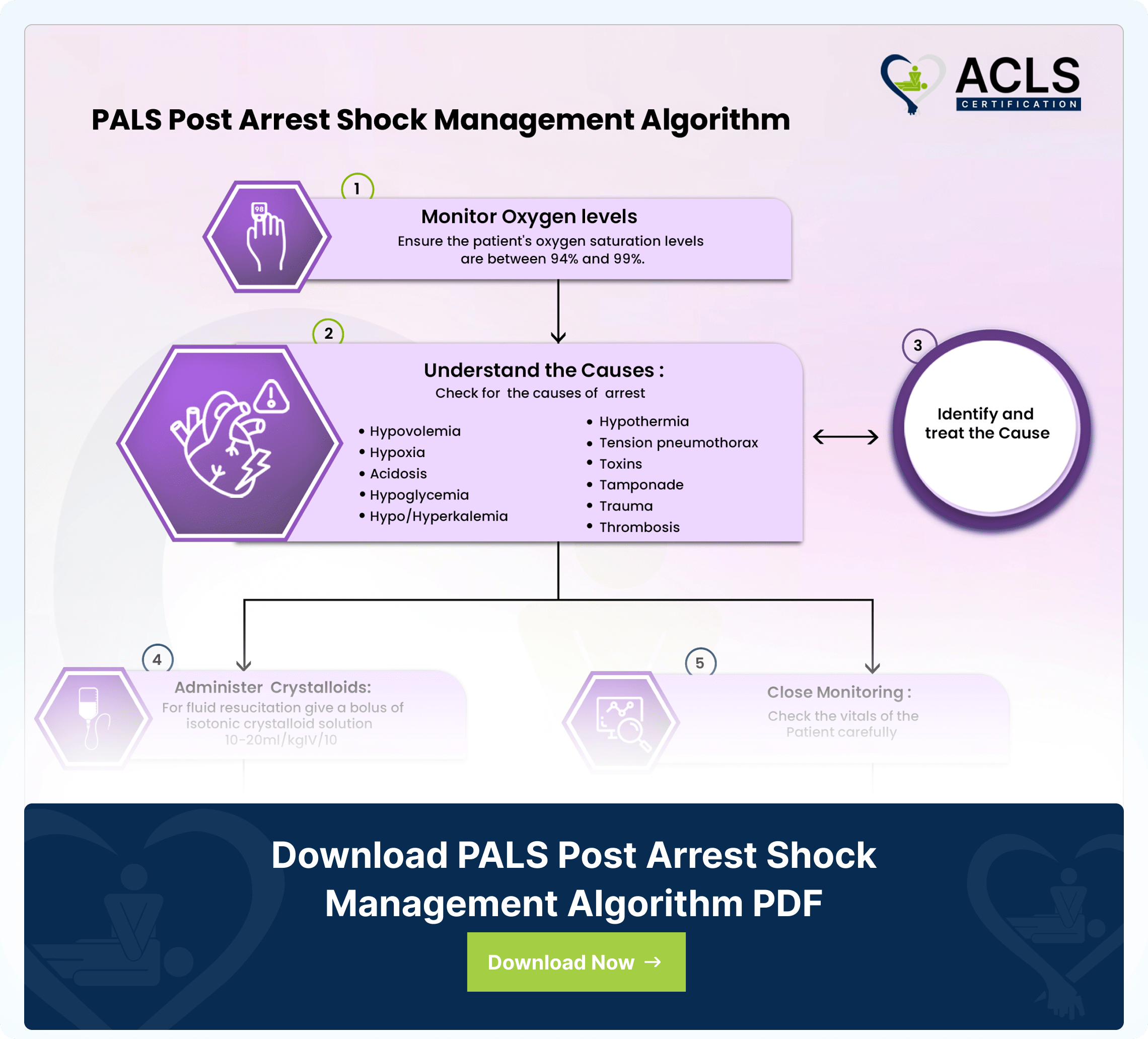
After a child's heart restarts (ROSC) following cardiac arrest, the PALS Post Arrest Shock Management Algorithm takes over. This crucial guide outlines essential steps to stabilize their condition and maximize recovery chances. From assessing and maintaining proper oxygen and breathing to optimizing their heart function with fluids and medication, the PALS algorithm covers it all. Monitoring for re-arrest and understanding the initial cause to prevent repeat occurrences are also key. By following the steps given below, healthcare providers can improve the child's hemodynamic stability and reduce the risk of their heart stopping again.
Understanding the Flow Chart
- Ensure Optimal Oxygen Saturation:
Maintain the patient’s oxygen saturation levels within 94% to 99%, ensuring adequate oxygenation. - Identify Underlying Causes with Hs and Ts:
Utilize the Hs and T’s mnemonic to explore potential causes of the arrest, including factors such as hypovolemia, hypoxia, hypoglycemia, electrolyte imbalances, pneumothorax, toxins, tamponade, trauma, and thrombosis. - Promptly Address Root Causes
Take immediate and appropriate actions to address any identified underlying causes of the cardiac arrest. - Administer Crystalloid Bolus
Initiate fluid resuscitation by administering a bolus of crystalloid solution - Close Monitoring
Vigilantly monitor the patient’s response to treatment and closely observe vital signs for any changes - Management of Hypotensive ShockIn cases of hypotensive shock, commence an infusion of Epinephrine or Norepinephrine within the recommended dosage range.
- Alternative Vasopressors
If hypotensive shock is not present, consider other vasopressors based on clinical judgment, such as Dobutamine, Dopamine, or additional doses of Epinephrine or Norepinephrine. - Continuous Assessment of Critical Parameters
Regularly monitor blood glucose levels, consciousness status, and serum electrolytes, and contemplate transfer to a tertiary care facility for specialized management if necessary. - Therapeutic Hypothermia Consideration
For unresponsive patients experiencing out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, contemplate the implementation of therapeutic hypothermia, adhering to specific temperature protocols for optimal outcomes
Essential elements of the PALS cardiac arrest algorithm include
The main elements of the PALS Post Arrest Shock Management Algorithm center on stabilizing pediatric patients post-return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) after cardiac arrest:
- Check Oxygenation and Ventilation: Ensure oxygen saturation remains within the range of 94% to 99% and maintain appropriate ventilation levels.
- Identification of Underlying Causes: Utilize the Hs and T’s framework to pinpoint potential causes like hypovolemia, hypoxia, and electrolyte imbalances.
- Addressing Identified Causes: Promptly and correctly treat any underlying causes detected.
- Initiate Fluid Resuscitation: Administer isotonic crystalloid boluses for fluid resuscitation to optimize intravascular volume.
- Employ Continuous Monitoring: Diligently monitor vital signs, including blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation, to evaluate the patient’s response.
- Go for Vasopressor Therapy: Initiate vasopressor therapy, such as an Epinephrine infusion, if the patient is experiencing hypotensive shock.
- Consideration of Alternative Vasopressors: Depending on the clinical context, contemplate alternative vasopressors like Dopamine, Norepinephrine, or Dobutamine.
- Comprehensive Monitoring and Transfer: Continuously monitor blood glucose levels, consciousness levels, arterial blood gases, and electrolytes. Consider transferring to a tertiary care center if specialized care is required.
- Consideration of Therapeutic Hypothermia: Assess and contemplate therapeutic hypothermia for unresponsive patients, adhering to specific temperature protocols to minimize neurological damage.
Download PALS Post Arrest Shock Management Algorithm PDF
Resources
- Importance of maintaining adequate oxygenation and ventilation during pediatric resuscitation https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.166573#d3e196
- Identifying the underlying causes of pediatric arrest https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/circulationaha.110.971002
- Administering crystalloid boluses for fluid resuscitation to optimize intravascular volume. https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/circulationaha.110.971002#d1e1557
- Post–Cardiac Arrest Oxygenation, blood pressure, and Ventilation Management https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000901
- Vasopressors for hypotensive shock https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6516856/#:~:text=First%E2%80%90line%20treatment%20for%20the,epinephrine%20and%20vasopressin%20are%20recommended
- Vasoactive Drugs for Use in Post–Cardiac Arrest Patients https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/circulationaha.110.971002#d1e1557
- Therapeutic Hypothermia After Cardiac Arrest https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.076851
- American Heart Association: A scientific statement on Pediatric Advanced Life Support Algorithms. https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000697
- Pediatric cardiac arrest algorithms. AHA https://osteopathicfounders.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/PALS-Algorithms-2020.pdf
- The effects of graded doses of epinephrine on regional myocardial blood flow during cardiopulmonary resuscitation in swine https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/01.CIR.75.2.491
- International Consensus on Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care Science With Treatment Recommendations https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7576321/
- Evaluation of hospital management of pediatric out-of-hospital cardiac arrest https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2666520423000760
- Experts' recommendations for the management of cardiogenic shock in children https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4754230/
All PALS Algorithms
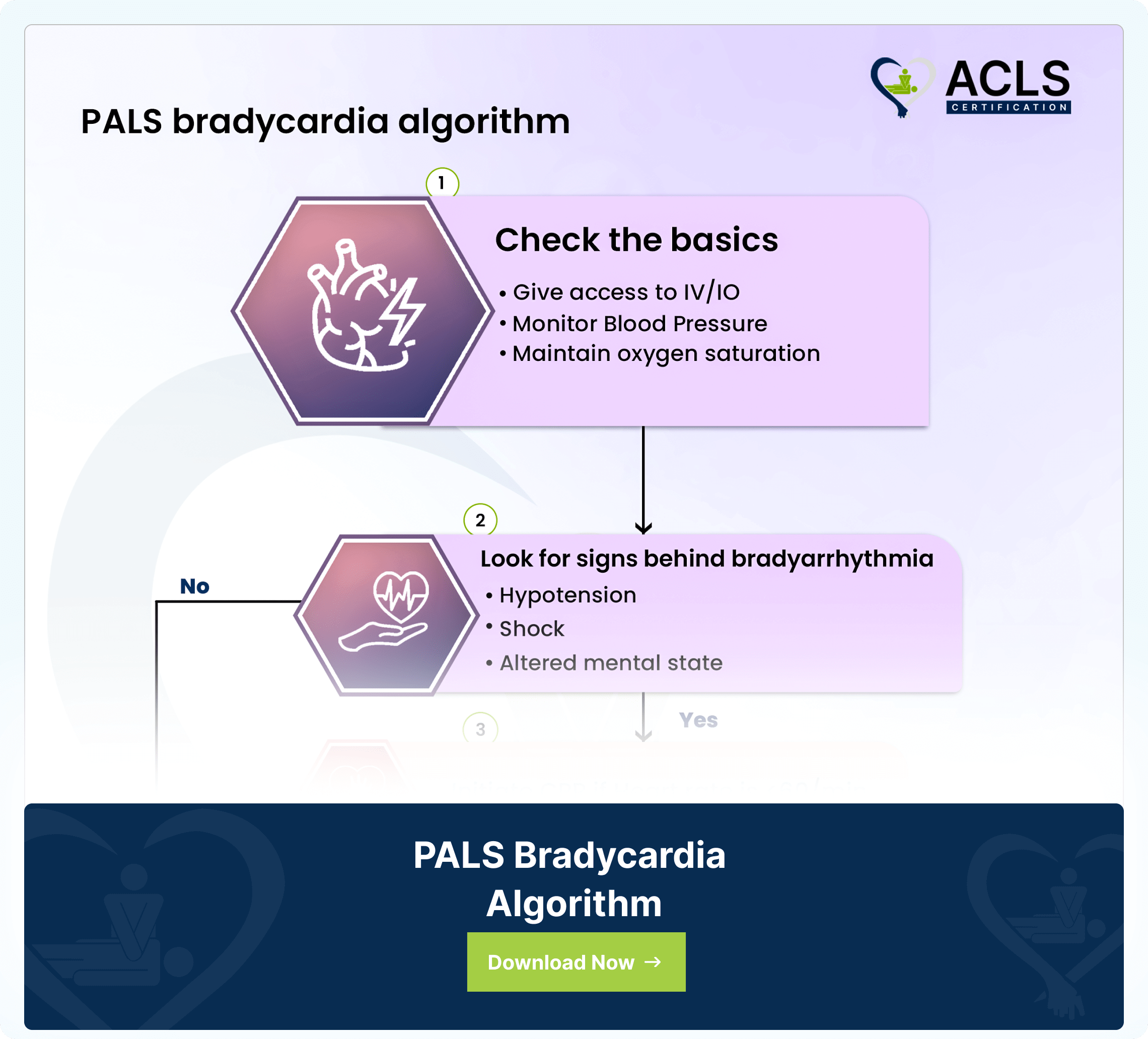
PALS Bradycardia Algorithm
The Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) Bradycardia Algorithm gives a systematic approach to managing slow heart rates
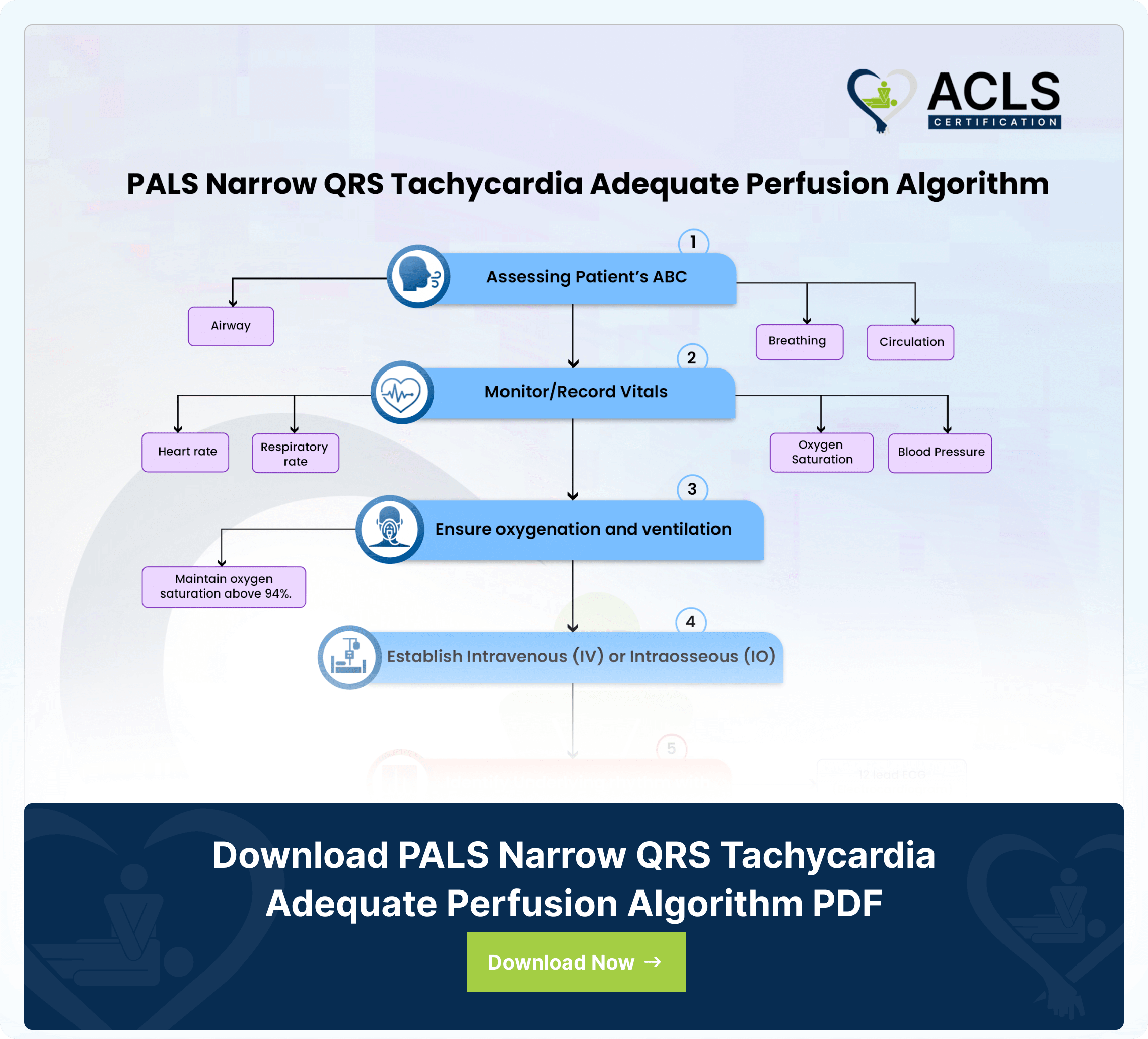
PALS Narrow QRS Tachycardia Adequate Perfusion Algorithm
The PALS Narrow QRS Tachycardia Adequate Perfusion Algorithm gives a structural approach for managing pediatric cardiac emergencies. The algorithm ensures effective treatment to maintain adequate perfusion in pediatric patients.
PALS Wide QRS Tachycardia Adequate Perfusion Algorithm
PALS Wide QRS Tachycardia Algorithm addresses critical pediatric cardiac conditions in an extremely systematic way. The flowchart helps medical professionals manage emergencies to ensure adequate perfusion in patients.