The BLS CAB algorithm in advanced cardiac life support is a step-by-step guide to help healthcare providers manage cardiac emergencies such as cardiac arrest. It builds on basic life support by adding advanced techniques such as defibrillation and airway management.
It focuses on chest compressions and gives shocks for certain heart rhythms. The algorithm helps teams work together by assigning role6s and tasks. It follows a structured approach and ensures that patients get the best possible care during emergencies, improving chances of survival and boosting recovery.
Explanation of flowchart
- Assess the Patient
- Quickly check for responsiveness, breathing, and pulse to determine if the patient requires intervention.
- Start Compressions
- Rate: Deliver 100–120 compressions per minute.
- Depth:
Adults: Compress to a depth of 2–2.4 inches (5–6 cm).
Children: Compress to about 1/3 the chest depth (~2 inches).
Infants: Compress to about 1/3 the chest depth (~1.5 inches). - Technique: Push hard and fast in the center of the chest.
- Allow full recoil after each compression to let the heart refill with blood.
- Open the Airway
-
- For adults and children: Perform a head tilt/chin lift to open the airway.
- For infants: Place the head in the “sniffing position” (a slightly neutral position) to maintain an open airway.
-
- Provide Breaths
-
- For an apneic patient with a pulse: Perform rescue breaths (mouth-to-mouth). Deliver one breath every 6 seconds (10 breaths per minute).
- For a pulseless patient:
Use a 30:2 compression-to-breath ratio (30 compressions followed by 2 breaths).Deliver each breath over 1 second and watch for visible chest rise.Avoid over-ventilation, as excessive air can reduce the effectiveness of resuscitation.
-
- Stay Updated
- Keep your skills sharp and knowledge current by scheduling regular recertification for BLS and ACLS training.
Key Components of the BLS CAB Algorithm
- Compressions (C): Perform chest compressions at 100–120 per minute with adequate depth and full chest recoil to circulate blood effectively.
- Airway (A): Open the airway using the head tilt/chin lift technique or the sniffing position for infants to allow unobstructed airflow.
- Breathing (B): Provide rescue breaths with proper timing and volume, ensuring visible chest rise while avoiding over-ventilation.
- Sequence: Follow the C-A-B order (Compressions, Airway, Breathing) to prioritize circulation before ventilation.
- Assessment: Continuously check for responsiveness, breathing, and pulse to adjust actions as needed.
- Recertification: Regularly update BLS training to ensure proficiency and adherence to the latest guidelines.
Download BLS C-A-B Algorithm
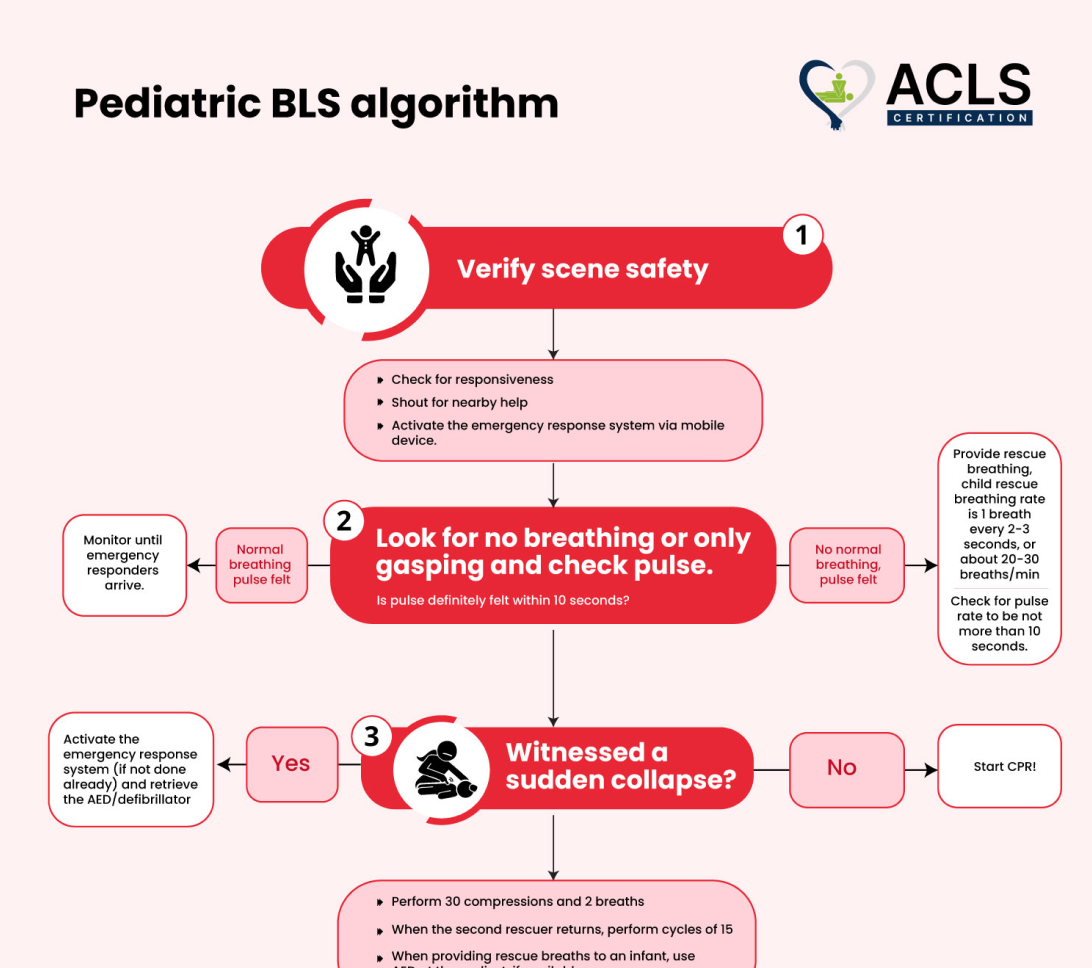
Pediatric BLS Algorithm
The Pediatric BLS algorithm offers high-quality chest compressions at a rate of 100-120 per minute. Start with 30:2 compressions to breaths for a single rescuer or 15:2 for two rescuers.
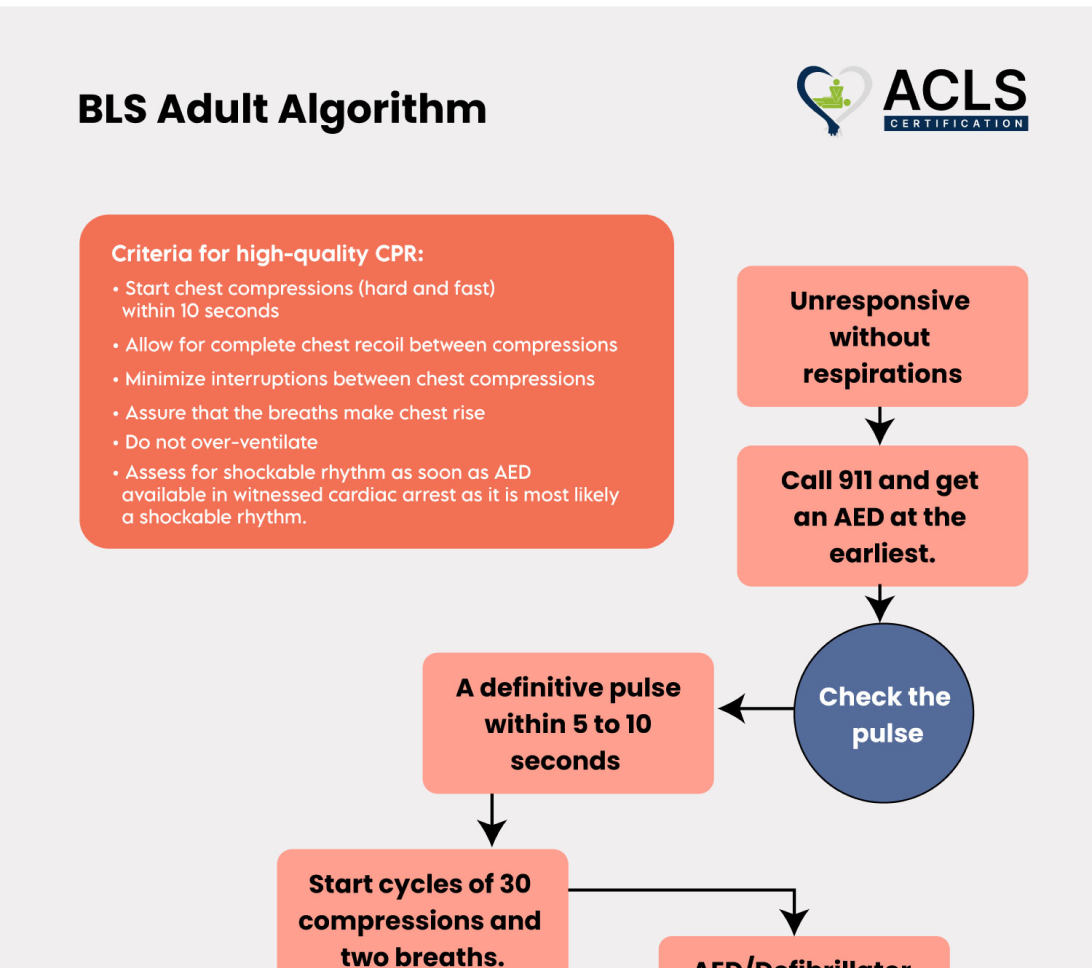
Adult BLS Algorithm
The Adult BLS algorithm begins with checking responsiveness and calling for help. Start chest compressions at a rate of 100-120 per minute, ensure an open airway, and provide rescue breaths in a 30:2 ratio if trained.
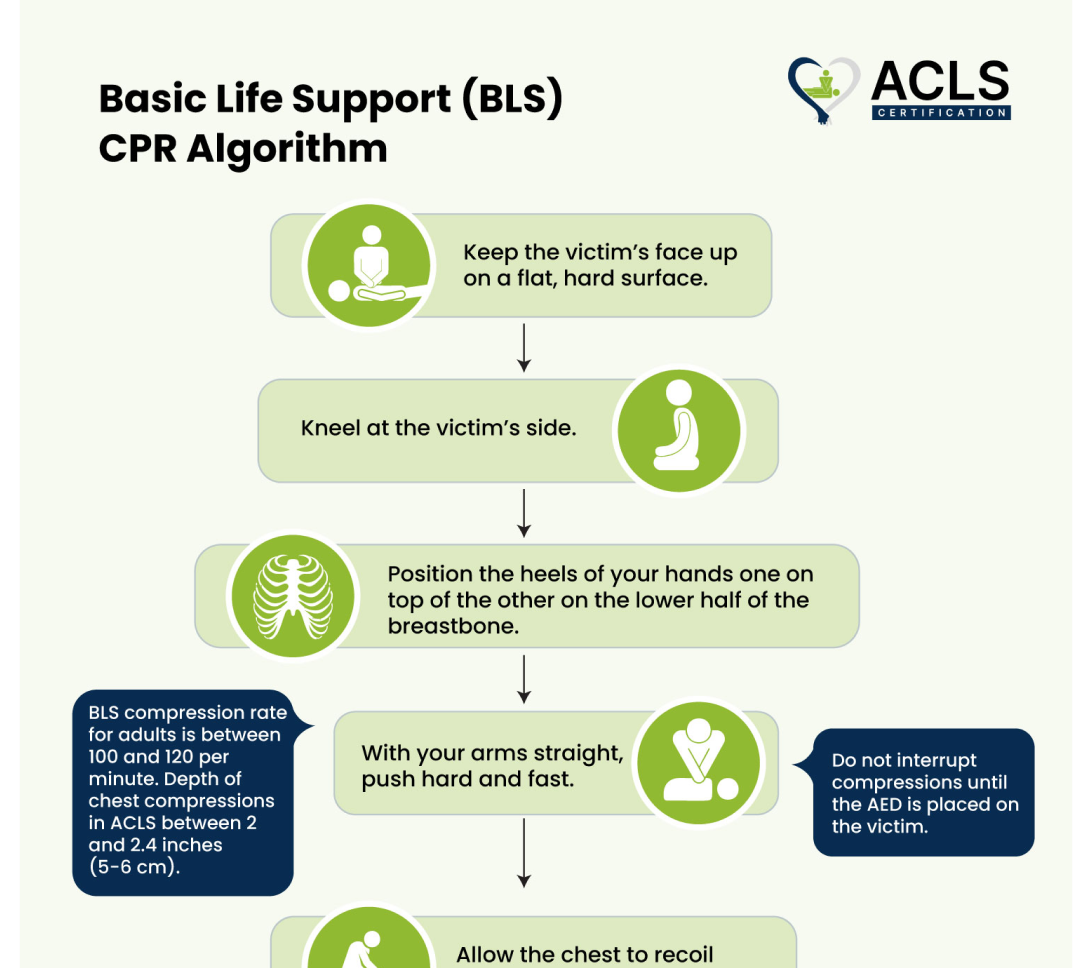
Basic Life Support (BLS) CPR Algorithm
The BLS CPR Algorithm is a simple guide for performing CPR and using an AED during a cardiac arrest. It recognizes the emergency, giving chest compressions, rescue breaths, and using a defibrillator early.