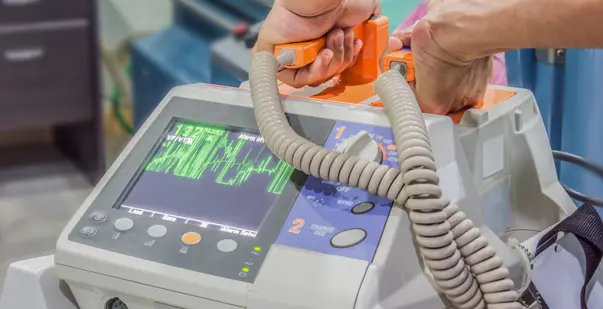
Ventricular fibrillation is an arrhythmia, causing malfunction of the heart’s normal pumping. Known as the most common arrhythmia, the lower chambers of your heart quiver instead of squeezing and expanding. This means they are not pumping blood as they should.
Why is ventricular fibrillation so dangerous?
When blood stops flowing, you have a few seconds before you pass out. This is known as sudden cardiac arrest and results in death in only a few minutes. Sudden cardiac arrest is the leading cause of natural death and accounts for most deaths.
What are coarse ventricular fibrillation and fine ventricular fibrillation?
Here is how the wave gets grouped into two categories, known as coarse and fine.
- Coarse ventricular fibrillation: The peaks are taller and the valleys are deeper. It is known as coarse because the line is not smooth.
- Fine ventricular fibrillation: When the valleys and peaks are short, this is known as fine vfib.
Coarse ventricular fibrillation is preferred as it is strongly associated with good outcomes. This is because coarse fibrillation is closer to normal heart activity than fine ventricular fibrillation.
Why is ventricular fibrillation so dangerous?
When blood stops flowing for this reason, you have a few seconds before you pass out. This is known as sudden cardiac arrest, which results in death in a few minutes without immediate care. Sudden cardiac arrest is the leading cause of death in the United States and accounts for half of all deaths from heart disease.
Read More: Reversible causes of cardiac arrest 4 “Ts” and 4 “Hs”
What is refractory v-fib?
This happens when ventricular fibrillation continues even after receiving three shocks from a defibrillator. This is difficult to treat; however, research is ongoing to overcome it.
What causes v-fib?
Ventricular fibrillation is caused by the following:
- Heart attack
- Heart disease
- Heart surgery
- Electrical shock
- Other arrhythmias
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Certain medications
What are the symptoms of v fib?
Here are the symptoms:
- Nausea
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Racing or an erratic pulse
- Chest pain
- Heart palpitations
- Shortness of breath
With these conditions, you may collapse with little or no warning. You can also gasp for breath.
Diagnosis and tests
What tests are done for ventricular fibrillation?
An electrocardiogram confirms ventricular fibrillation, especially after resuscitating a person from cardiac arrest. This helps determine the heart’s ability to function going forward.
How to manage and treat V-Fib?
The condition is a life-threatening medical emergency where every minute counts. These steps of treatment for v fib acls can help save the life of someone undergoing sudden cardiac arrest because of ventricular fibrillation.
- Stay calm and call an emergency provider.
- Start CPR: Chest compressions are a vital and life-saving step, especially until you can use an AED or until first responders arrive.
- Use an automated external defibrillator (AED): Ventricular fibrillation is a ‘shockable’ arrhythmia. An AED is used in the first three minutes after a person collapses. The survival rate of fibrillation is high. Individuals who survive ventricular fibrillation ACLS are more likely to face it again. Hence, healthcare providers will run tests to find out the reasons and follow-up options.
- Antiarrhythmic medications: These medications normalize your heart rhythm,
- Implanted device: Most individuals survive ventricular fibrillation when an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator is placed. This device is beneficial in detecting arrhythmias and delivering electric shock to restore your heart to a normal rhythm. These are permanent.
Read More: Elements of Effective Team Dynamics in ACLS
What is the difference between atrial fibrillation and ventricular fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation is similar to ventricular fibrillation. This takes place in the upper chambers of the heart. During this, the heart tends to beat very fast. This causes the blood to collect in the atria, causing it to enlarge and stretch.
When blood gets collected in one place, it likely increases the risk of forming a clot. This can go from the heart to the brain. Thus, atrial fibrillation is not that dangerous but can cause a stroke.
Is v-fib the same as a heart attack?
Ventricular fibrillation is a malfunction of the normal beating rhythm of the lower chambers of the heart. It is different from a heart attack as it is caused by blockages in the blood vessels that supply the heart with enough oxygen. It helps to keep the heart pumping.
What is the difference between ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation?
They are closely related, and the difference between the two is in ventricular tachycardia. Here, the lower chambers of the heart beat faster than they should. In ventricular fibrillation, the beating process is not happening in the right order.
Ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation are life-threatening as they can collapse and lead to cardiac arrest. During emergencies, both are treated with defibrillation. Both are treated with surgically implanted cardioverter defibrillators.
Conclusion
Thus, it can be concluded that ventricular fibrillation is a serious form of heart arrhythmia. There are several reasons you may have VF, and the cause may be controllable. If you have symptoms of VF, you must seek urgent help. If you have been diagnosed with VF, you must let your family and friends know.