BLS for adults focuses on doing several tasks simultaneously. The focus was primarily on one-rescuer CPR. In most situations, more than one person is available to perform CPR. This method comprises performing chest compressions, managing the airway, and delivering rescue breaths.
When you coordinate effectively, a team of rescuers can save a life when each second matters. The adult BLS algorithm is a simple guide to saving someone’s life during a cardiac arrest. Use an automated external defibrillator that is available and follow the BLS steps for adults.
Explanation of flowchart
- Unresponsive without normal breathing
If the person does not respond to you and is not breathing normally, it is an emergency. - Call 911 and get an AED
Call for emergency help at the earliest and ask someone to bring an automated external defibrillator, if available. - Check for a pulse
Feel for a pulse on the neck for 5 to 10 seconds. If you cannot feel a pulse or are not sure, act as if there is no pulse. - Start CPR
Start cycles of chest compressions. Push hard and fast in the middle of the chest, followed by giving 2 rescue breaths. Continue this pattern. - Use an AED
When the AED arrives, turn the device and follow the voice prompts. Attach the pads as shown in the AED’s instructions. - Check for a shockable rhythm
The AED will analyze the heart rhythm. It will tell you if the rhythm requires a shock.
Key components of the algorithm
- Automated external defibrillator (AED)
This portable device detects the heart’s rhythm and delivers a shock if needed to restart it. - Shockable rhythm
A life-threatening heart rhythm that can be treated with a shock from an AED - Non-shockable rhythm
A heart rhythm that cannot be treated with a shock and needs continued CPR. - Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
A lifesaving technique that involves chest compressions and rescue breaths to help maintain blood flow and oxygenation. - Return of circulation
The goal of resuscitation, where the person’s heart starts beating again on its own.
Download Adult BLS Algorithm
All BLS Algorithms
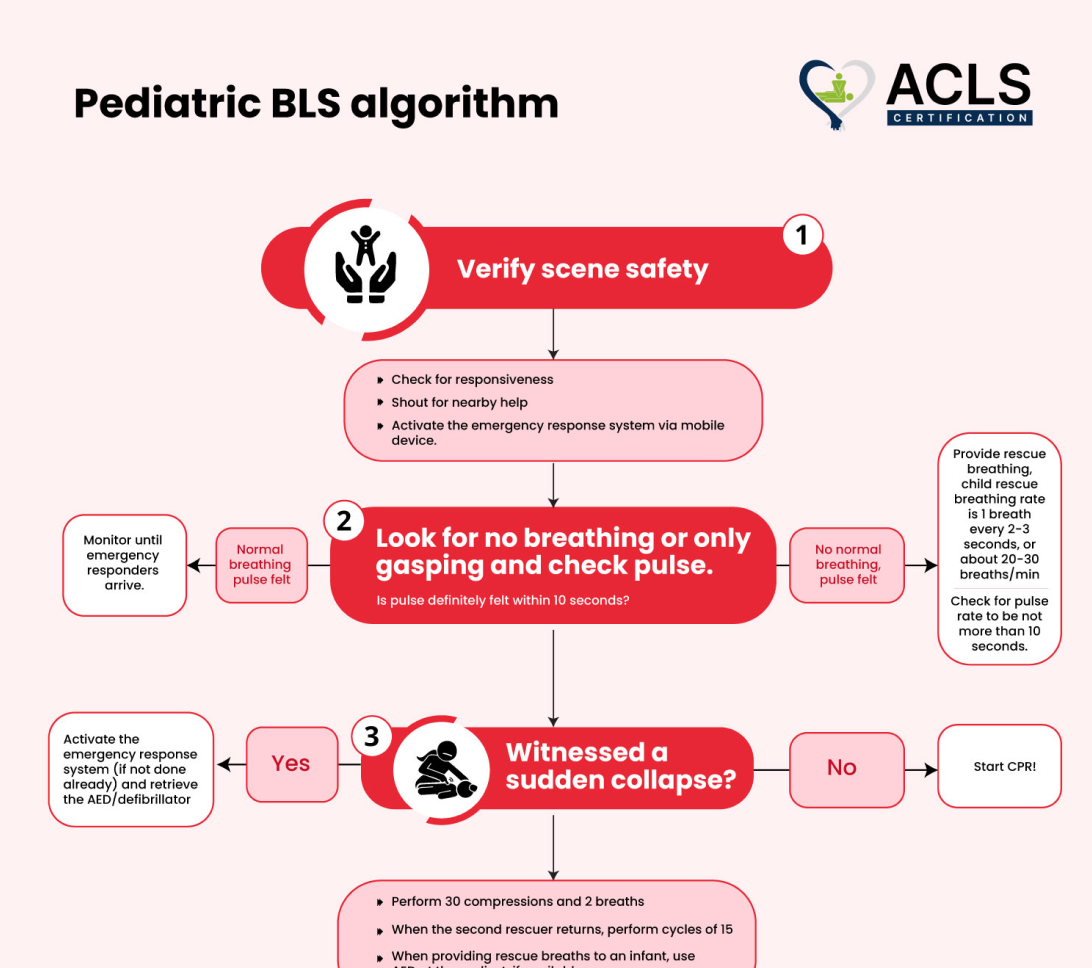
Pediatric BLS Algorithm
The Pediatric BLS algorithm offers high-quality chest compressions at a rate of 100-120 per minute. Start with 30:2 compressions to breaths for a single rescuer or 15:2 for two rescuers.
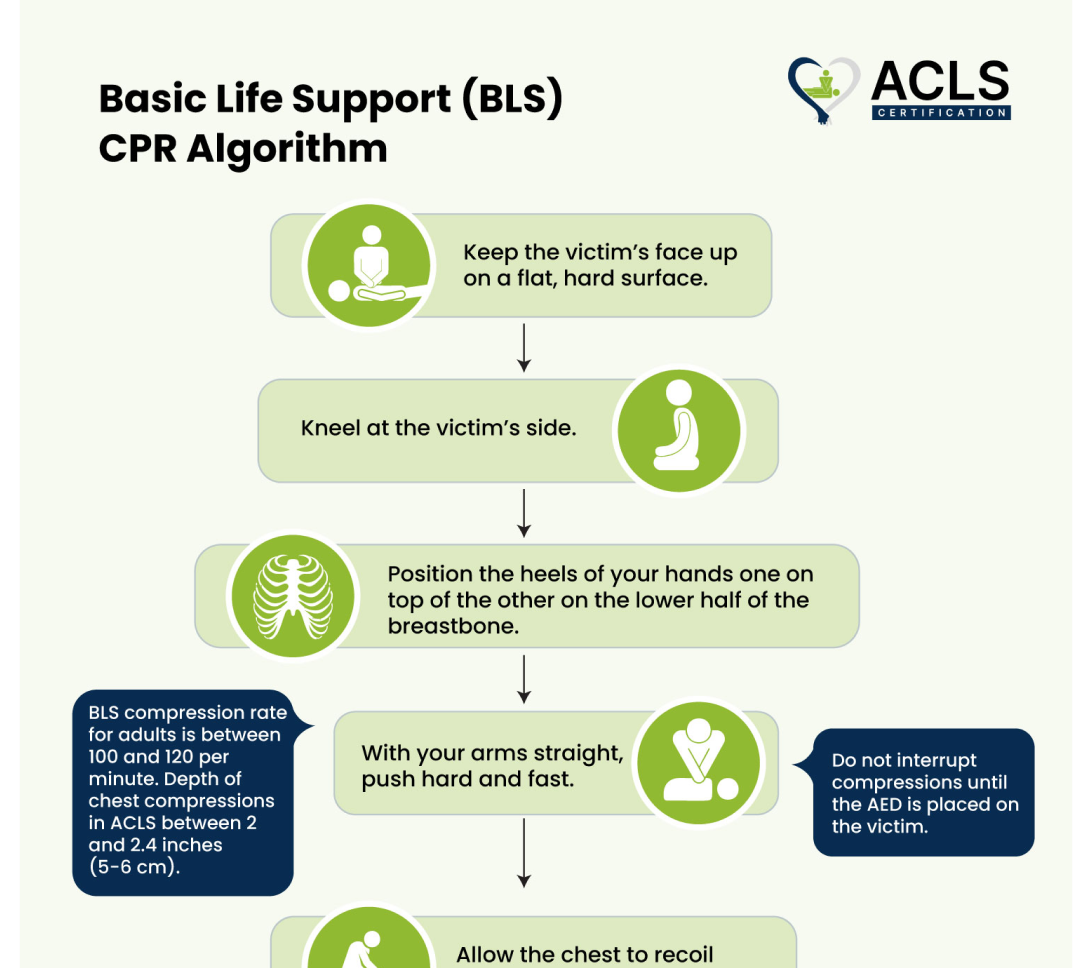
Basic Life Support (BLS) CPR Algorithm
The BLS CPR Algorithm is a simple guide for performing CPR and using an AED during a cardiac arrest. It recognizes the emergency, giving chest compressions, rescue breaths, and using a defibrillator early.
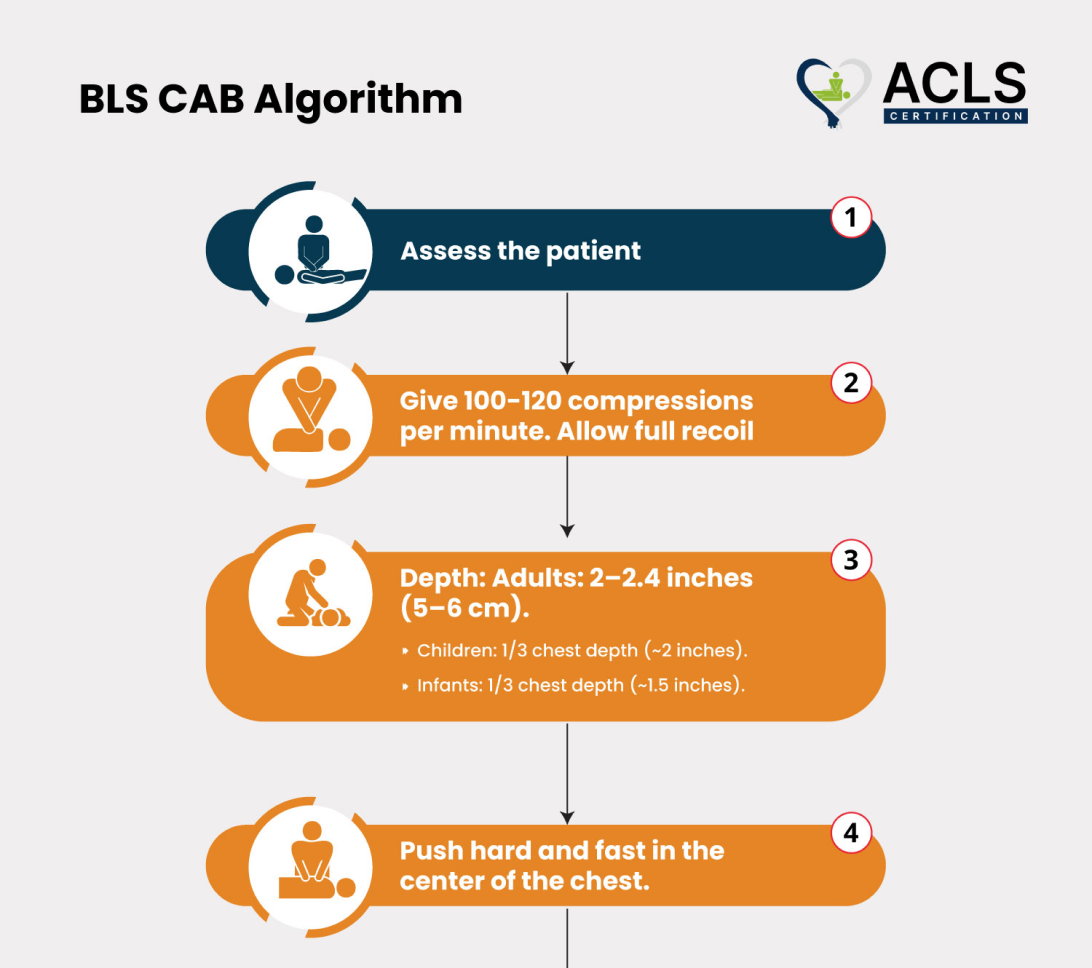
BLS C-A-B Algorithm
The BLS (Basic Life Support) CAB algorithm focuses on Circulation, Airway, and Breathing. Start chest compressions immediately for circulation, then check and open the airway, and provide rescue breaths if needed.