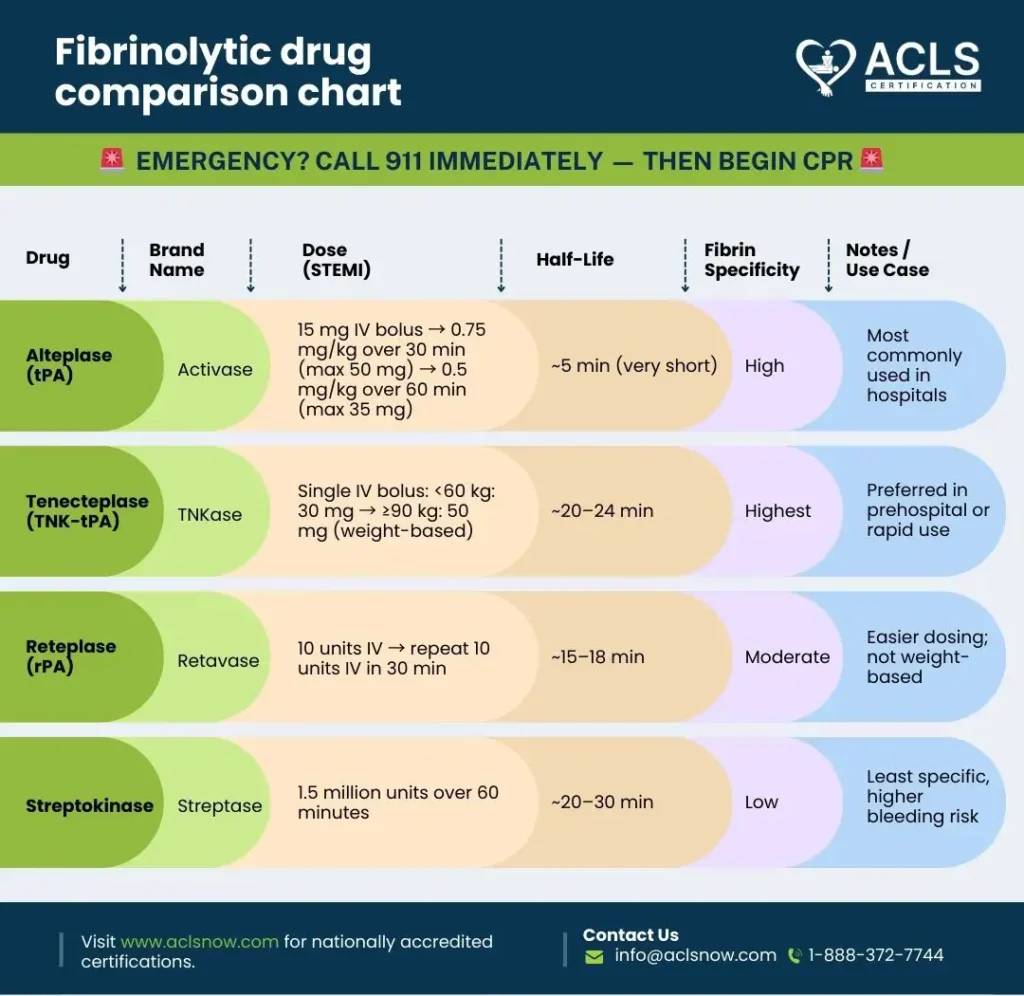
Table Of Content(s)
- Fibrinolytic Drug: Uses, Benefits & Side Effects in ACLS
- What are the uses of fibrinolytic drugs?
- Fibrinolytic Therapy Contraindications: Important Considerations
- What are the potential side effects of Fibrinolytic Drugs?
- Conclusion
Fibrinolytic therapy in ACLS or Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support plays a very critical role in managing acute myocardial infarction. Fibrinolytic drugs are mostly used to deserve blood clots. By preventing blood clots, it improves blood flow and prevents damage to tissues and organs. Fibrinolytics, also known as thrombolytics, rapidly dissolves clots and restores normal blood circulation immediately. Timely administration of ACLS fibrinolytic therapy can be lifesaving, but it comes with potential risks and side effects. Understanding the benefits, adverse effects and clinical considerations help improve patient health and reduce complications.
Master ACLS Now
Get ACLS certified with confidence
In this blog, we will explore how these drugs are used in emergencies and the benefits they offer in improving patient care.
Fibrinolytic Therapy Contraindications: Important Considerations
In the management of acute myocardial infarction, fibrinolytic drugs are a critical component in advanced cardiovascular life support. Certain conditions and patient factors make fibrinolytic therapy contraindicated. Understanding these contradictions ensure decisive action to eliminate adverse outcomes:
- Active Bleeding: Patients with ongoing bleeding, such as gastrointestinal or intracranial hemorrhage, are at higher risk of worsening bleeding complications.
- Recent Stroke: A history of stroke within the past three months, especially if it was hemorrhagic, increases the risk of severe bleeding events.
- Recent Major Surgery: Patients who have undergone major surgery within the last two weeks may be at a higher risk for bleeding.
- Severe Hypertension: Uncontrolled high blood pressure, particularly if it is greater than 180/110 mmHg, can increase bleeding risks.
- Pregnancy: The use of fibrinolytics in pregnant women is generally contraindicated due to potential risks to both the mother and the fetus.
- Known Allergies or Hypersensitivity: Allergic reactions or severe hypersensitivity to fibrinolytic agents can cause serious adverse effects.
- Recent Trauma: Significant trauma or recent injury increases the risk of bleeding complications when fibrinolytics are administered.
- Liver Disease: Severe liver disease can affect the metabolism and clearance of fibrinolytics, increasing bleeding risks.
- End-Stage Renal Disease: Patients with advanced kidney failure may have altered drug metabolism. This increases the risk of bleeding.
Read More: Is ACLS Medical Training Legit?
What are the uses of fibrinolytic drugs?
Fibrinolytic drugs are powerful drugs that are used to dissolve blood clots in various cardiovascular emergencies. What is most important is timely administration. Timely administration reduces the risk of side effects, or further complications. These are the clinical application usage of fibrinolytic drugs:
- Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI): Fibrinolytics are used to dissolve clots in the coronary arteries during a heart attack. This restores blood flow to the heart muscle and minimizes damage.
- Pulmonary Embolism (PE): These drugs are administered to dissolve clots in the lungs. This improves blood flow and reduces the chance of severe complications.
- Acute Ischemic Stroke: In certain cases of stroke caused by a clot blocking blood flow to the brain, fibrinolytics can be used to dissolve the clot and restore circulation, provided the treatment is administered within a specific time window.
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): Fibrinolytics can be used to break down clots in deep veins, reducing the risk of complications like pulmonary embolism.
- Severe Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): In cases where clots cause significant obstruction in peripheral arteries. Fibrinolytics help restore blood flow and reduce symptoms.
What are the potential side effects of Fibrinolytic Drugs?
Side effects of fibrinolytic drugs range from mild to severe. Healthcare workers must carefully consider and go through patient history before administering these medications. The potential side effects include:
-
Bleeding:
- Intracranial hemorrhage
- Gastrointestinal bleeding
- Genitourinary bleeding
- Superficial bleeding at puncture sites
-
Allergic Reactions:
- Rash
- Itching
- Anaphylaxis (rare)
-
Reperfusion Arrhythmias:
- Ventricular fibrillation
- Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
-
Hypotension:
- Sudden drop in blood pressure
-
Fever:
- Mild to moderate fever
-
Nausea and Vomiting:
- Common gastrointestinal symptoms
-
Cholesterol Embolization:
- Dislodging of cholesterol plaques leading to embolization
-
Systemic Effects:
- Muscle pain
- Back pain
Read More: Cardioversion and defibrillation Overview
Conclusion
Fibrinolytic therapy in ACLS helps treat several conditions like myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, and pulmonary embolism. These drugs dissolve blood clots, restores blood flow and minimizes tissue damage. However the administration of fibrinolytic drugs comes with potential risks. The decision to use them requires a thorough evaluation of the patient’s condition. This helps weigh the potential benefits against the risks. Proper training and adherence to ACLS guidelines is important to ensure safe and effective use of these life-saving medications.