Do you ever feel your heart pounding fast, even when you’re resting? As per the Virtual Sign Assessment by the National Library of Medicine(NIH), the typical human heart rate is 60 to 100 beats per minute. However, an abnormally high heart rate may sometimes lead to symptoms like dizziness, shortness of breath, or chest pain and may sometimes reflect an underlying issue.
One of the most effective ways to slow a racing heart is through vagal maneuvers. These maneuvers stimulate the vagus nerve, which controls the heart rate. In some cases, they can restore a normal rhythm without medication. This article explains how to lower heart rate immediately using vagal maneuvers, different techniques, when to apply them, and when to consult a doctor.
Master ACLS Now
Get ACLS certified with confidence
What Is Vagal Maneuver?
According to a study by the National Library of Medicine, 40% of patients who get these treatments can return to a normal sinus rhythm and can lower their heart rate immediately. Vagal maneuvers are easy techniques for treating specific patient arrhythmias. The vagus nerve is a key part of your parasympathetic nervous system, which regulates many bodily functions, including heart rate.
Vagal maneuvers activate the vagus nerve, which runs from your brainstem to your abdomen. These techniques are a first-line intervention for SVT. and can stabilize the heart rate without medication.
How Vagal Maneuvers Affect the Heart?
Heart disease remains a leading health problem in the United States. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 805,000 Americans experience a heart attack every year. 605,000 of them are first attacks, and 200,000 of them are recurrent attacks.
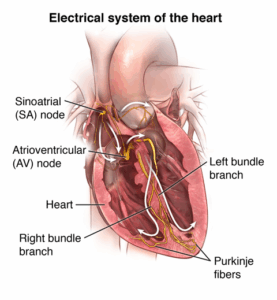
A normal heartbeat begins with an electrical impulse generated at the sinoatrial (SA) node. The impulse then follows this pathway:
Sinoatrial (SA) node → Atrial tissue → Atrial contraction → Atrioventricular (AV) node → Bundle of His → Right and left bundle branches → Purkinje fibers → Ventricular myocardium → Ventricular contraction
Source link: Hopkinsmedicine
With the help of vagal nerve stimulation, you can slow down the pulse and stabilize the victim’s condition. Additionally, these techniques are a successful non-pharmacological emergency treatment method that can be administered to the patient rapidly and without the need for any medicine.
How Vagal Maneuvers Help in SVT?
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is a common heart condition that causes a fast heart rate. It refers to any tachycardia that starts above the ventricles, involving the atria or atrioventricular(AV) node.
The vagus nerve, sometimes referred to as the tenth cranial nerve (CN X), is a vital component of the body’s parasympathetic nervous system. It stands for the neurological system’s “rest and digest” component, which promotes relaxation. From the brainstem to the abdomen, the vagus nerve supports several bodily processes, such as immunological response, mood management, and digestion.
Vagal maneuvers reduce the electrical activity in the AV node, a heart structure, by stimulating the vagus nerve. Moreover, these maneuvers can regulate the autonomic nervous system. When performed correctly, they can lead to:
- Increased Intrathoracic Pressure: Efforts such as pushing or holding one’s breath create increased pressure in the chest region.
- Stimulation of Baroreceptors: It activates baroreceptors (pressure receptors) within vessels. Baroreceptors continuously detect changes in blood pressure.
- Activation of the Vagus Nerve: Baroreceptor activation tells the vagus nerve to slow electrical transmission through the atrioventricular (AV) node.
- Reduction of Heart Rate: Blocking the electrical impulse slows the heart rate and stabilizes rhythm.
Vagal Maneuver Techniques To Lower Heart Rate Immediately
According to the National Library of Medicine, SVT affects approximately 3 in every 1,000 people. Vagal maneuvers are simple and non-invasive techniques that can be effective in managing SVT. In medicine, vagal maneuvers are performed in several forms. Some of the most common ones are depicted below:
-
Coughing
A forceful and repeated cough can help slow the heart rate. It increases pressure in the chest and stimulates the vagus nerve. To perform this, take a deep breath and cough hard and deep. Perform this several times in a row. This method is sometimes used in emergencies to manage arrhythmias.
An arrhythmia is an irregular heartbeat. In simple terms, your heart may beat too quickly, too slowly, or with an irregular rhythm. Coughing can be most effective when done immediately after symptoms begin.
-
Cold Stimulus to the Face
This method involves applying a cold stimulus to the face to slow the heart rate. The patient can submerge their face in ice-cold water, place an ice pack, or use a cold washcloth for about 10 seconds. This triggers the Diver’s Reflex, a natural response that slows the heart rate by activating the vagus nerve.
The following steps can help you understand how to bring down your heart rate using the ice water facial immersion technique:
- Get a basin of ice-cold water ready.
- In step two, ask the patient to hold their breath.
- Immerse the patient’s face in the water for a few seconds (not exceeding 10 seconds).
- After completing this technique, check their heart rate.
-
Carotid Massage
Only a qualified medical practitioner should perform the carotid sinus massage. By activating the carotid sinus nerve endings, this technique lowers the heart rate and helps treat SVT. This happens because the carotid sinus contains baroreceptors that detect changes in blood pressure. During the massage, these receptors send signals to the autonomic nervous system to adjust the heart rate.
The following steps can help you understand how to bring down your heart rate using carotid massage:
- In the first step, have the patient lie down with their head turned slightly away from the area that will be massaged.
- Press gently on the carotid artery, which is situated in the neck slightly behind the jaw.
- While keeping an eye on the patient’s heart rate, massage the area for five to ten seconds.
- If necessary, the massage can be repeated on the opposite side, but never on both sides at the same time, as this could dangerously reduce blood flow to the brain.
-
Bearing Down
One of the best ways to lower heart rate immediately is by using the Valsalva maneuver, a technique that activates the vagus nerve through bearing down. This is carried out by taking a deep breath and holding it while sitting or lying down in a comfortable position.
The following steps are used to execute Valsalva maneuvers in clinical settings:
- The patient should lie down in a partially reclined position. That means the upper body should be slightly elevated.
- They should exhale forcefully and against resistance for about 15 seconds into a big syringe or a manometer, which measures pressure, to reach 40 mmHg.
- As part of the modified Valsalva maneuver, the healthcare professional will passively raise the patient’s legs to about a 45-degree angle while the patient lies flat.
- The patient can resume the partially reclined position after 15 seconds.
The patient’s blood pressure and heart rate should be regularly checked throughout the procedure.
-
Gagging
Gagging can help stop an SVT episode by stimulating the vagus nerve. A healthcare professional may do this by touching the back of the patient’s throat with a tongue depressor. A tongue depressor is a flat wooden tool typically used to press down the tongue for medical examination.
Gagging activates the gag reflex. This is the body’s natural response to prevent choking. It happens when something touches the back of the throat, causing a sudden tightening or coughing sensation.
In some cases, a cotton swab may be used to stimulate the throat gently. This technique should only be used under a doctor’s supervision to avoid pain or harm.
Read more: SVT with Aberrancy or Ventricular Tachycardia
Are Vagal Maneuvers Safe?
Vagal maneuvers are generally safe for most people. However, caution is needed when trying to lower heart rate quickly using these techniques.
- Talk to Your Doctor: Always take a doctor’s opinion before you try these techniques, particularly if you have diseases such as heart disease or glaucoma.
- Avoid Repeated Use: Several attempts that fail may cause problems such as dizziness or unconsciousness.
- Professional Supervision: Procedures such as carotid sinus massage must only be performed under the supervision of health professionals because of possible hazards such as a reduction in brain blood supply.
Who Is Not A Candidate For Vagal Maneuvers?
While vagal maneuvers are effective in many cases, they are not suitable for everyone. Individuals with certain conditions should avoid these techniques due to potential risks. Some of these risk factors include the following:
-
Low Blood Pressure
If your blood pressure is low, it may be a sign that your body is not receiving an adequate supply of blood. Vagal maneuvers can further lower blood pressure and cause dizziness or fainting.
-
Chest Pain
Having pain or tightness in the chest may be a sign of severe heart complications. Vagal maneuvers can temporarily alter heart rhythm. As a result, it may worsen chest pain or indicate an underlying cardiac issue.
-
Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath could be an indication that your body is not receiving sufficient oxygen. Since vagal maneuvers can slow the heart rate, they might further reduce oxygen circulation. It can make breathing difficulties worse.
-
Insufficient Blood to the Organs
If your organs do not receive sufficient blood, it might lead to problems. Vagal maneuvers can further lower heart rate and blood pressure, . T thus reducing blood flow to vital organs. It may increase the risk of complications.
-
Pregnancy (Third Trimester)
Greater pressure in maneuvers is dangerous for the mother and the fetus. Vagal maneuvers can affect blood circulation during the third trimester. It reduces the oxygen supply to the baby. In fact it can cause complications during pregnancy.
-
Eye Conditions
Steer clear if you have glaucoma or elevated intraocular pressure, as the maneuvers can exacerbate them. Generally, performing vagal maneuvers can increase pressure. It results in high intraocular pressure and can worsen eye conditions.
-
Brain or Blood Vessel Disorders
Disorders such as cerebral arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) or recent stroke/TIA in the past three months are contraindications for these maneuvers. Vagal maneuvers can alter blood pressure and blood flow, which may increase the risk of stroke or further complications. Thus, it should be performed with proper stroke management to minimize risks.
-
Severe Hypertension
In malignant hypertension, vagal maneuvers can be complicated. Sudden drops in heart rate or blood pressure can be risky for people with severe hypertension.
-
Carotid Artery Issues
Carotid sinus massage should not be done on patients with carotid artery stenosis or a carotid bruit. These conditions increase the risk of stroke. Pressing on the carotid artery can reduce blood flow to the brain. This may further raise the chance of a stroke.
Read more: How to manage a Respiratory Arrest?
Learn Vagal Maneuvers to Lower Heart Rate Immediately!
A racing heart can be alarming, but in many cases, simple vagal maneuvers can help slow it down naturally. If you’re wondering how do you slow heart rate, vagal maneuvers are a common approach. They are responsible for stimulating the vagus nerve, which controls the heart rate. Some of the popular vagal maneuver techniques are coughing, exposing the skin to a cold stimulus, carotid massage, valsalva maneuver (Bearing down), and gagging. Those suffering from a health condition such as low blood pressure, carotid artery stenosis disease, or underlying heart conditions must see their physician first.
Cardiac emergencies can occur unexpectedly. You can master useful techniques for handling emergencies by enrolling in ACLS certification courses. Sign up now and improve your life-saving skills!
References:
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/22227-vagal-maneuvers
- https://www.healthline.com/health/vagal-maneuvers
- https://www.nuemblog.com/blog/vagal-maneuvers-simplified
- https://cpraedcourse.com/blog/vagal-maneuvers/#
- https://cprcare.com/blog/vagal-maneuvers/
- https://www.uptodate.com/contents/vagal-maneuvers
- https://acls.com/articles/vagal-maneuvers/