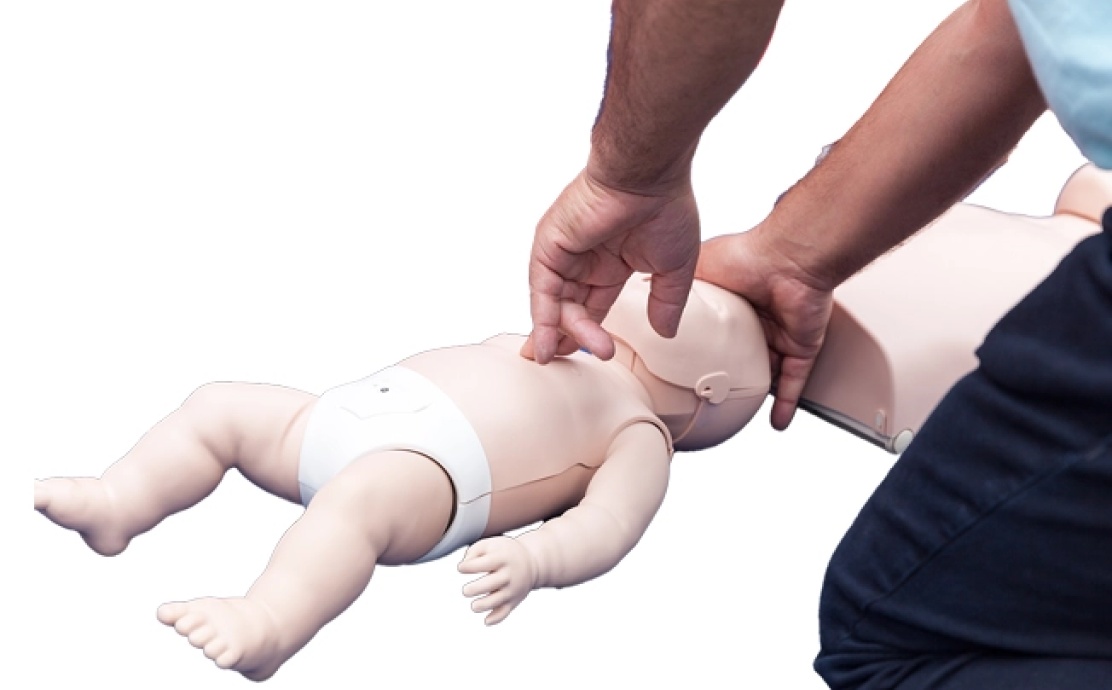
Pediatric basic life support is a set of simple steps to help save a child’s life during emergencies such as choking or cardiac arrest. These steps offer a guided approach to things to do, such as checking if the child is responsive, giving chest compressions, and using reduced breaths.
The steps are easy to follow, and anyone can help in an emergency. It keeps the child’s heart pumping and ensures that oxygen reaches their brain. Stay calm and follow these steps to make a difference and save lives when it matters the most. Study this infant BLS algorithm to respond confidently and save a child’s life.
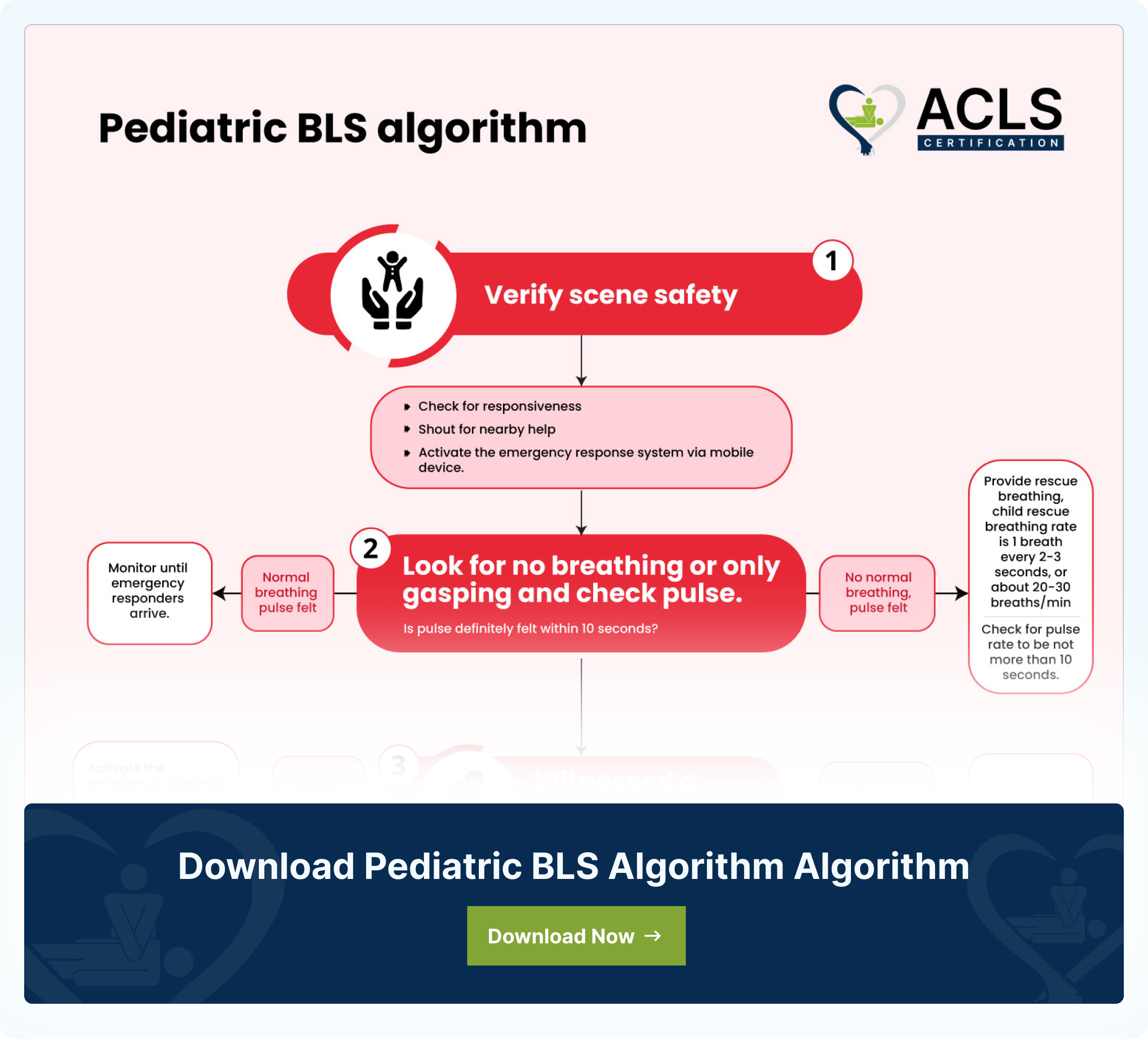
Explanation of flowchart
- Ensure the scene is safeMake sure the area around you is safe for both you and the child. Once it’s safe:
- Check if the child is responsive by gently tapping them or speaking to them.
- If they don’t respond, shout for help from people nearby.
- Use a mobile phone to activate emergency services.
- Check breathing and pulse
- Look to see if the child is breathing normally or just gasping.
- At the same time, check for a pulse (use the neck or wrist) for no more than 10 seconds.
- If there is normal breathing and a pulse, then monitor the child and stay with them until help arrives.
If there is no normal breathing but a pulse, then start rescue breathing. Give 1 breath every 2-3 seconds (20-30 breaths per minute). Recheck the pulse every 2 minutes.
- Was the collapse sudden?If you saw the child collapse suddenly:
- Immediately call for emergency help if you haven’t already.
- Retrieve an AED (automated external defibrillator) if available.
If the collapse wasn’t sudden or the child is unresponsive: - Start CPR immediately.
- Perform CPR
- Perform 30 chest compressions followed by 2 rescue breaths.
- If another rescuer is available, switch to 15 compressions and 2 breaths per cycle.
- Use the AED as soon as you have it.
- After 2 minutesIf you are alone and haven’t already, activate the emergency response system and get the AED.
- Check the heart rhythm with the AED
- If the AED detects a shockable rhythm, deliver 1 shock and immediately resume CPR for 2 minutes. Continue until emergency help arrives or the child responds.
- If the AED detects a non-shockable rhythm, resume CPR immediately for another 2 minutes. Keep going until help arrives or the child shows signs of life.
Key components of the BLS algorithm of a child include:
- Scene Safety: Make sure the environment is safe for you and the child before starting.
- Checking Responsiveness: Check if the child is conscious by tapping or calling out to them.
- Checking Breathing and Pulse: Look for normal breathing and check for a pulse within 10 seconds to determine the next steps.
- Chest Compressions: Deliver high-quality compressions at the correct depth and rate (100-120 per minute) to keep blood circulating.
- Rescue Breathing: The rescue breathing rate for children is a ratio of 30:2 (or 15:2 with two rescuers) to deliver oxygen to the lungs.
- AED Use: Use an automated external defibrillator to analyze the heart rhythm and deliver a shock if needed.
- Reassessment: Regularly check the rhythm, pulse, and breathing every 2 minutes to adjust care as needed.
Download Pediatric BLS Algorithm Algorithm
Resources
- https://cpr.heart.org/-/media/CPR-Files/CPR-Guidelines-Files/Algorithms/AlgorithmBLS_Ped_2_Rescuers_200624.pdf?sc_lang=en
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3741664/
- https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Part-13%3A-pediatric-basic-life-support%3A-2010-Heart-Berg-Schexnayder/a81890e5b67b875746406fec047e3e7cae0334f9
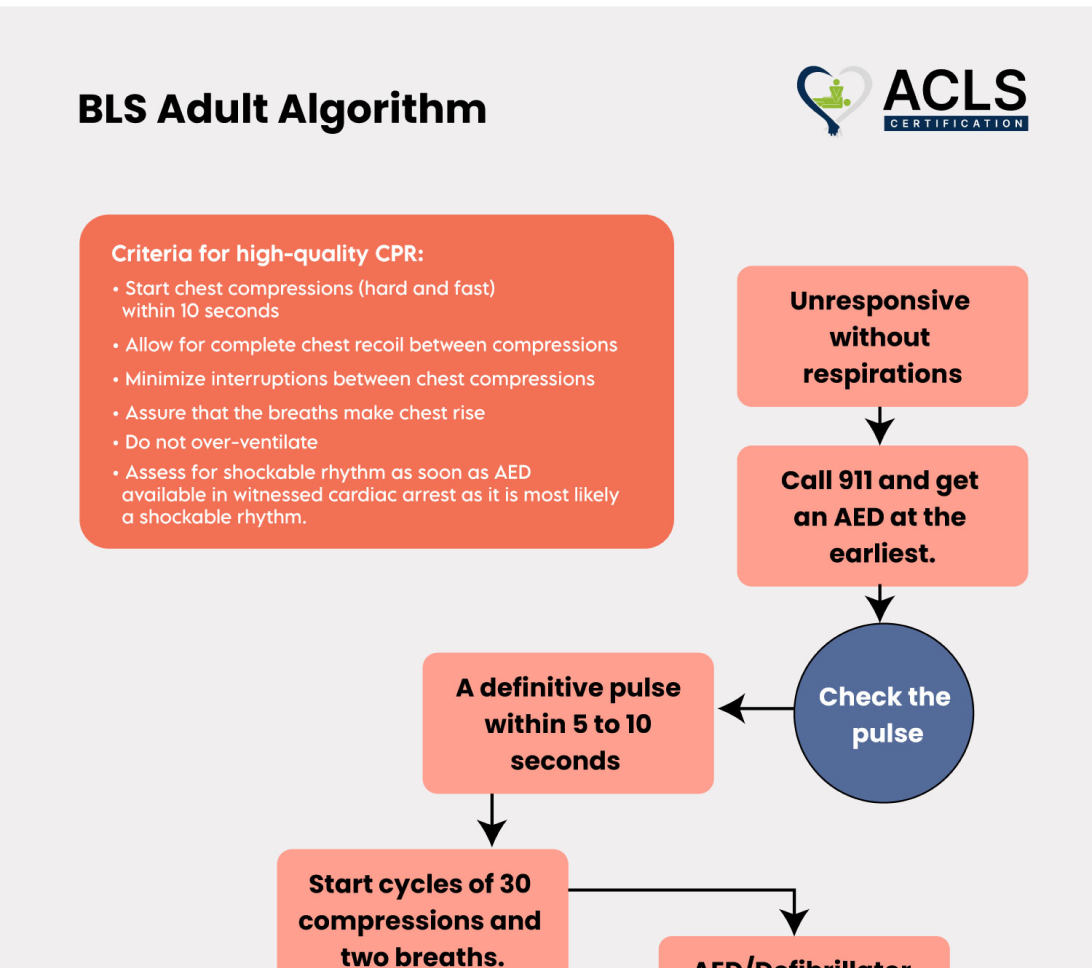
Adult BLS Algorithm
The Adult BLS algorithm begins with checking responsiveness and calling for help. Start chest compressions at a rate of 100-120 per minute, ensure an open airway, and provide rescue breaths in a 30:2 ratio if trained.
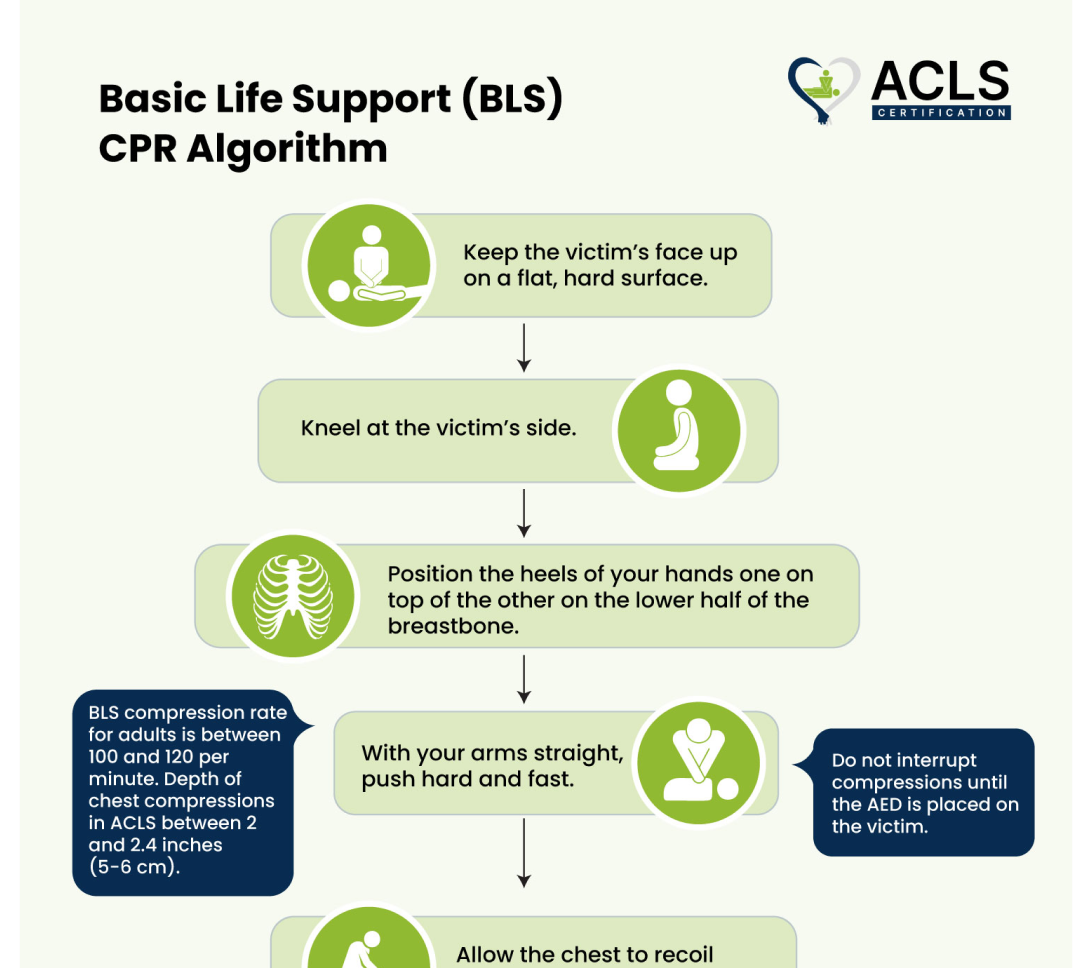
Basic Life Support (BLS) CPR Algorithm
The BLS CPR Algorithm is a simple guide for performing CPR and using an AED during a cardiac arrest. It recognizes the emergency, giving chest compressions, rescue breaths, and using a defibrillator early.
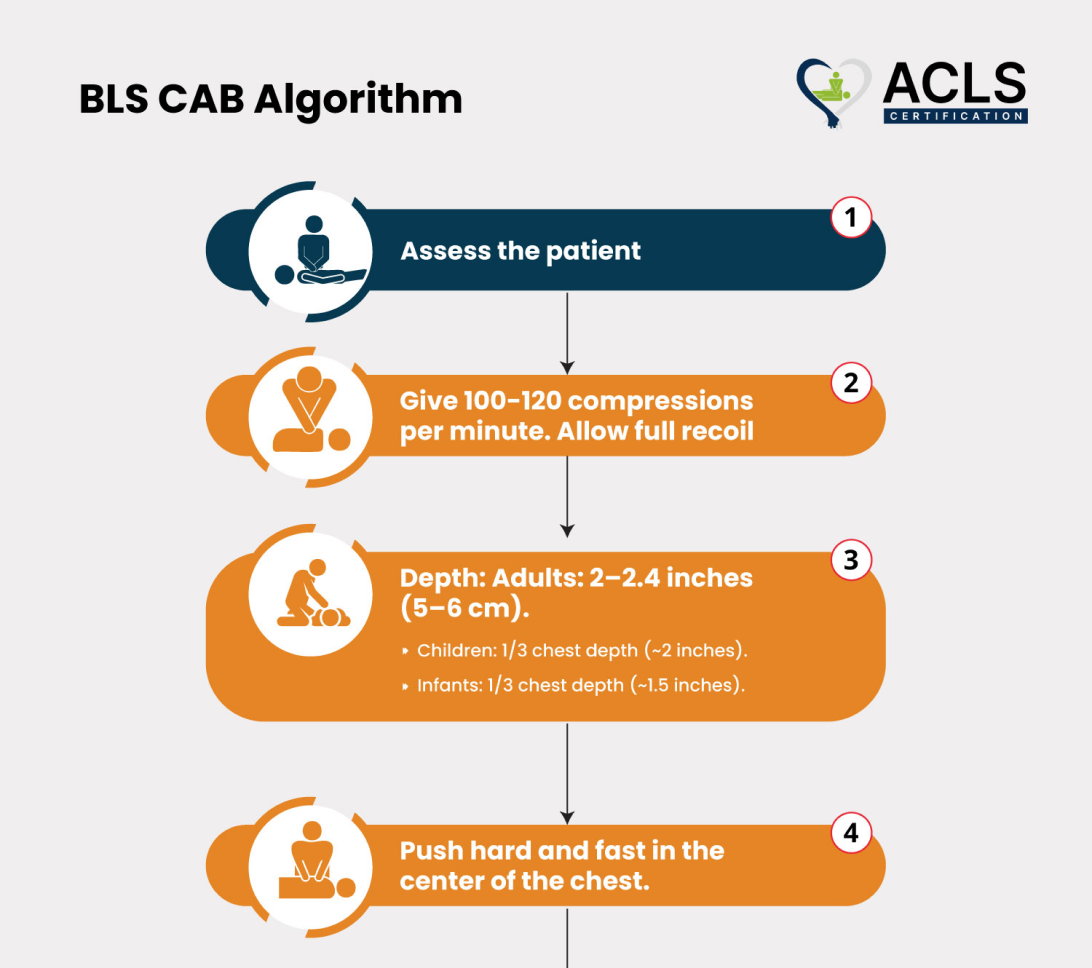
BLS C-A-B Algorithm
The BLS (Basic Life Support) CAB algorithm focuses on Circulation, Airway, and Breathing. Start chest compressions immediately for circulation, then check and open the airway, and provide rescue breaths if needed.