Table Of Content(s):
- Introduction
- What is Sinus Rhythm?
- Characteristics of a Normal Sinus Rhythm
- Key Components of Sinus Rhythm on an ECG
- Normal Intervals and Measurements
- How to Identify Sinus Rhythm on an ECG
- Common patterns and what they mean
- Clinical Significance of Sinus Rhythm
- Abnormalities Related to Sinus Rhythm
- Practical Tips for Interpreting ECGs
- Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Final Thoughts
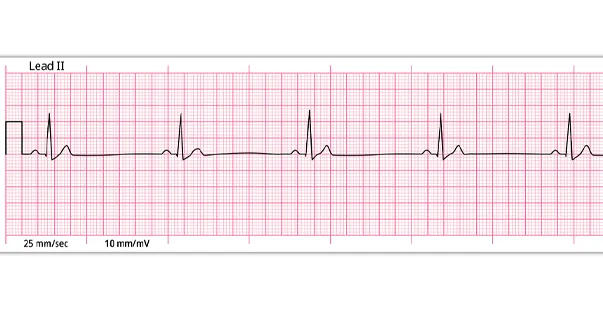
On an Electrocardiogram (ECG), the normal sinus rhythm (NSR) appears as a consistent and orderly pattern, indicating healthy heart function. NSR, also known as the heartbeat, is driven by electrical signals from the Sinus Node. These signals travel through the heart’s valves and cause contraction and expansion to facilitate blood flow.
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a quick and simple diagnostic tool that records the heart’s electrical activity. It evaluates heart health and diagnoses various cardiac conditions by analyzing the impulses that prompt the heart to pump blood efficiently throughout the body.
Master ACLS Now
Get ACLS certified with confidence
Importance of Interpreting ECGs
Analyzing and interpreting a sinus rhythm ECG is like identifying the complex workings of the heart. It is not some random, wavy lines on paper, it effectively represents the sinuous work process of the heart. Here’s the reason why interpreting those lines is so significant:
- Detecting Heart Problems Early: An ECG clearly recognizes irregularities in the rhythm of heartbeats and even the slightest signs of damage to the heart muscle. The nature of the change, as evaluated from an ECG, would permit timely treatment and prevent serious cardiovascular events.
- Heart Function: Every portion of an ECG graph carries its message. Learning to read ECG reports enhances our knowledge about the functioning of the heart and increases our understanding of cardiac function.
- Thorough Diagnosis of the Heart: ECGs record the electrical activity of the heart and hence provide a detailed graph of its rhythm, rate, and any abnormality. This graph enables doctors to diagnose many heart-related problems, such as arrhythmia, heart attack, and other cardiac problems.
What is Sinus Rhythm?
Did you ever wonder how your heart keeps beating steadily and nonstop without you even being concerned about its pounding activity? Well, it’s a well-organized system of the sinus rhythm– a fundamental part of our heart that regulates the heart’s function flawlessly. Now, you must be wondering what is sinus rhythm in ECG?
Sinus rhythm is the heart’s normal electrical activity, especially generated by the Sinus Node (SA), which is located in the right atrium and is also considered the heart’s natural pacemaker.
Role of the Sinus Node (SA) in the Heart
After understanding sinus rhythm meaning, you must learn the role of the sinus node in the heart. The sinus node or sinoatrial node (SA) originates electrical stimuli continuously 60 to 100 times in a minute under a normal condition. Then, the atria are activated. The electrical stimuli pass down the conduction pathways and make the ventricles of the heart contract and pump out blood.
So, the SA node generally produces the electrical signal that causes the upper chambers of the heart, known as the atria, to contract. The signals then transmit through the Atrioventricular node (AV) to the lower heart chambers (ventricles), making them contract or pump.
Characteristics of a Normal Sinus Rhythm
To clarify the question, is sinus rhythm normal, the following is the data for the sinus rhythm of a healthy 18-year-old male as a reference.
- The regular rhythm ranges between 60 and 100 beats per minute (BPM)
- The P wave morphology should be normal
-
QRS complexes must be narrow (<100 ms wide)
-
Constant PR interval
Normal Sinus Rhythm vs. Arrhythmias
Sinus rhythm is the heart’s natural beat, and arrhythmias occur when a disruption in the heart’s natural beat occurs. For example, a normal sinus rhythm shows a steady, predictable pattern on an ECG. This indicates the heart is beating normally. In contrast, an arrhythmia, such as atrial fibrillation, appears as an irregular, chaotic pattern on the ECG, which can signal issues like a higher risk of stroke or heart failure. The readings can vary from harmless asymmetries to serious conditions requiring medical attention. So, it’s important to understand the difference, as this will help you recognize the symptoms early and get the treatment on time.
Master ACLS Now
Get ACLS certified with confidence
Key Components of Sinus Rhythm on an ECG
Knowing what is sinus rhythm and the key components of ECG is extremely important. These components provide valuable information about the heart’s electrical activity and rhythm.
-
P Wave: Origin and Significance
The P wave on ECG sinus rhythm appears as a small and upward curve that represents the atria’s electric depolarization in a healthy heart. It originates in the sinoatrial node in the upper right atrium and passes through the left atrium.
The P waves consist of two parts: the initial portion, which is responsible for depolarizing the left atrium, and the terminal portion, which generally depolarizes the inferior wall of the right atrium and left atrium.
-
PR Interval: Normal Range and Importance
The PR interval refers to the time it takes for the electric impulses to spread from the atria to the ventricles of the heart.
It is generally measured from the beginning of the upslope of the P wave to the beginning of the ORS wave. In adults, the PR interval limit should lie between 120 and 200 milliseconds (ms) or 0.12 to 0.2 seconds.
-
QRS Complex
The QRS complex is the main spike in the sinus rhythm on ECG status and the most clearly visible part of the ECG. It refers to the depolarization of the ventricles (lower chambers of the heart). The QRS wave is a small downward deflection represented by point Q. It follows the path of the P wave.
After Q, there is a sharp apex, represented by point R, followed by downward deflection, represented by point S. We can get a person’s heartbeat rate by counting the QRS complex produced in a minute. The duration of the QRS complex is considered ideal when it is 80- 120 ms.
-
T Wave: Role and Appearance
The T wave is an important component of an electrocardiogram (ECG) that shows ventricular myocardium repolarization.
The T wave on the ECG appears as a round and smooth waveform following the QRS complex. Its duration and amplitude vary depending on different factors, including electrolyte balance, heart rate, and cardiac health.
The T wave assesses repolarization and arrhythmia detection and monitoring medication.
Also Read: ECGs in Acute Myocardial Infarction
-
Normal Intervals and Measurements
It is crucial to examine various intervals and measurements on an ECG to assess the normalcy of a sinus heart rhythm. These intervals reflect specific phases of the cardiac cycle and help determine if the electrical system is functioning correctly.
- The P wave interval lies between 0.08-0.11 seconds.
- The PR interval should be ranging from 0.12 to 0.20 seconds.
- In terms of duration, the QRS complex should range from 0.06 to 0.11 seconds.
- The ideal QT interval lies between 0.36 to 0.44 seconds.
How to Identify Sinus Rhythm on an ECG
With the advancement of technology, various methods have been developed for the evaluation of cardiovascular disease, and ECG remains the prime method. Some guides to effectively reading ECG are:
- Monitor the QRS segment of the ECG. This helps to determine whether the depolarisation among the ventricles is normal.
- Calculate the heart rate. Taking a 6-10-second radial pulse and then multiplying it for a one-minute reading will give a proper idea about the heart rate.
- Diagnose the P waves correctly. If the P waves are upright, present and followed by a QRS segment, then the electrical impulse begins with a SA node.
- Measure the PR intervals. The Normal P-R interval is 0.12 to 0.20 seconds; longer PR intervals suggest delay or blockage. Also, measure the QR intervals. The normal QRS duration is 0.04 to 0.10 seconds; a more prolonged one denotes a branch block.
- Check the T waves. The ideal T waves should follow the QRS segment and Upright.
- Monitor the ectopic beats. Counting ectopic beats helps determine the heart’s shape and interval.
- Determine the origin of all the elements, such as the Sinus, Ventricular, Atria, Paced rhythm, and a few others, to ensure optimum heart health.
- Identify the rhythm, as this helps the physicians to direct their treatment in a specific way.
Common Patterns and What They Mean?
One of the most crucial questions is what sinus rhythm means. A person’s normal sinus rhythm denotes a healthy heart. In adults, the ideal sinus rhythm denotes a heart rate between 60 and 100 BPM.
Anything between this range is considered normal, and there are conditions where the heart rate falls below 60 BPM or rises above 100 BPM. These can be considered normal if any kind of activity is involved, such as exercising or sleeping, but if they occur in rest conditions, then they are considered harmful.
Master ACLS Now
Get ACLS certified with confidence
Clinical Significance of Sinus Rhythm
After learning what does sinus rhythm mean, let’s now explore the clinical significance of Sinus Rhythm:
-
Why It Matters in Diagnosis
The ideal heart rate is 60 to 100 BPM, a beat is called normal sinus rhythm. The main significance of the sinus rhythm or the heat beat is to pump a sufficient amount of oxygenated blood. A normal heartbeat denotes a healthy heart, and a healthy heart ensures a healthy body.
-
Common Conditions Associated with Sinus Rhythm
There are generally two conditions involved with sinus rhythm irregularities. These two conditions arise when the heart rate varies beyond the ideal range of 60 to 100.
One such condition is Sinus Bradycardia and another one is Sinus Tachycardia. Both of these conditions have been discussed in the later parts.
-
Impact on Patient Management And Treatment
The sinus rhythm has a profound effect on patient management and treatment. Sinus rhythm refers to the electrical activity generated in the sinoatrial node (SA), which constantly drives ventricular and atrial contraction.
Abnormalities Related to Sinus Rhythm
Abnormalities related to sinus rhythm can indicate irregularities in the heart’s natural pacemaker. Some of the abnormalities are:
-
Sinus Bradycardia
This condition is opposite to Sinus Tachycardia and occurs when the sinus node sends pulses very slowly, resulting in a heart rate of less than 60 BPM. This particular condition can be experienced in times of deep sleep. Other reasons that can cause these conditions are inflammation, infection, and others.
Read More: What Is Sinus Bradycardia? Causes, Symptoms and Treatments
-
Sinus Tachycardia
This condition occurs when the sinus node sends more electrical pulses rapidly, leading to a heart rate higher than 100 bpm. It can be experienced while exercising or feeling stressed. Factors such as fear, excessive exercise, and the use of certain pharmaceutical drugs cause it.
-
Sinus Arrhythmia
This is a condition in which an abnormal heart rhythm is observed. The most common issue is that the time between the heartbeats can be long or short, depending on whether the person is inhaling or exhaling.
The heart rate increases when a person breathes in and slows down when the individual breathes out. This is considered normal under certain circumstances, but when a person is in a stationary condition, it is a sign of heart abnormality. In severe cases, it can lead to pulseless electrical activity, where the heart’s electrical system functions, but the heart does not contract effectively. This requires immediate medical intervention.
Practical Tips for Interpreting ECGs
An ECG reading can go wrong if electrode placement is incorrect or if the patient moves. You must properly know the four key areas:
- The P wave must be two to three small squares in terms of duration (0.08-0.11 seconds).
- The PR interval should be three to five squares in the duration field ( 0.12 to 0.20 seconds).
- In terms of duration, the QRS complex should be 1.5 – 2.5 minute squares ( 0.06 to 0.11 seconds).
- Nine to eleven small squares are the ideal QT interval ( 0.36 to 0.44 seconds).
Knowing these four variables properly gives the practitioners a proper understanding of the ECG readings and graphs.
Final Thoughts
Normal sinus rhythm and accurately interpreting ECGs are fundamental skills for healthcare professionals. However, if you want to truly excel in managing cardiovascular emergencies, completing an ACLS-certified course is essential.
This certification equips healthcare providers with the advanced skills and knowledge needed to handle critical cardiac situations, ensuring that they can provide the highest level of care during emergencies.
Through ACLS training, professionals learn to recognize and treat severe arrhythmias, perform high-quality CPR, and use advanced airway management techniques, which improves patient outcomes in life-threatening scenarios.