Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- What is an AED?
- What is Defibrillation?
- Types of AEDs
- Wrapping Up
When it comes to saving lives during a sudden cardiac arrest, having the right defibrillator is key. You need to be ready to act fast, and knowing the different defibrillator types can make all the difference. Whether you’re at home, work, or in a public place, understanding these devices gives you the power to help someone in need.
In this guide, you’ll learn about the various defibrillator types and how each one works. From the simplest models that anyone can use to those meant for trained professionals, you’ll discover the key features that set them. By the end, you’ll know which type suits your needs best, whether for personal safety or professional use.
Master ACLS Now
Get ACLS certified with confidence
What are AEDs?
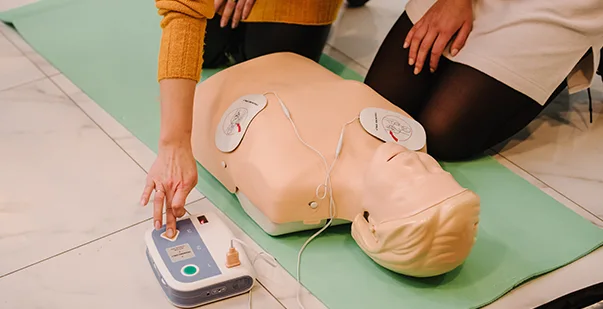
An AED, or Automated External Defibrillator, is a device that can save lives in emergencies. It is used when someone’s heart suddenly stops beating, a condition called cardiac arrest. The AED checks the heart’s rhythm and sends an electric shock to help the heart beat normally again.
You don’t need to be a medical expert to use an AED. The device provides clear instructions so you know exactly what to do. It’s designed to be simple, even if you’ve never used one before.
In simple terms, the defibrillator de finition refers to a device that helps restart a heart that’s stopped. It’s like having a life-saving tool at your fingertips. When you have an AED nearby, you’re prepared to act quickly, and that can make all the difference in an emergency.
What is Defibrillation?
Defibrillation is a life-saving process used when a person’s heart suddenly stops beating properly. During defibrillation, an electric shock is delivered to the heart to restore its normal rhythm. This shock helps stop the irregular heartbeat, allowing the heart to start pumping blood again.
You can learn how to act in an emergency and save someone’s life until professional help comes. Using online courses, you can learn what you need to do if someone’s having a sudden heart attack or needs your help in any sudden medical emergency.
Read more: When to Replace an Old AED?
Types of AEDs
There are numerous defibrillator types, each designed for specific environments and users. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right one for your needs. In this section, you’ll learn about the main types of AEDs, their features, and where they are commonly used. Here are the different types of defibrillators:
Public Access AEDs
Public Access AEDs are special cardiac defibrillators designed for use in public spaces where sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) can happen to anyone at any time. They are placed at airports, shopping malls, schools, or gyms so that they’re readily accessible to the general public.
Public Access AEDs are extremely user-friendly. They’re built to be intuitive, so even someone with no medical training can operate them in an emergency. When someone collapses and an AED is needed, the device provides clear, step-by-step voice prompts to guide the user through the process. Anyone, regardless of experience, can deliver potentially life-saving treatment.
Public Access AEDs come equipped with pads that are easily applied to the chest. Once the pads are in place, the AED automatically analyzes the heart’s rhythm. If a shock is necessary, the device will either deliver it automatically or prompt the user to press a button. This simplicity and reliability are what make these AEDs so effective in public settings, where every second counts.
Public Access AEDs are an important part of emergency preparedness because they’re easily accessible and simple to use. They empower everyday people to act quickly and confidently during cardiac emergencies, dramatically increasing their chances of survival.
Professional Use AEDs
Professional-use AEDs are sophisticated devices tailored for medical professionals and emergency responders who regularly face cardiac emergencies. Their advanced features allow better control and the ability to make quick decisions in emergencies.
One of the primary features of professional-use AEDs is the ability to monitor the heart’s electrical activity in real time. This is made possible through built-in ECG monitors, which display the heart’s rhythm on a screen. The real-time data helps medical professionals understand the situation accurately and determine a better course of action. If a shock is required, these AEDs provide options for both automatic and manual administration, depending on the situation and the responder’s judgment.
Another key aspect of professional use of AEDs is their adaptability in various emergency settings. These devices have to be quickly accessible during cardiac situations. They often come with multiple modes, allowing for adjustments based on the patient’s condition. Professional AEDs can switch between adult and pediatric settings.
In addition to their advanced monitoring capabilities, professional AEDs often include features like manual override. This function gives trained responders the ability to override automatic analysis and deliver a shock when they believe it is necessary, even if the AED hasn’t indicated one. In emergencies, a clear understanding of the patient’s condition comes in handy. That’s where this flexibility of Professional AEDs helps.
Home Use AED
Home-use AEDs are designed specifically for non-medical environments. They offer peace of mind to individuals at high risk of sudden cardiac arrest (SCA). They are compact, easy to operate, and a lifesaver during emergencies.
What sets home use AEDs apart is their user-friendly design. They are typically equipped with clear voice prompts that guide you through each step, from placing the electrode pads on the patient’s chest to delivering a shock if necessary. The device automatically assesses the heart’s rhythm and determines whether a shock is needed. Regardless of medical training, it ensures that anyone can respond confidently in a crisis.
Many home-use AEDs also feature a simple, lightweight design, making them easy to store and transport within the home. They often come with child-specific pads or settings, adjusting the delivery of shock for young patients and making them useful for family members.
Using a home use AED involves minimal steps. Place the pads on the patient as indicated, follow the device’s voice instructions, and let the AED do the rest. They’re a valuable tool for family members with heart conditions or at higher risk of SCA.
Wearable AEDs
Wearable AEDs are a type of defibrillator designed for individuals at high risk of sudden cardiac arrest (SCA). The only difference between them and others is that they’re worn like a vest around the chest. They continuously monitor the heart rhythm of the person wearing it. When the device detects any arrhythmia, it delivers shocks to restore a normal heartbeat.
One of the standout features of wearable AEDs is their constant vigilance. They are always on guard, ready to act without the need for user intervention. This makes it valuable for those who aren’t under direct medical supervision, offering continuous protection through wearable AEDs.
To use a wearable AED, the user simply wears the device as instructed, ensuring the electrode pads are in proper contact with the skin. The device does the rest of the work. It monitors the heart, detects abnormalities, and delivers shock waves if required. The wearable AED will even alert the wearer if a shock is about to be delivered, allowing time to stop it if the situation is not critical.
Wearable AEDs offer peace of mind, especially for those who might wonder what a cardioverter defibrillator device is and how it can help. These devices provide an extra layer of security for individuals awaiting surgery or those who have recently suffered a heart attack.
Manual AEDs
Manual AEDs are sophisticated devices primarily used by trained medical professionals in hospitals, ambulances, and emergency settings. These AEDs provide full control over the defibrillation process, allowing the user to decide when and how to deliver a shock.
Unlike automated AEDs, manual AEDs require the operator to interpret the patient’s heart rhythm, typically displayed on an ECG monitor. Based on their assessment of the heart rhythm and the situation at hand, the decision to administer a shock is entirely in the user’s hands. This capability is critical in complex scenarios where precision and expert judgment are required.
Manual AEDs come with adjustable energy settings, allowing the operator to choose the appropriate shock level based on the patient’s condition. This flexibility is vital in situations where one size does not fit all, particularly in cases involving children or patients with specific medical conditions.
To use a manual AED, the healthcare provider places the electrode pads on the patient’s chest and evaluates the heart rhythm displayed on the device. If a shockable rhythm is detected, the provider selects the energy level and manually presses the button to deliver the shock.
Automated AEDs
Automated AEDs are life-saving devices that anyone can use, even without medical training. They help during sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) by checking the heart’s rhythm and, if necessary, giving a shock to get the heart beating normally again.
When you place the electrode pads on a person’s chest, the AED does most of the work. It quickly analyzes the heart’s rhythm and, if it finds a problem, either delivers a shock automatically or tells you when to press a button. Automatic AEDs give clear voice instructions so you know exactly what to do.
These AEDs are found in many public places like schools, airports, and offices because they are simple to use and can save lives. Automated AEDs give someone the help they need in an emergency. Even when there’s no medical professional around. It’s a straightforward and effective way to take action when every second counts.
Hybrid AEDs
Hybrid AEDs combine the best features of manual and automated AEDs, offering flexibility in emergency situations. They are easily used by both professional responders and bystanders.
When you use a hybrid AED, you have the option to let the device analyze the heart’s rhythm and deliver a shock automatically, much like a fully automatic AED. However, if you’re more experienced or working in a professional setting, you can switch to manual mode.
Hybrid AEDs are especially useful in environments where both trained professionals and the general public might need to use the device. For example, in schools, sports facilities, or large corporate offices, having a hybrid AED ensures that help can be provided quickly and effectively, no matter who is on hand.
Read More: Will an AED Detect a Pulse?
Wrapping Up
Now that you know about the different defibrillator types, you’re better prepared to help in a cardiac emergency. Each defibrillator type has its purpose and can make a big difference in saving lives. By understanding these defibrillator types, you can choose the right one for your needs, whether it’s for home, work, or public places.
Remember, having the right AED nearby could save a life when every second counts. You don’t need to be a medical expert to make a difference. With a little knowledge and the right defibrillator, you can step in and help someone in need. Stay prepared, stay confident, and know that you have the power to make a life-saving impact with the right defibrillator by your side.