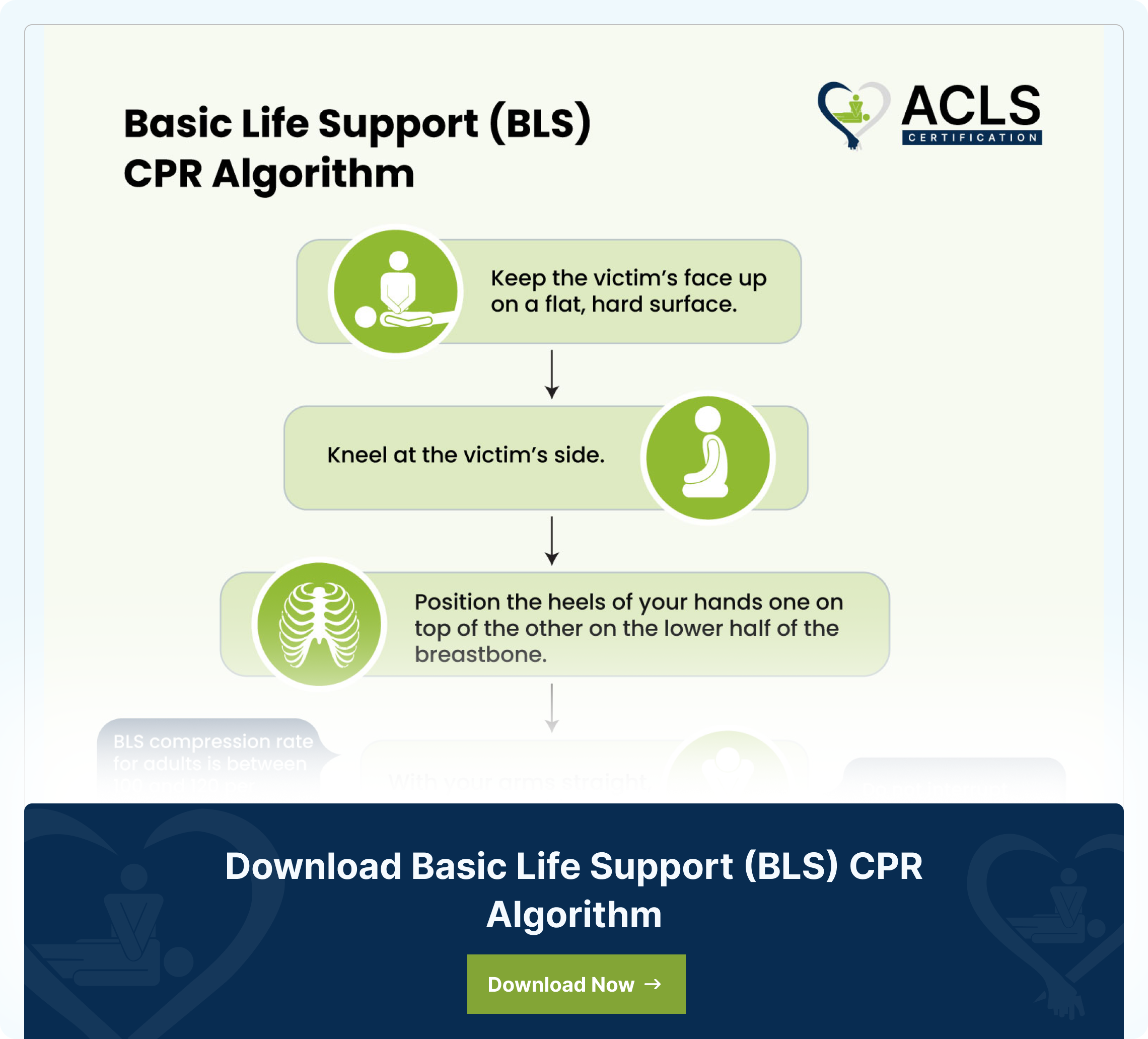
The basic life support (BLS) CPR algorithm is a step-by-step guide to save lives during cardiac emergencies such as a heart attack. It includes chest compressions, giving breaths, and using a defibrillator.
The algorithm provides clear instructions on what to do to help save a life, including checking for responsiveness, starting chest compressions, and using an automated external defibrillator. The CPR algorithm BLS helps rescuers take quick and effective action that keeps blood and oxygen flowing to the brain and vital organs.
Step by step analysis of flowchart
- Position the victim:
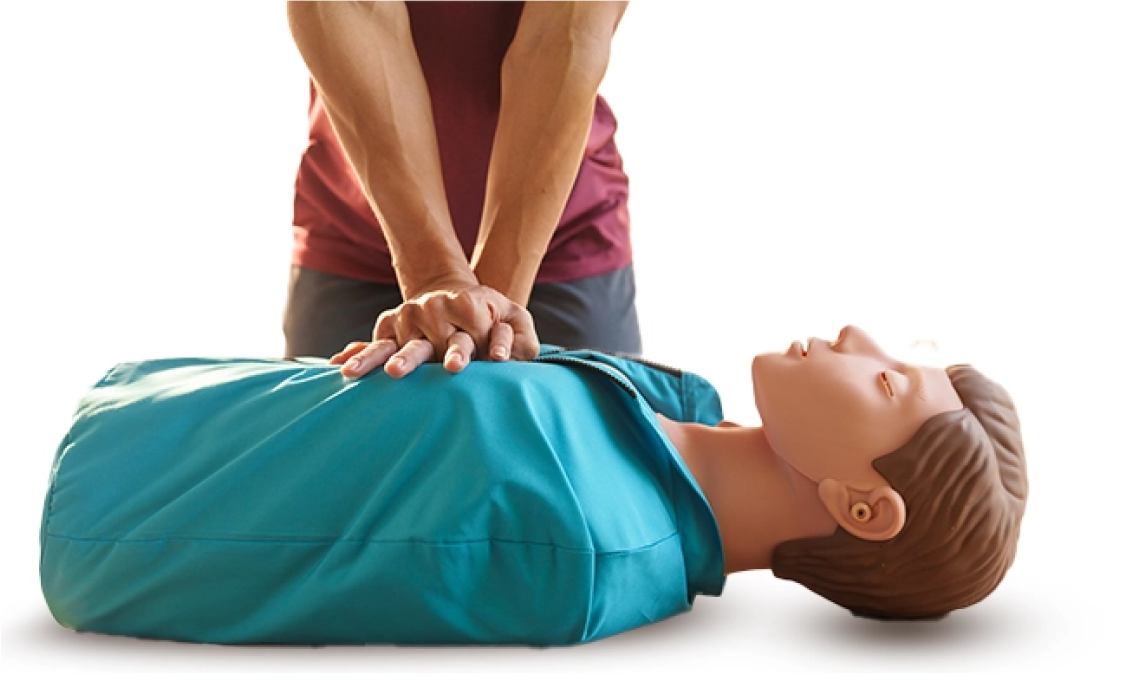
Place the victim on their back on a flat, hard surface. - Kneel beside the victim:
Kneel down at the side of the victim to get in the proper position for CPR. - Position your hands for compressions:
Place the heel of one hand on the lower half of the victim’s breastbone. Put your other hand on top and clasp the fingers together. - Perform chest compressions:
Keep your arms straight and press down hard and fast. Aim for a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute and a depth of 2-2.4 inches. Make sure the chest fully recoils between compressions. Continue performing compressions until the AED is ready to use or professional help arrives. - Open the airway:
Use the head tilt/chin lift method or jaw thrust to open the airway. - Deliver rescue breaths:
Give 2 slow breaths. Make sure each lasts about 1 second, and watch the chest to rise. - Resume compressions:
Return to chest compressions immediately after delivering the breaths. Complete cycles of 30 compressions and 2 breaths continuously.
Key components of this algorithm
- Victim Positioning:
The victim must lie face-up on a flat, hard surface to give effective compressions. - Chest Compressions:
Perform compressions hard and fast in the center of the chest to keep blood circulating to vital organs. - Airway Management:
Use the head tilt/chin lift or jaw thrust to open the airway and prepare for rescue breaths. - Rescue Breaths:
Deliver 2 slow breaths to provide oxygen and ensure that the chest rises with each breath. - Compression-to-Breath Ratio:
Follow the 30 compressions to 2 breaths cycle for effective CPR. - AED Use:
Use an automated external defibrillator as soon as it’s available to restore a normal heart rhythm. - Chest Recoil:
Allow the chest to fully return to its normal position after each compression for proper blood flow.
Download Basic Life Support (BLS) CPR Algorithm
All BLS Algorithms
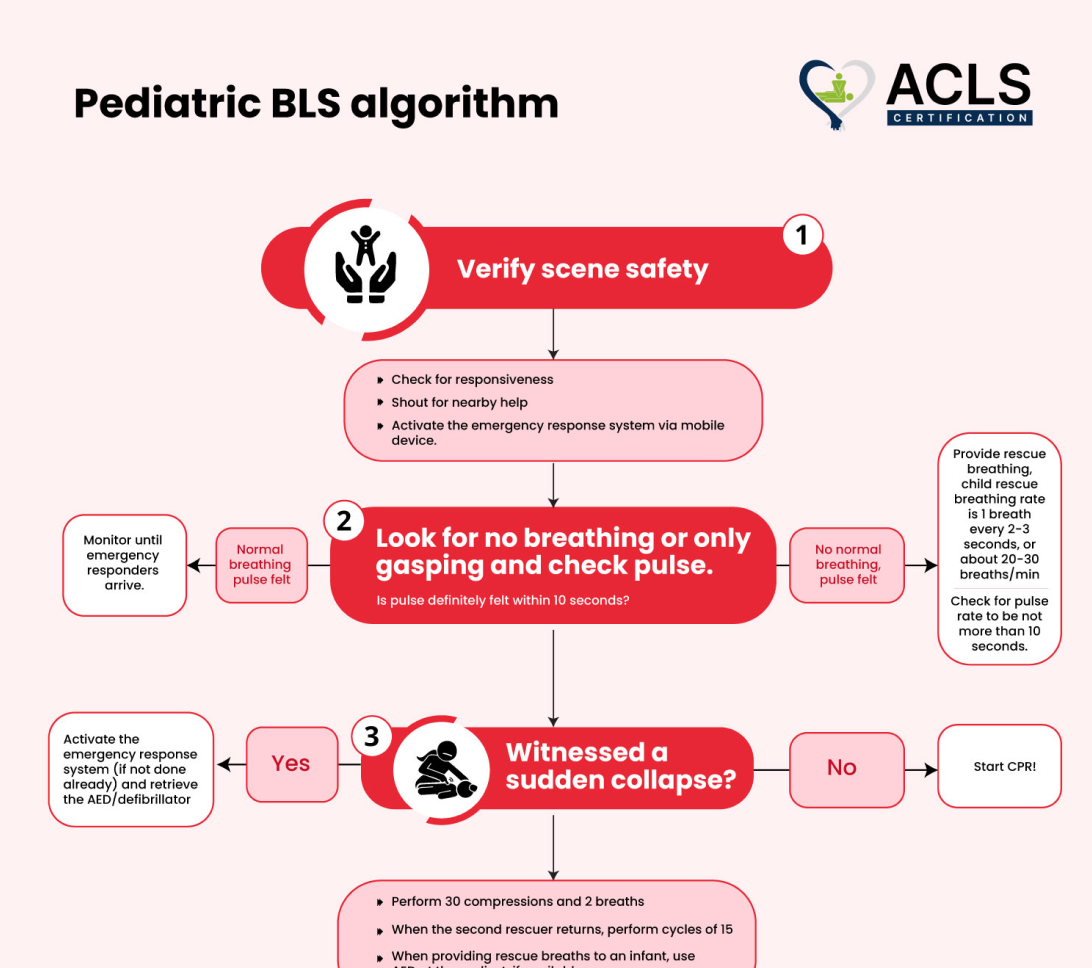
Pediatric BLS Algorithm
The Pediatric BLS algorithm offers high-quality chest compressions at a rate of 100-120 per minute. Start with 30:2 compressions to breaths for a single rescuer or 15:2 for two rescuers.
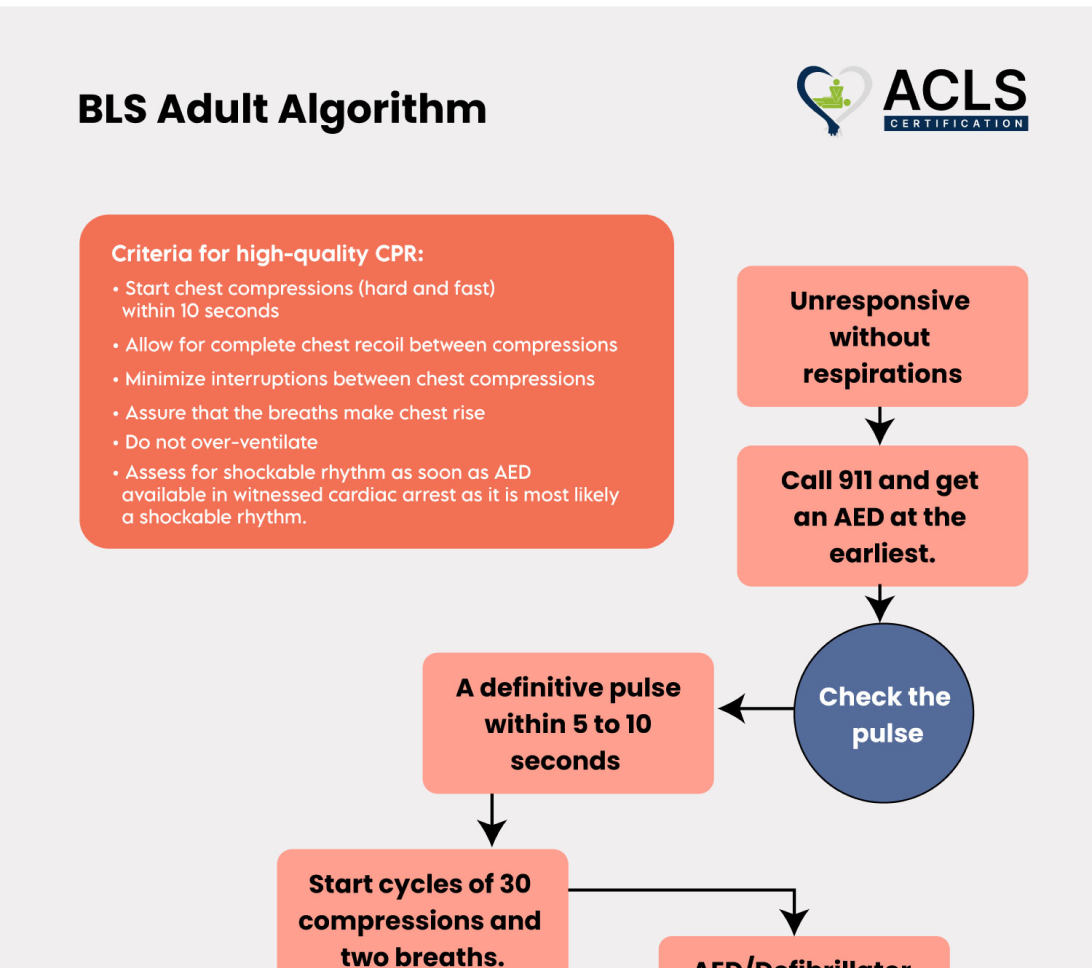
Adult BLS Algorithm
The Adult BLS algorithm begins with checking responsiveness and calling for help. Start chest compressions at a rate of 100-120 per minute, ensure an open airway, and provide rescue breaths in a 30:2 ratio if trained.
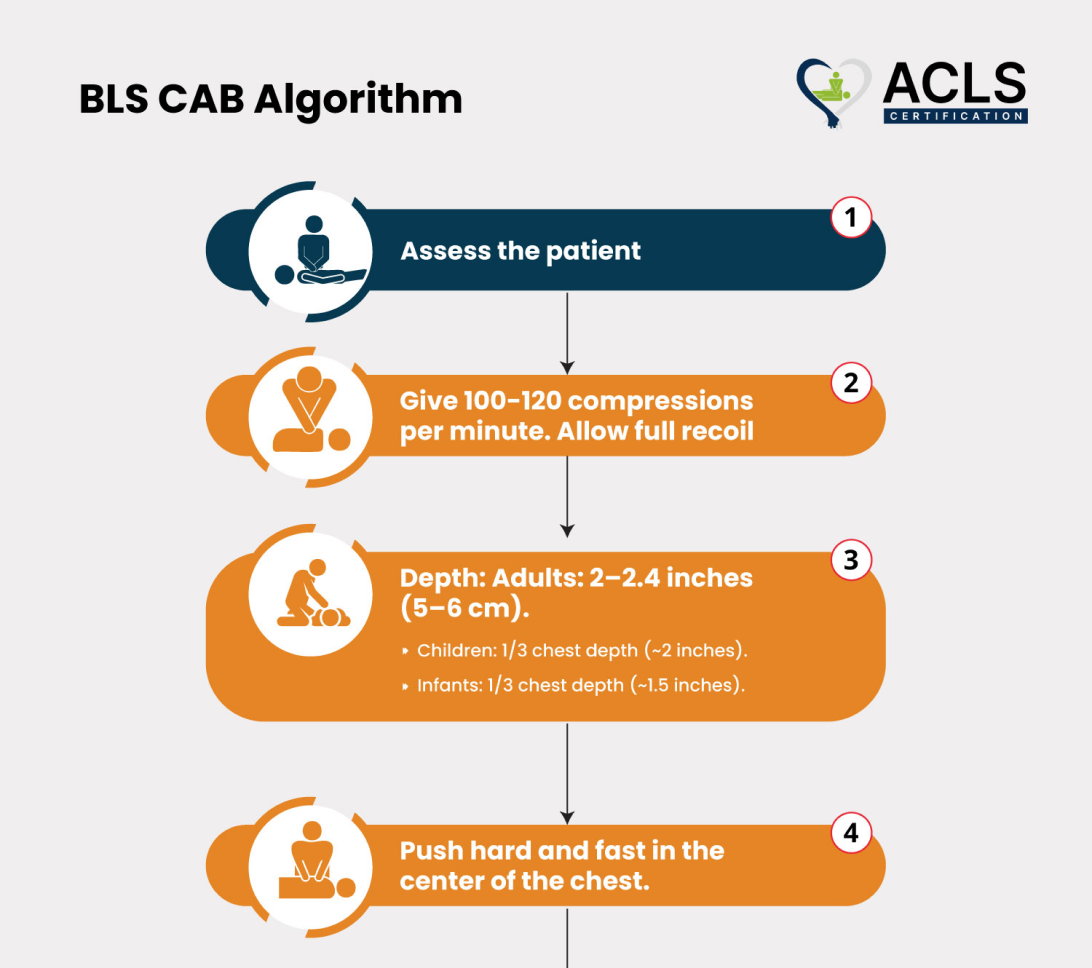
BLS C-A-B Algorithm
The BLS (Basic Life Support) CAB algorithm focuses on Circulation, Airway, and Breathing. Start chest compressions immediately for circulation, then check and open the airway, and provide rescue breaths if needed.