Table Of Content(s)
- Introduction
- What is excessive ventilation?
- What are the effects of excessive ventilation?
- Understanding the Risks of Gastric Inflation
- What are the practical tips to prevent excessive ventilation?
- What is the role of training in reducing the risks of over-ventilation?
- Why does precision matter in CPR?
- Mastering CPR Techniques: Avoiding the Pitfalls of Over-Ventilation
- Conclusion
Do you know what is the most critical yet frequently overlooked factor when administering cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR)? This factor known as “excessive ventilation” significantly impacts the quality of CPR administered. When performing CPR, the focus is mainly on chest compressions and resuscitation. But the role of ventilation is just as crucial.
Over-ventilation like delivering too many rescue breaths or forceful ones can have serious consequences and side effects. It leads to serious complications like decreased cardiac output, increased intrathoracic pressure, and even gastric inflation.
Let’s find out more about the effects of excessive ventilation to ensure that your resuscitation efforts are as effective and safe as possible.
Master ACLS Now
Get ACLS certified with confidence
What is Excessive Ventilation?
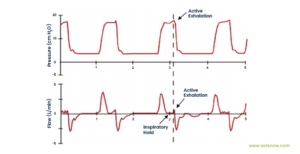
Excessive ventilation refers to the act of delivering rescue breaths too quickly or forcefully. This brings down the overall quality of the CPR administered, as the dynamics exceed the recommended guidelines.
Excessive ventilation often leads to intrathoracic pressure, which reduces venous return to the heart and lowers cardiac output.
What are the effects of excessive ventilation?
Excessive ventilation can have a negative impact on patient outcomes. Even though it may seem that providing more air is beneficial, over-ventilation actually hampers the resuscitation process. To perform CPR effectively and safely, it is important to understand the potential risks associated with excessive ventilation.
-
Decreased Cardiac Output
By increasing intrathoracic pressure, excessive ventilation reduces the return of blood to the heart. This leads to reduced cardiac output and compromised cardiac circulation.
-
Gastric Inflation
Delivering breaths too forcefully can cause air to enter the stomach instead of the lungs. This leads to a condition called gastric inflation. Gastric inflation leads to vomiting, aspiration and further complications.
-
Risk of Barotrauma
High pressure breaths cause damage to the lungs. This leads to Barotrauma, which is injury of lung tissues due to excessive pressure.
-
Reduced Perfusion Pressure
Essential for the heart’s own blood supply, excessive ventilation can lower coronary perfusion pressure. This reduces the chances of successful defibrillation.
-
Changed Blood-Gas Levels
Over-ventilation can lead to abnormal levels of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the blood. This negatively affects the brain and the heart.
Master ACLS Now
Get ACLS certified with confidence
Understanding the Risks of Gastric Inflation
Gastric inflation occurs when air is pushed into the stomach instead of the lungs during CPR. This complicates resuscitation efforts. It also negatively impacts the health of the patient. Understanding the risks associated with gastric inflation is crucial for effective CPR. Here are the key risks:
- Air in the stomach can lead to vomiting, which raises the risk of aspiration into the lungs. This creates further complications.
- Gastric inflation increases abdominal pressure. This interferes with chest compressions and reduces their effectiveness.
- The added pressure in the abdomen from gastric inflation can impede the return of blood to the heart, further decreasing cardiac output.
- Excessive air in the stomach can make it harder to deliver effective breaths to the lungs, diminishing the overall quality of ventilation.
- The process of gastric inflation can cause discomfort and potential injury to the patient. This makes the resuscitation process more challenging.
What are the practical tips to prevent excessive ventilation?
Preventing excessive ventilation during CPR is crucial for effective resuscitation and improving patient outcomes. It’s easy to get caught up in the urgency of the moment, but maintaining control and following guidelines is key. Here are some practical tips to help you avoid over-ventilation:
- Stick to the Recommended Rate: Provide one breath every 6 seconds for adults. Count out loud to stay on track.
- Use Proper Volume: Deliver just enough air to see the chest rise. Over-inflating the lungs can cause more harm than good.
- Avoid High Pressure: Breathe steadily and gently. Forceful breaths increase the risk of barotrauma and gastric inflation.
- Utilize Feedback Devices: Some CPR training kits include devices that guide ventilation rate and pressure. These tools help you stay within safe limits.
- Practice Regularly: Regular CPR practice reinforces the right techniques and helps build muscle memory, reducing the risk of excessive ventilation in real situations.
- Work as a Team: In a team setting, communicate clearly about who is responsible for ventilation and remind each other of the proper rate and technique.
Read More: Oxygen: Uses, Interactions, and Mechanisms of Action
What is the role of training in reducing the risks of over-ventilation?
Training plays a crucial role in reducing the risks of over-ventilation during CPR. Proper training ensures that rescuers are well-versed in the correct techniques. Read through the below mentioned points to understand the role of training in reducing the risks of over-ventilation.
- Familiarity with Guidelines: Training helps individuals learn and remember the recommended ventilation rates and volumes, ensuring they follow current best practices.
- Skill Development: Hands-on practice builds muscle memory, allowing rescuers to perform ventilation techniques correctly and consistently under pressure.
- Use of Feedback Devices: Training often includes tools that provide real-time feedback on ventilation, helping trainees adjust their technique to avoid over-ventilation.
- Reinforcement of Techniques: Regular refresher courses keep skills sharp and reinforce the importance of proper ventilation, reducing the likelihood of mistakes.
- Team Coordination: Training emphasizes the importance of clear communication and coordination among team members, ensuring everyone follows the same ventilation guidelines.
- Confidence Building: Proper training increases confidence, allowing rescuers to perform CPR effectively without over-ventilating due to stress or uncertainty.
Read More: Is ACLS Medical Training Legit?
Why does precision matter in CPR?
Maintaining precision when administering CPR is critical for maximizing the chances of successful resuscitation. Every detail, from chest compression depth to ventilation rate plays a vital role. It ensures that the patient receives optimal care. Without precision, the effectiveness of CPR is compromised, leading to poorer outcomes. Here’s why precision matters so much in CPR:
- Maximizes Blood Flow: Accurate chest compression depth and rate help maintain effective circulation, ensuring that vital organs, especially the heart and brain, receive adequate blood flow.
- Avoids Over-Ventilation Risks: Providing the correct number and volume of breaths prevents complications such as decreased cardiac output and gastric inflation, which can hinder resuscitation efforts.
- Enhances Defibrillation Success: Properly performed CPR improves the chances of successful defibrillation by maintaining a stable internal environment for the heart to respond to shocks.
- Prevents Injuries: Precise technique reduces the risk of causing additional injuries, such as rib fractures or lung damage, which can occur from improper compression or excessive pressure.
- Improves Overall Effectiveness: Adhering to guidelines ensures that each component of CPR—compressions, ventilations, and defibrillation—is performed effectively. This enhances the overall likelihood of survival.
Mastering CPR Techniques: Avoiding the Pitfalls of Over-Ventilation
Mastering CPR techniques involves more than just knowing the steps. It requires careful attention to avoid common mistakes like over-ventilation. Over-ventilation comprises the effectiveness of CPR. It also harms the patient. Here’s how to avoid the pitfalls of over-ventilation:
- Follow Recommended Rates: Deliver one breath every 6 seconds for adults to ensure you provide the right amount of oxygen without over-ventilating.
- Ensure Chest Rise: Give just enough air to cause the chest to rise visibly. Avoid excessive force to prevent complications like gastric inflation.
- Monitor and Adjust: Pay attention to feedback from training devices or colleagues to ensure your ventilation technique is effective and not causing over-ventilation.
- Use a Barrier Device: If available, use a barrier device with a proper seal to help control the amount of air delivered and prevent unnecessary inflation.
- Practice Regularly: Regular training and simulation exercises help reinforce proper techniques and build the muscle memory needed to avoid over-ventilation during real-life situations.
- Communicate in Team Settings: Clearly communicate with team members about the ventilation plan and ensure everyone adheres to the same guidelines to avoid inconsistencies.
Conclusion
Excessive ventilation during CPR can significantly impact the quality of resuscitation. Providing adequate ventilation for oxygenation is required but over-ventilating can introduce several risks. This includes reduced cardiac output, increased intrathoracic pressure, and gastric inflation. These complications nullify the effect of CPR and cause problems while defibrillating the patient.
By understanding and sticking to the guidelines, practitioners can eliminate the risks associated with CPR. Ongoing training, regular practice, and clear communication are vital in mastering the correct ventilation techniques. An ideal ACLS (Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support) training will ensure that CPR is performed with precision. Through careful attention to these practices, we can ensure that resuscitation efforts are as effective as possible.