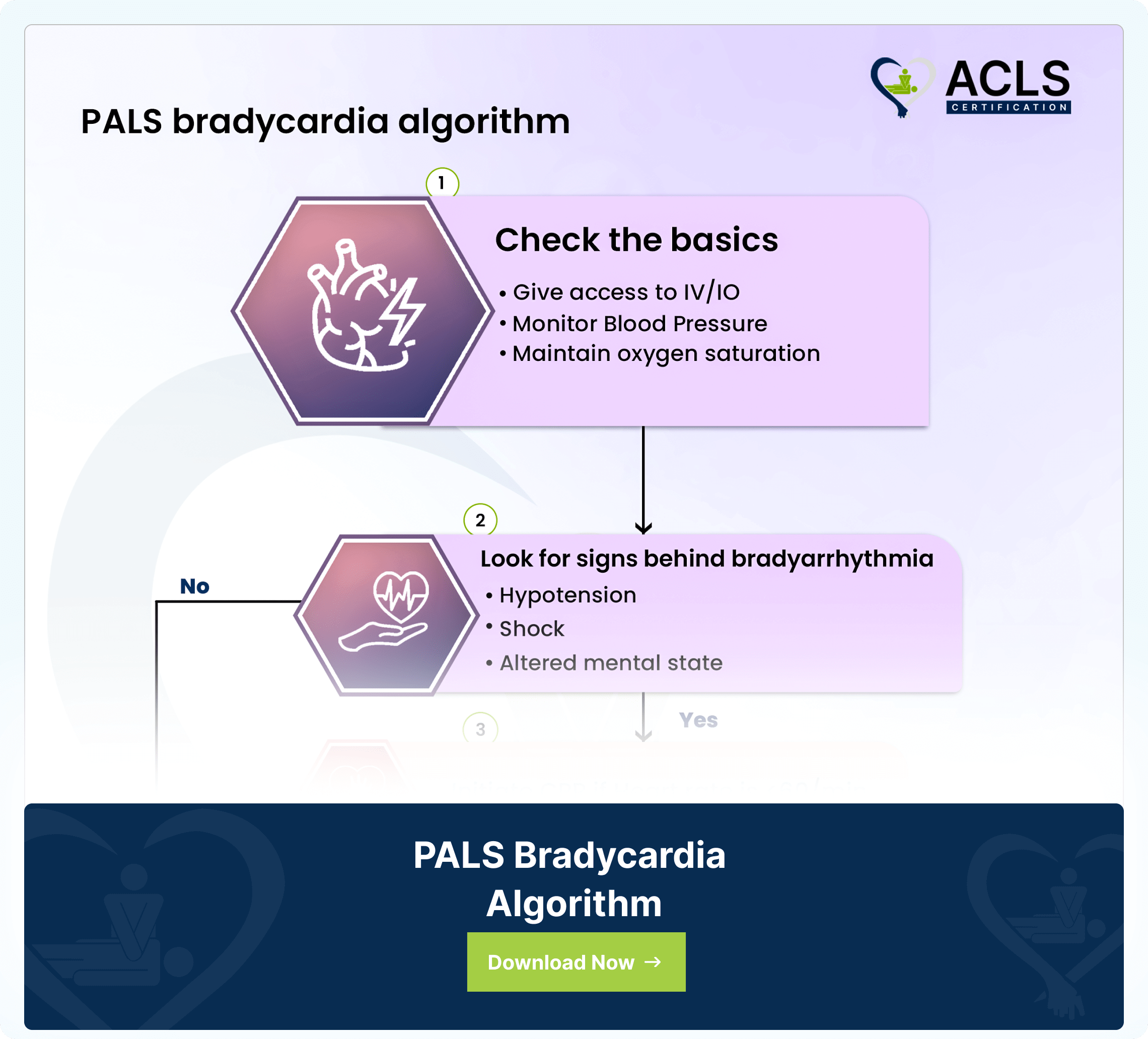
PALS Bradycardia Algorithm
The Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) Bradycardia Algorithm gives a systematic approach to managing slow heart rates
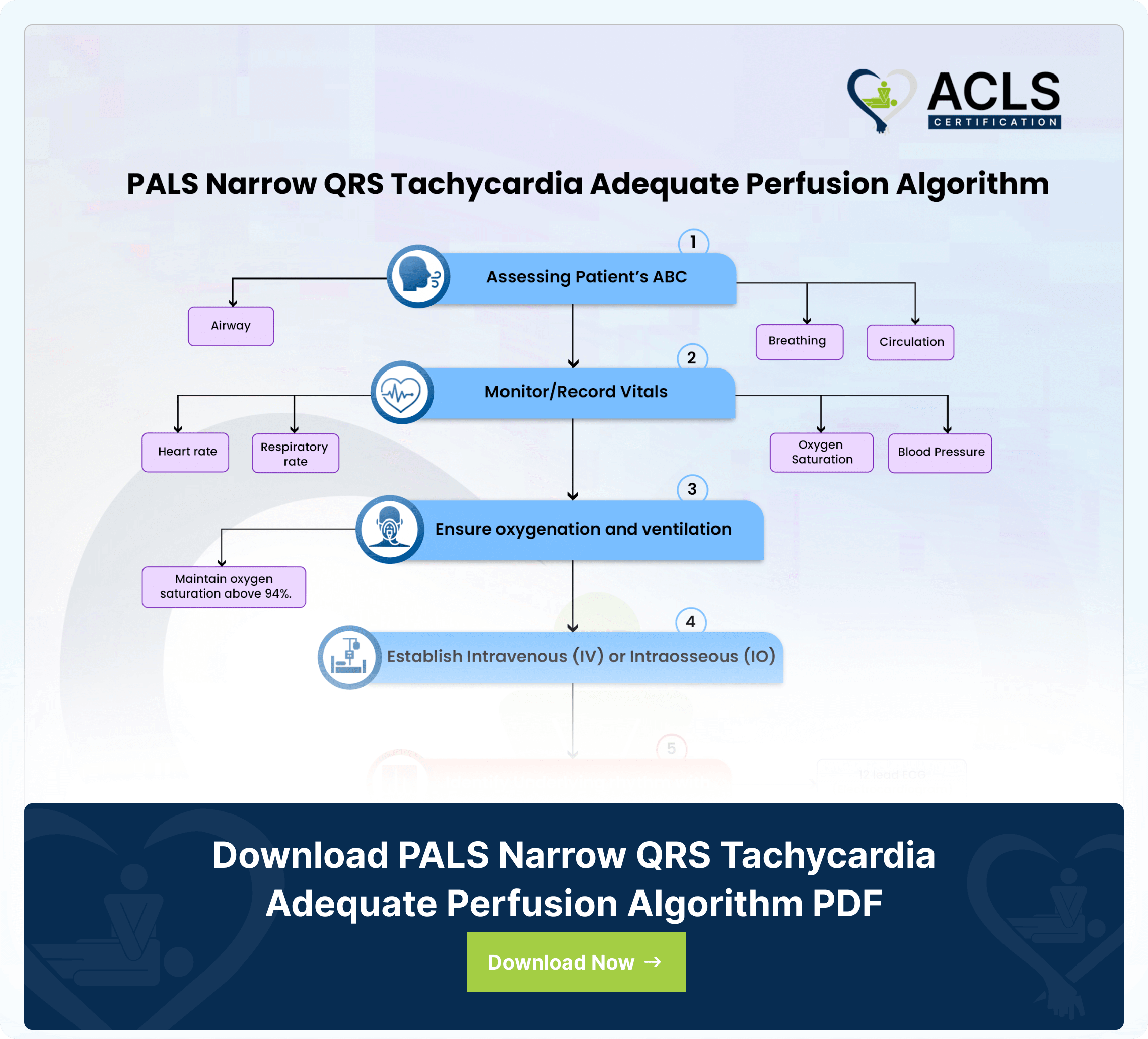
PALS Narrow QRS Tachycardia Adequate Perfusion Algorithm
The PALS Narrow QRS Tachycardia Adequate Perfusion Algorithm gives a structural approach for managing pediatric cardiac emergencies. The algorithm ensures effective treatment to maintain adequate perfusion in pediatric patients.
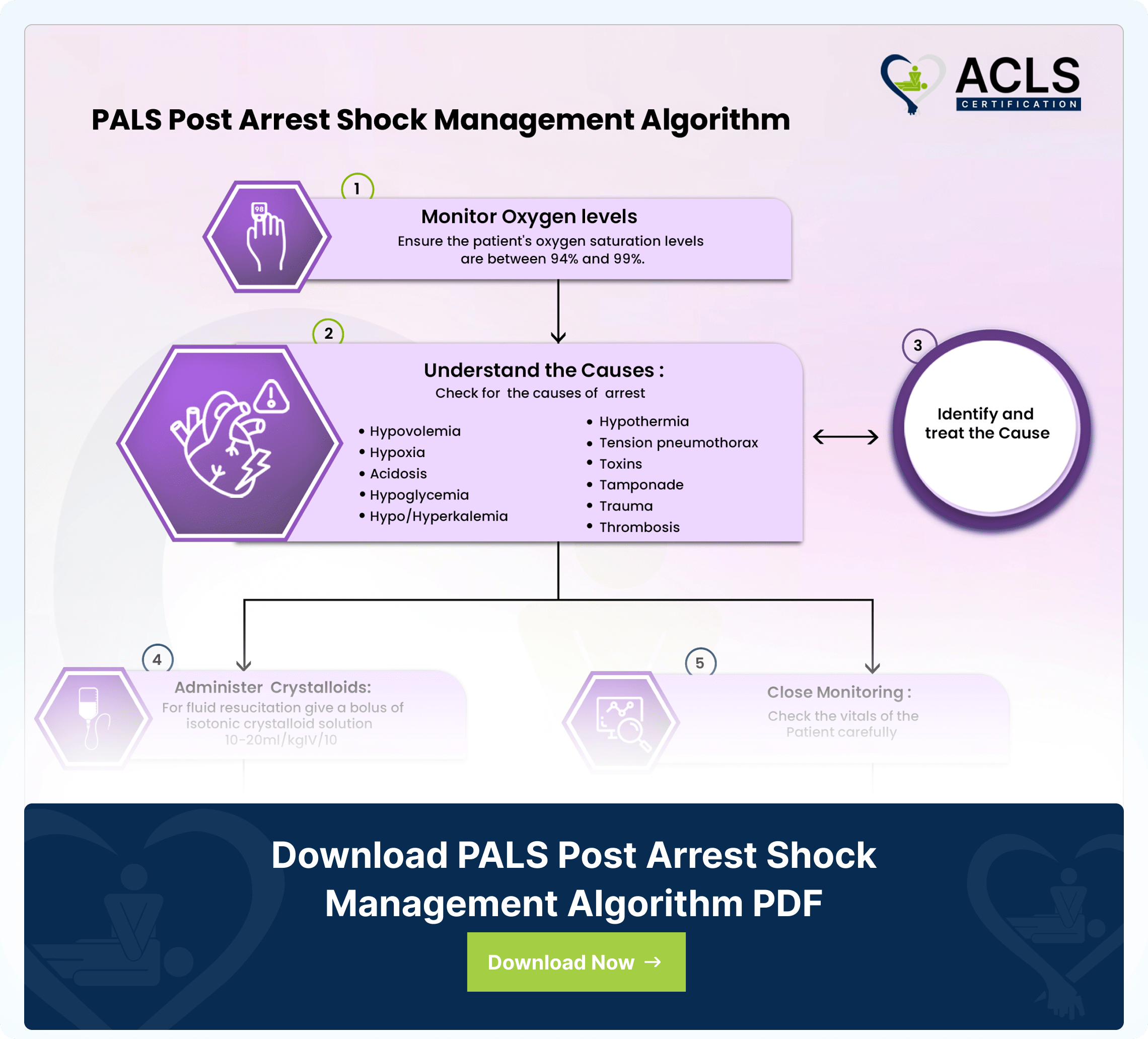
PALS Post Arrest Shock Management Algorithm
The PALS Algorithm Stabilizes pediatric patients’ post-cardiac arrest optimizing recovery through targeted interventions