Table of Content(s)
- Introduction
- What are the key differences between NSTEMI and STEMI
- NSTEMI on EKG Vs STEMI on EKG
- Causes of NSTEMI: What Leads to This Type of Heart Attack?
- Common and atypical symptoms of NSTEMI
- Treatment Options for NSTEMI
- Survival Rates and Potential Complications
- How to reduce risk of NSTEMI?
- Conclusion
A non ST segment myocardial infarction or NSTEMI on EKG is identified as a type of heart attack that is often misdiagnosed. Unlike a common heart attack (STEMI), NSTEMI doesn’t show typical signs on an EKG. It is extremely tricky to diagnose this problem at an early stage. NSTEMIs account for about 30% of heart attacks in the U.S. Understanding the warning signs saves lives. Read on to learn more about this silent, yet serious, condition.
What Are The Key Differences Between Nstemi And Stemi?
NSTEMI and STEMI are both types of heart attacks. However, they differ in their severity and how they appear on an ECG.
| NSTEMI | STEMI |
| Does not show ST elevation, often resulting from a partial blockage of a coronary artery. | Shows clear ST elevation on an ECG. Indicates a complete blockage of a coronary artery. |
| NSTEMI involves comparatively less damage to heart muscles. | STEMI tends to be more severe with extensive heart muscle damage. |
| NSTEMI allows for more time to plan a proper treatment, once diagnosed. | STEMI requires immediate intervention like Angioplasty. |
| NSTEMI symptoms are mostly subtle and hence difficult to diagnose. | Symptoms of STEMI cause chest pain. |
Read More: Stroke Algorithm Cincinnati Prehospital Stroke Scale (CPSS)
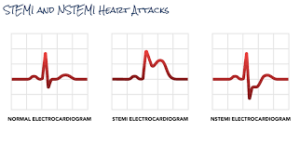
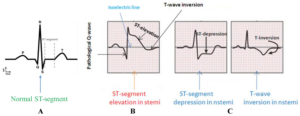
NSTEMI on EKG Vs STEMI on EKG
NSTEMI and STEMI can be distinguished on an EKG based on their characteristic patterns of heart activity.
STEMI (ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction):
- Shows ST segment elevation on the EKG, indicating complete artery blockage.
- Often displays a new left bundle branch block (LBBB).
- Clear and dramatic changes in the ST segment.
NSTEMI EKG (Non-ST Segment Myocardial Infarction):
- No ST segment elevation is seen.
- May show subtle changes, such as ST depression or T-wave inversion.
- Less obvious signs compared to STEMI but confirmed by elevated cardiac enzymes.
Read More: Bradycardia ECG Vs Normal ECG
Causes of NSTEMI: What Leads to This Type of Heart Attack?
NSTEMI is typically caused by reduced blood flow to the heart. This happens due to partial blockage of a coronary artery.
- Atherosclerosis: Plaque buildup in the arteries can narrow the vessels. This restricts blood flow.
- Coronary Artery Spasm: Sudden tightening of a coronary artery can limit blood supply to the heart.
- Blood Clots: Partial clotting within a coronary artery can obstruct blood flow, leading to NSTEMI.
- Microvascular Disease: Damage to smaller blood vessels can reduce oxygen delivery to heart tissue.
- High Blood Pressure: Increased pressure in the arteries can lead to weakened blood vessels and contribute to NSTEMI.
Common and atypical symptoms of NSTEMI
NSTEMI symptoms can range from typical chest pain to more subtle or atypical signs that are easy to overlook.
Common Symptoms include:
- Chest pain or discomfort, often described as pressure or tightness.
- Shortness of breath, especially during exertion.
- Pain radiating to the jaw, neck, back, or arms.
- Nausea, dizziness, or lightheadedness.
Atypical Symptoms include:
- Fatigue or weakness, particularly in women and older adults.
- Indigestion or heartburn-like discomfort.
- Cold sweats without obvious cause.
- Mild, intermittent chest discomfort rather than severe pain.
Treatment Options for NSTEMI
Treatment for NSTEMI focuses on restoring blood flow to the heart and preventing further damage.
Medications:
- Aspirin: To reduce blood clot formation.
- Blood Thinners (Anticoagulants): To prevent clot growth.
- Nitroglycerin: To relieve chest pain and improve blood flow.
- Beta-blockers: To reduce heart workload and blood pressure.
- Statins: To lower cholesterol levels and stabilize plaque.
Interventions:
- Angioplasty and Stenting: To open partially blocked arteries.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): For more severe cases to reroute blood flow.
Lifestyle Changes:
- Stop smoking, opt for a healthier diet. Exercise regularly to prevent future heart issues.
Survival Rates and Potential Complications
Survival rates for NSTEMI are generally higher than those for STEMI. However, timely treatment is crucial to avoid long-term complications.
Survival Rates:
- With early diagnosis and treatment, NSTEMI survival rates can exceed 90%.
- Delayed treatment or misdiagnosis increases the risk of serious complications and lowers survival chances.
Potential Complications:
- Heart Failure: Weakened heart muscle may struggle to pump blood effectively.
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heartbeats may develop due to damaged heart tissue.
- Recurrent Heart Attacks: Patients with NSTEMI are at higher risk for future cardiac events.
- Stroke: Reduced blood flow and clot formation may lead to a stroke.
- Cardiogenic Shock: The heart’s inability to pump blood effectively can cause life-threatening low blood pressure.
How To Reduce Risk Of Nstemi?
Reducing the risk of NSTEMI involves adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle. It includes managing existing health conditions.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while limiting saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity each week to strengthen the heart and improve overall health.
- Quit Smoking: Avoid tobacco in all forms. Smoking significantly increases the risk of heart disease.
- Manage Stress: Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises to improve heart health.
- Control Blood Pressure and Cholesterol: Regularly monitor and manage blood pressure and cholesterol levels through lifestyle changes and medication if necessary.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Achieve and maintain a healthy weight to reduce strain on the heart and lower the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Regular Health Screenings: Stay proactive with regular check-ups to monitor heart health and address any risk factors promptly.
Conclusion
NSTEMI on EKG is a critical cardiac event that needs prompt intervention. Unlike STEMI, NSTEMI presents with subtle symptoms. Awareness in NSTEMI ECG findings can literally be a gamechanger for proper management and positive outcome. Knowing the causes, symptoms and importance, eliminates potential complications. Adopt a heart healthy lifestyle and manage risk factors to reduce the chances of experiencing NSTEMI. Protect your long term wellbeing by being proactive towards your heart health.